Using only built‑in tools, you can turn your Windows device into a software-based Wi‑Fi router (hotspot/access point) to share your Internet connection with other wireless devices. This software-based Wi‑Fi hotspot on Windows can be used to create a simple local wireless network (for example, for file and printer sharing) or to share an Internet connection across multiple wireless devices (computers, laptops, phones, TVs, tablets, and other devices).
In this article, we’ll show you how to configure a virtual Wi-Fi hotspot running on a Windows 11 or 10 device. Assume that your computer has two network adapters: one providing Internet access (such as a wired Ethernet or mobile 3G/4G/5G connection) and a separate wireless Wi‑Fi adapter. The goal is to create a virtual Wi‑Fi router on this Windows device to share its Internet connection with other devices.
- How to Enable Mobile Hotspot in Windows 11 and 10
- How to Automatically Turn on the Mobile Hotspot on Windows Startup
- Configuring a Hosted Ad-Hoc Wireless Network on Windows
- Start a Hosted Wi-Fi Hotspot on Windows Using CMD
- Allow Internet Access for Wi-Fi Hotspot Clients
- Common Hosted Wi-Fi Access Point Issues on Windows
There are two options for setting up a software hotspot (SoftAP) in Windows:
- The Mobile Hotspot feature is available in Windows 11 and Windows 10 (version 1607 and above) and can be enabled via the Settings panel’s graphical interface. Mobile Hotspot mode is built on the WLAN Device Driver Interface (WDI) management framework, which enables the creation of a software-based access point even without dedicated hardware support at the Wi‑Fi adapter or driver level.
- Wireless Hosted Network – a legacy feature that enables the creation of a software access point via Wi-Fi adapter virtualization (Virtual Wi-Fi). The wireless adapter driver must support the Hosted network mode (a functionality that is not supported by most modern Wi-Fi adapter drivers). This is suitable for running a software access point on old versions of Windows, including Windows 10, 8.1, and 7.
How to Enable Mobile Hotspot in Windows 11 and 10
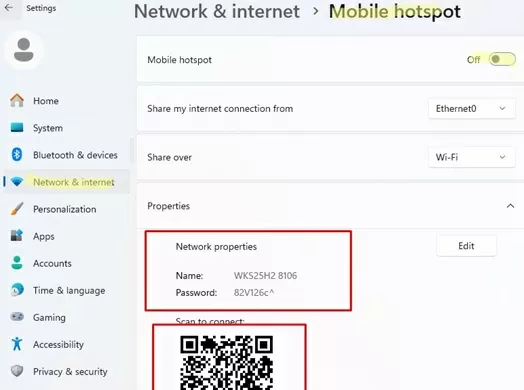
In Windows 11 and Windows 10 (version 1607 and later), you can configure the Mobile Hotspot feature through the Settings app. Go to Settings -> Network and Internet -> Mobile hotspot) or run the ms-settings quick access command: ms-settings:network-mobilehotspot
Several options are available here:
- Turn on/turn off the Mobile Hotspot.
- Share my internet connection from: if your computer has multiple active network adapters, you can choose which one you want to allow other users to use to access the internet (in my case, it is an Ethernet 0 connection).
- The Wi-Fi network name (SSID) and password are generated automatically and can be changed if required.
- Power Saving – automatically turns off the mobile hotspot if no devices are connected (the power-saving feature is enabled by default)
- The access point settings also allow you to select the access point frequency range, which can be 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz or 6 GHz (if supported by the WLAN adapter).
To connect to the mobile hotspot you have created, either scan the QR code on another device or select the SSID and enter the password manually.
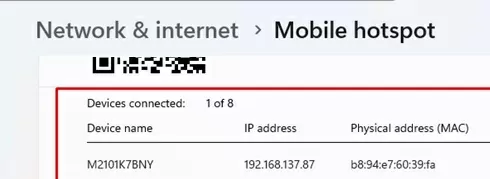
The graphical interface of the Mobile Hotspot page displays a list of the devices currently connected to your access point, including their device name, IP address, and MAC address (up to 8 devices can be connected simultaneously).
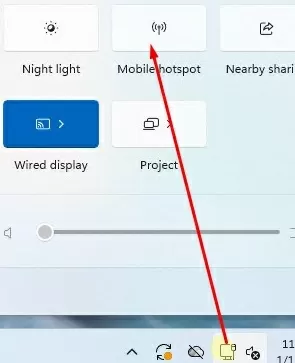
You can quickly enable the mobile hotspot feature by opening the notification panel in the taskbar. Tap the network connection icon, then tap the mobile hotspot icon in the quick settings panel.
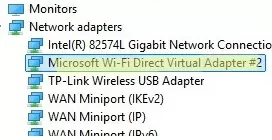
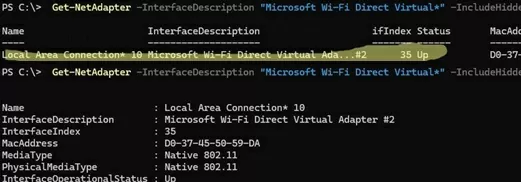
Enabling a mobile hotspot creates a Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter on your device. This adapter is used for sharing an internet connection.
This network adapter is hidden, so it is not displayed in the Network and Sharing Center. Such a network adapter can be managed using PowerShell:
Get-NetAdapter -InterfaceDescription "Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual*" -IncludeHidden
Use the following commands to enable mobile hotspot in Windows 11 from the PowerShell command prompt:
$connProfile = [Windows.Networking.Connectivity.NetworkInformation,Windows.Networking.Connectivity,ContentType=WindowsRuntime]::GetInternetConnectionProfile()$tethManager = [Windows.Networking.NetworkOperators.NetworkOperatorTetheringManager,Windows.Networking.NetworkOperators,ContentType=WindowsRuntime]::CreateFromConnectionProfile($connProfile)$tethManager.StartTetheringAsync()
Check whether the WLAN hotspot point is running:
$tethManager.TetheringOperationalState()
Stop the mobile hotspot:
$tethManager.StopTetheringAsync()
So, the ‘Mobile Hotspot’ feature in Windows 11 enables you to set up a wireless access point with a single click, eliminating the need for manual configuration via the command line.
How to Automatically Turn on the Mobile Hotspot on Windows Startup
By default, the mobile hotspot doesn’t start automatically after the computer is powered off or rebooted. To automatically turn on the mobile hotspot when Windows boots, you need to run a simple PowerShell script through the Task Scheduler.
- Run the command
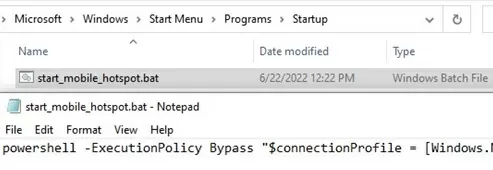
Win+R->shell:startup - Create a text file named start_mobile_hotspot.bat;
- Copy the following PowerShell code into the file and save it:
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass "$connectionProfile = [Windows.Networking.Connectivity.NetworkInformation,Windows.Networking.Connectivity,ContentType=WindowsRuntime]::GetInternetConnectionProfile(); $tetheringManager = [Windows.Networking.NetworkOperators.NetworkOperatorTetheringManager,Windows.Networking.NetworkOperators,ContentType=WindowsRuntime]::CreateFromConnectionProfile($connectionProfile); $tetheringManager.StartTetheringAsync();"
- Now your wireless hotspot will automatically start when a user logs in computer (or in the case of Windows autologon enabled).
- To start the mobile hotspot on Windows startup, create a new scheduler task using PowerShell (the task is run on behalf of SYSTEM):
$Trigger= New-ScheduledTaskTrigger –AtStartup
$User= "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
$Action= New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "c:\scripts\start_mobile_hotspot.bat"
Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName "RunHostSpot" -Trigger $Trigger -User $User -Action $Action -RunLevel Highest –Force
Configuring a Hosted Ad-Hoc Wireless Network on Windows
If you’re using an older version of Windows (earlier than Windows 10, version 1607) or are unable to enable the mobile hotspot for any reason, consider running the access point in hosted network mode instead. This is a more complex, legacy method of creating an ad-hoc wireless access point on a Windows computer. It requires configuration via the command line and is not compatible with many modern WLAN adapters.
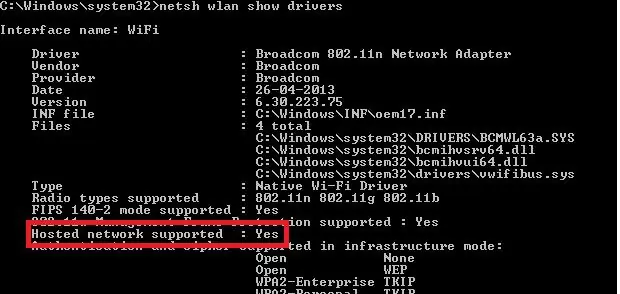
Firstly, ensure that your Wi-Fi adapter’s driver supports the virtual access point (Ad-Hoc) operation mode. To do it, run this command
netsh wlan show drivers
This command provides information about the Wi-Fi adapter driver in use and its supported options.
“Hosted network supported: Yes” message indicates that this driver supports Ad-Hoc access point mode. Otherwise, try to update the driver version or use another Wi-Fi adapter.
Start a Hosted Wi-Fi Hotspot on Windows Using CMD
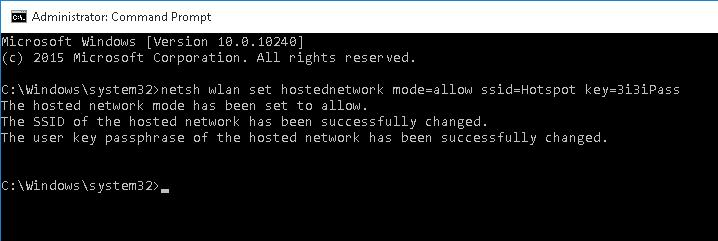
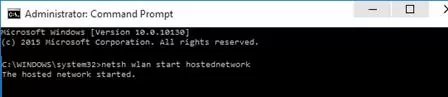
Now, let’s look at how to create a virtual Wi-Fi access point in Windows using the netsh wlan command. I will create a wireless network named Hotspot (this is the SSID of the network) with the ZiZiPass security key (password). Open a command prompt (as an administrator) and run the following command:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=Hotspot key=ZiZiPass
If everything is correct, the command will return the following message:
The hosted network mode has been set to allow. The SSID of the hosted network has been successfully changed. The user passphrase of the hosted network has been successfully changed.
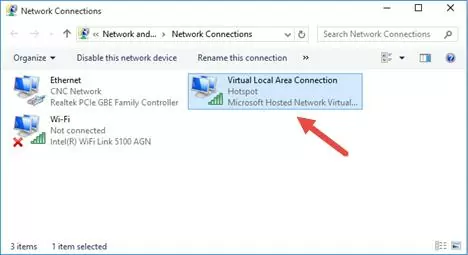
This command creates a new virtual Wi-Fi adapter (Microsoft Hosted Network Virtual Adapter) on a computer. Other wireless devices in the network can use this adapter as an access point. Now, enable the created virtual adapter:
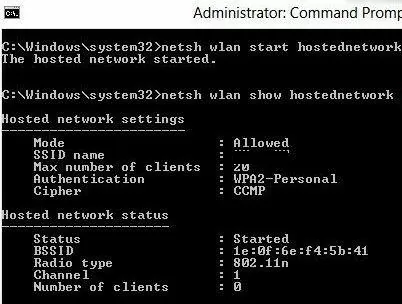
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
The ‘Hosted network started’ message indicates that a software Wi-Fi hotspot has been successfully started. A new wireless connection named Hotspot will appear in the Network and Sharing Center.
If you scan for available Wi-Fi networks on other devices, they will see your wireless hotspot and be able to connect to it using the password. Devices connected to such a network can share files, folders, and printers, but Internet access through such a WiFi hotspot is not yet possible.
Allow Internet Access for Wi-Fi Hotspot Clients
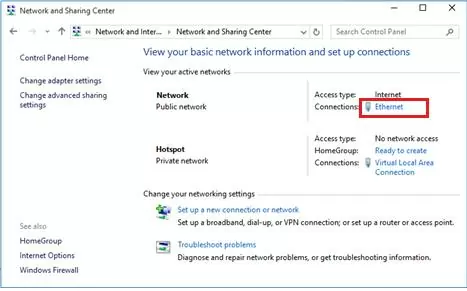
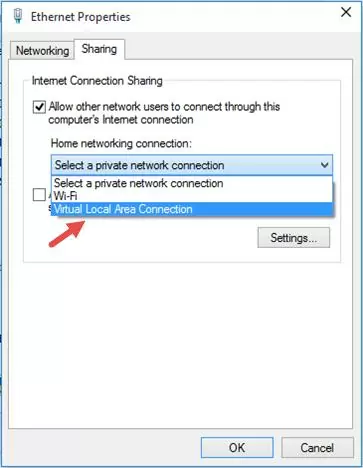
Next, allow devices connected to your virtual Wi-Fi hotspot to access the internet via a wired network connection. Go to the Network and Sharing Center and click on the name of the network adapter through which you can access the internet. In my example, this is a connection named Ethernet.
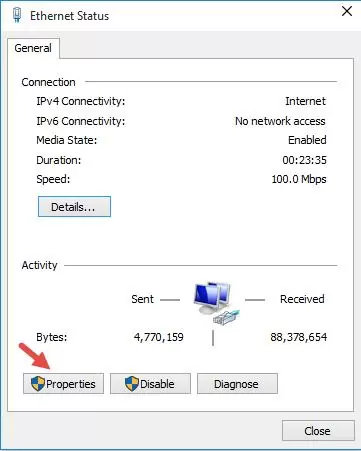
Click the Properties button on the network adapter status screen.
Allow Internet sharing for this connection. In the Ethernet Properties form, go to the Sharing tab. Check the box “Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection” and select the name of the virtual adapter created earlier in the dropdown list.
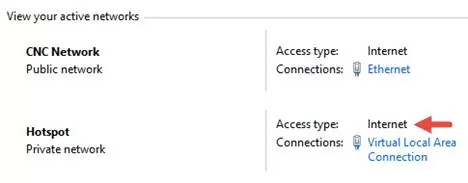
Save the changes. In the Network and Sharing Center, the type of Hotspot network will be changed to the Internet. That means that this network (and all devices connected to it) now have Internet access.
Any devices that connect to your Windows hotspot will now have internet access via your computer’s external network interface.
Check the current Wi-Fi access point settings using the command:
Netsh wlan show hostednetwork
The command displays:
- The network name (SSID)
- The supported authentication and encryption types
- The maximum number of devices that can simultaneously use this hotspot (Max number of clients)
- The current number of connected clients (Number of clients).
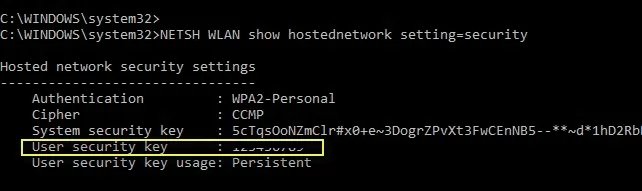
To view the Wi-Fi hotspot’s security settings, including the connection password (User security key), run:
Netsh wlan show hostednetwork setting=security
Common Hosted Wi-Fi Access Point Issues on Windows
Answer. Start the hosted network manually using the command:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
You don’t need to re-enter the network name or password.
The Wireless AutoConfig Service (wlansvc) is not running. The hosted network couldn’t be started.
Answer. Start the WLAN AutoConfig service using either the services.msc console or from the command prompt:
net start WlanSvc
and restart the virtual hotspot.
The hosted network couldn’t be started. The group or resource is not in the correct state to perform the requested operation.
Answer. Make sure that your Wi-Fi network adapter is enabled. Then open the Device Manager, select Show hidden devices in the View menu. Find the Microsoft Hosted Network Virtual Adapter in the Network Adapters section and enable it.
If it doesn’t help, run these commands one by one:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=disallow
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow
Then re-create the hosted hotspot:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=Hotspot key=ZiZiPass
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
If you have previously created a Wi-Fi hotspot on this device, try to clean the Hosted Virtual Adapter settings in the registry. Delete the HostedNetworkSettings DWORD registry parameter under the HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WlanSvc\Parameters\HostedNetworkSettings reg key.
reg delete hklm\system\currentcontrolset\services\wlansvc\parameters\hostednetworksettings /v hostednetworksettings
Answer
netsh wlan show hostednetwork
Answer. To stop your wireless access point, run the command:
netsh wlan stop hostednetwork
Then, remove the hosted network in Windows, and clear the SSID and network security key (password): netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=disallow
Answer: Check the DNS server settings on the client device. Try specifying the address of the public Google DNS server (8.8.8.8) manually in your client’s network settings. Also, try restarting the Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) service or disabling and re-enabling the network adapter through which your Windows device connects to the Internet.
Other common issues that can cause software Wi-Fi access points on Windows not to work include:
- The built-in firewall in third-party anti-virus software may block Internet connection sharing. Try temporarily disabling any third-party firewall (or only network protection module) and see if the problem persists.
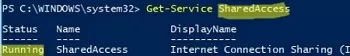
- Ensure that the Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) service is enabled on the Windows device sharing its internet connection via Wi-Fi. Check the service state using the services.msc snap-in or with the PowerShell command:
Get-Service SharedAccess - Start the Network Adapter Troubleshooter tool by running the
msdt.exe /id NetworkDiagnosticsNetworkAdaptercommand. This tool will check the current network adapter settings and attempt to automatically fix any found problems - Reset the Windows network settings (Settings -> Network -> Network Reset) and recreate the Wi-Fi hotspot.
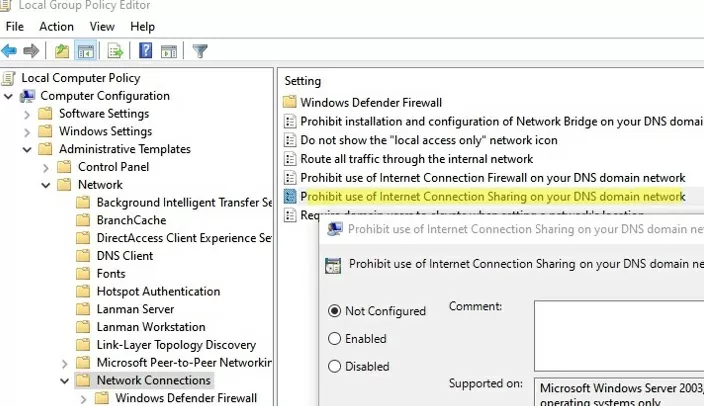
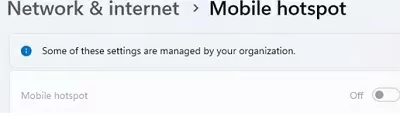
- The Mobile Hotspot switch is inactive (grayed out) with the Some of these settings are managed by your organization message displayed. For security purposes, a domain administrator can disable the Mobile Hotspot feature on computers joined to an Active Directory domain by using the Prohibit use of Internet Connection Sharing on your DNS domain network GPO option (under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections). Check that this policy is not configured using the local Group Policy Editor (
gpedit.msc) or with Group Policy resulting tools (gpresult.exeorrsop.msc). - An error appears when trying to turn on the mobile point:
We can’t set up mobile hotspot. Check the value of the NC_ShowSharedAccessUI parameter in the registry keyHKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Network Connections. If the value is set to 0, the restriction on creating a software access point in Windows is enabled. To allow mobile hotspot creation, delete the parameter or change its value to 1.
40 comments
This is the best instruction on the issue I have found, and it worked splendidly. However, after using this for three weeks for so, for some reason it has stopped working. The device (a smartphone) I’m trying to use to access my shared connection does show that it has established a connection, but no data is transferred. This issue has been confirmed on two other devices. Every time I make an access point using these instructions, a connection can be established but no data is being moved – even though these instructions did work well for a couple of weeks. Any idea how so solve this issue?
Try to re-create your acess point as follow:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=disallownetsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allownetsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=Hotspot key=ZiZiPassnetsh wlan start hostednetworkHow do I edit the max clients that can join my hotspot?
after creating hotspot connections but still does not work?
after creating hotspot connections but the internet still does not work?
That’s OK, its running successfully. But I want to create a Hidden ssid so its not visible to all. Is this case possible
It is impossible to hide the SSID of Windows software hotspot. You can disable WI-FI Broadcast only on hardware access point .
In hotspot network supported it says no…what should i do…?????
Update your WiFi adapter driver
i want to to keep running this hotspot even when my pc is in sleep mode
It’s impossible. Windows disables the Wi-Fi adapter in sleep mode
how to set hotspot without password?
samsung phone display ap not currently in use
Thanks a lot for this subject .. My greetings.
It seems we should add DNS setting on the client otherwise we could not connect to the Internet.
Thank you man! This worked! Tried everything before, but this worked! Had to change the ip to static on the client device and set the google DNS.
I have been facing following trouble.what i have to do?
The hosted network couldn’t be started.The group or resource is not in the correct state to perform the requested operation.
oi,estou usando o programa my wifi router 1.0.consegui criar rede wifi,mas nao tem conexao com internet,ja liberei no compartilhameneto do w10,mas nada vc pode ajudar:::
got an error ip configuration failed
having issues obtaining ip address on my android
I use this technology to create a private wifi network. In order to manage domain names, I have created my own dns server in order to answer a specific ip to all devices connected to the network. When I start this DNS server on the port 53 on a windows 7 (the one emitting the wifi), the DNS server is automatically detected by the peers on the network and everything works well. However it is not the case on windows 10. Do you any idea why ?
Thanks
Thanks for the excellent guidelines!
I did everything, but there was no internet access on any device, I tried few things and at last I disabled the virtual LAN and it disappeared.
After that when I try to start the hosted network, there is a message:
“The hosted network couldn’t be started.
The group or resource is not in the correct state to perform the requested operation.”
And I cannot start the hosted network. Any suggestions?
good description with some notes, had to set a static IP and after that the mobile did connect to the created hot spot but it does not download anything so something else is still missing
Thanks for sharing this brief knowledge about how to create the Hotspot in windows 10.
Is there a way to automatically turn on the Hotspot upon booting up the PC?
If you have already created your hotspot with the command:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=Hotspot key=ZiZiPass
To run adhoc, just execute the command:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
You can create a runadcoh.bat with the command above file and add it to your Windows 10 Startup folder(Win+R->shell:startup)
Or run this command from the Windows task scheduler at the computer boot (At startup trigger).
I did what you suggested but seems running the .bat file does not trigger to turn on the hotspot upon boot up or just by clicking it. it may have something to do as i’m running Windows 10.
HI,
Can enable WPS Feature for windows hostednetwork (Soft AP)?
If Yes,
Please explain how to do it/
I didn’t find etailed technical information about the support or examples of usage Wi-Fi Protected Setup mode (WPS) on the Windows hostednetwork, but on the MSFT website there is such an info:
The wireless Hosted Network interacts with Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) , another important new feature in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 with the Wireless LAN Service installed. The wireless Hosted Network and WPS support a scenario that provisions a WPS-capable device for a non-WPS capable hardware AP. In this case, the SoftAP hosted on Windows is invoked in the background to push the hardware AP profile onto the WPS-capable device.
Thanks for your response,
Please update if you got any information about it.
Something is wrong in this article.
Win10 mobile hotspot is not implemented with hostednetwork. so you can’t enable mobile hotspot with command “netsh wlan start hostednetwork”.
How make to hide SSID?
Hope all of you are healthy & safe with your family.
I have a unique issue with Windows 10 – Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter. I am unable to view Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Network & Sharing window.
Let me explain my issue in detail. I had Windows-7 OS and TP link wifi adapter and uses Baidu Software to create internet hotspot.
I connect internet using Dailup connection then insert TP link wifi adapter in USB slot and it automatically display Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Network & Sharing window which I use to share my internet and create a Hotspot.
Now I have upgraded my OS from Windows-7 to Windows-10 and I used same method to connect internet but it doesn’t display Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Network & Sharing window to share internet and create Hotspot. However, it display Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Device Manager and it is working correctly.
Now to display missing Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Network & Sharing window I have troubleshooted below steps but there is no luck.
1. Uninstalling and reinstalling driver from device manager.
2. Enabling and disabling driver from device manager.
3. Network Reset
4. Windows Troubleshoot to fix network issue.
5. Netsh command to enable hosted network.
6. Reverting Windows-10 to Windows-7 (Works great on win-7 again)
7. Commands such as IP release and renew, ip flushdns, etc
8. Downloading updates for Windows-10 & troubleshooting again.
None of the above steps have helped me to display missing Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Network & Sharing window.
Please help me to display this missing Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter on Network & Sharing window.
Any Registry Key or Services changes required let me know I will do it.
Note:1. When I open Windows-10 Settings > Networking > Status I can see Microsoft Virtual Wifi Miniport Adapter there with an asterisk sign but not visible on Network & Sharing window.
Note:2. I have connected LAN wire to PC directly to create Dailup connection. I don’t have any router at present.
First, use the “netsh wlan show drivers” command to verify that your your tplink wireless adapter supports hostednetwork
After running netsh wlan show drivers it says hostednetwork – No for my TP link wifi adapter.
Hi,
I am using Windows 10 LTSC 2019 on HP ZBook G3. I check and it shows that my laptop can be used Hotspot. I have a LAN connection, and want to share internet over wifi card. However, when I click to open wifi or Mobile hotspot, it will be automatically turned off (and shows “We can’t set up mobile hotspot”).
I had tested on any new Windows 10 (windows 10 1900, windows 10 ltsc 2019, windows 10 2016), it can be turn on Mobile hotspot successfully after installation. However, after update some packs, it lost this function. I think Microsoft turn off this function because of something reasons, eg. security.
Have you had any ideas to solve this situation?
It has been working great for two weeks. Now when hotspot is on, pc browsers (all of them, Windows 10) stop working. The same using mobile hotspot gui and command line method. Hotspot is working and my cell is connected to Internet. When hotspot is switched off all browsers are ok again. I can not understand that as I did not modify anything in setup. PC was not even restarted.
After installing KB5014699, Windows devices might be unable to use the Wi-Fi hotspot feature. When attempting to use the hotspot feature, the host device might lose the connection to the internet after a client device connects.
Workaround: To mitigate the issue and restore internet access on the host device, you can disable the Wi-Fi hotspot feature.
Can I know which LAN card supports AP mode? Could i get the model name?
List saved wireless network SSIDs and passwords in Windows (PowerShell one-liner to display passwords of all WLAN profiles ):
(netsh wlan show profiles) | Select-String “\:(.+)$” | %{$name=$_.Matches.Groups[1].Value.Trim(); $_} | %{(netsh wlan show profile name=”$name” key=clear)} | Select-String “Key Content\W+\:(.+)$” | %{$pass=$_.Matches.Groups[1].Value.Trim(); $_} | %{[PSCustomObject]@{ PROFILE_NAME=$name;PASSWORD=$pass }} | Format-Table –Wrap