Windows has many tools for diagnosing problems in TCP/IP networks (ping, telnet, pathping, etc.). But not all of them allow you to conveniently check the status or scan opened network ports on a remote server. The Portqry.exe utility is a convenient tool to check the response of TCP/UDP ports on remote hosts to diagnose issues related to the operation of various network services and firewalls in TCP/IP networks. Most often, the Portqry utility is used as a more functional replacement for telnet command, and unlike telnet, it also allows you to check open UDP ports.
Scanning Open UDP/TCP Ports with PortQry
The first version of PortQry for Windows Server 2003 doesn’t work correctly in newer OS versions (Windows Server 2008 and newer), so the second version of the utility, PortQryV2, has been released. It is the version that you should use today (you can download PortQryV2 here).
Download and extract the PortQryV2.exe archive. Run the command prompt and go to the directory with the utility, for example:
cd c:\tools\PortQryV2
For example, to check the availability of a DNS server from a client, you need to check if 53 TCP and UDP ports are open on it. The syntax of the port check command is as follows:
PortQry -n server [-p protocol] [-e || -r || -o endpoint(s)]
- -n is the name or IP address of the server, which availability you are checking;
- -e is the port number to be checked (from 1 to 65535);
- -r is the range of ports to be checked (for example, 1:80);
- -p is the protocol used for checking. It may be TCP, UDP, or BOTH (TCP is used by default).
In our example, the command looks like this:
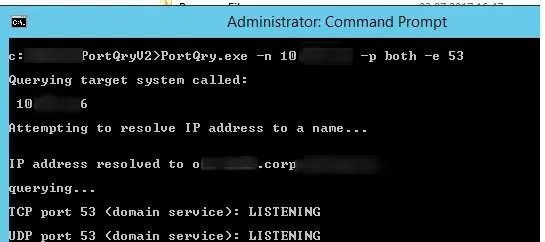
PortQry.exe –n 10.0.25.6 -p both -e 53
Portqry will return one of three available port states:
- Listening – means that the port is opened (accepts connections), a response has been received from it;
- Not Listening – shows there isn’t any process (service) on the target system that accepts connections on the specified port. The PortQry received an ICMP response “Destination Unreachable – Port Unreachable” when checking the UDP port, or TCP packet with the Reset flag;
- Filtered – means that PortQry hasn’t received any response from the specified port or the response has been filtered. I. e., this port is not listening on the target system, or the access to it is restricted by a firewall or some system settings. By default, TCP ports are polled 3 times, and UDP is one.
In our example, the DNS server is available from the client both over TCP and UDP ports.
TCP port 53 (domain service): LISTENING UDP port 53 (domain service): LISTENING
Using -o attribute, you can specify the sequence of ports to check their availability:
portqry -n 10.0.25.6 -p tcp -o 21,110,143
The next command scans the ranges of the well-known TCP/IP port numbers and returns the list of ports that accept the connections (works as TCP Port Scanner):
portqry -n 10.0.25.6 -r 1:1024 | find ": LISTENING"
You can save the open ports scan result to a text file:
portqry -n 10.0.25.6 -p tcp -r 20:500 -l scan_port_log.txt
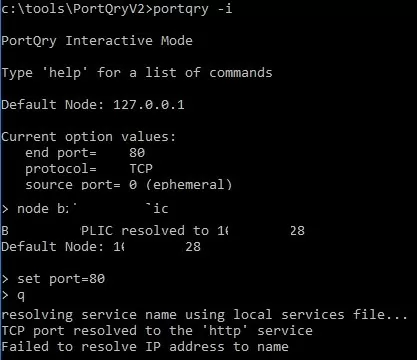
The portqry utility has an interactive mode:
portqry –i
Now, at the PortQry Interactive Mode prompt, you can specify the name of the remote computer and port number:
node srv-lic
set port=80
To check the port on the specified server, press q and Enter.
Using the -wport and -wpid arguments, you can monitor the status of the specified port (wport), or all ports associated with the specified process (wpid) on the local host.
For example, the following command will monitor the response of the specified local port within 10 minutes (for example, RDP port 3389), and if its status changes, it will notify the administrator about this (a detailed log will be available in the LogFile.txt). To stop port monitoring, press Ctrl-C:
portqry -wport 3389 -wt 600 –l LogFile.txt -y -v
You can get information about opened ports and active TCP/UDP connections on the local computer:
portqry.exe -local
Advanced Network Services Open Ports Status in PortQry
PortQry has built-in support for some network services. These are LDAP, Remote Procedure Calls (RPC), e-mail protocols SMTP/POP3/IMAP4, SNMP, FTP/ TFTP, NetBIOS Name Service, L2TP, etc. In addition to checking port availability, the tool performs protocol-specific requests to obtain the status of services.
For example, using the following command you can check the availability of the RPC endpoint mapper service (TCP/135) and get the list of names of RPC endpoints registered on the computer (including their names, UUID, the address they are bounded to, and the application they are related to).
portqry -n 10.0.25.6 -p tcp -e 135
TCP port 135 (epmap service): LISTENING Using ephemeral source port Querying Endpoint Mapper Database… Server’s response: UUID: d95afe72-a6d5-4259-822e-2c84da1ddb0d ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [49152] UUID: 8975497f-93f3-4376-9c9c-fd2277495c27 Frs2 Service ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [5722] UUID: 6b5bd21e-528c-422c-af8c-a4079be4a448 Remote Fw APIs ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [63006] UUID: 12345678-1234-abcd-ef22-0123456789ab IPSec Policy agent endpoint ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [63006] UUID: 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-912345001003 ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [63002] UUID: 50cda2a3-574d-40b3-1d66-ee4aaa33a076 ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [56020] …….. UUID: 3c4428c5-f0ab-448b-bda1-6ce01eb0a6d5 DHCP Client LRPC Endpoint ncacn_ip_tcp:10.0.25.6 [49153] Total endpoints found: 61 ==== End of RPC Endpoint Mapper query response ==== portqry.exe -n 10.0.25.6 -e 135 -p TCP exits with return code 0x00000000.
Or you can check the availability and response from the SQL Server Browser service running on the Microsoft SQL Server:
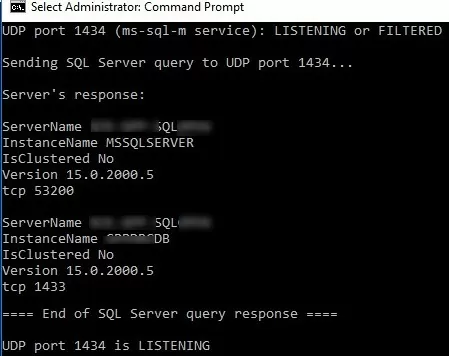
PortQry.exe -n rome-sql01 -e 1434 -p UDP
UDP port 1434 (ms-sql-m service): LISTENING or FILTERED Sending SQL Server query to UDP port 1434... Server's response: ServerName ROME-SQL01 InstanceName MSSQLSERVER IsClustered No Version 15.0.2000.5 tcp 53200 ServerName ROME-SQL01 InstanceName DBINVENT IsClustered No Version 15.0.2000.5 tcp 1433 ==== End of SQL Server query response ==== UDP port 1434 is LISTENING
As you can see, the PortQry tool showed not only the availability of the 1434/UDP port but also the version of the SQL server and the names of the instances running on the SQL server and their TCP ports. The first DBINVENT instance listens on the default port TCP/1433, and the second MSSQLSERVER uses a fixed TCP/53200 port from the RPC range.
You can poll the SNMP port on the device by specifying the community name:
portqry -n rome-sql1 -cn !snmp_trap! -e 161 -p udp
When checking port TCP/25 on an SMTP server, you can get the service SMTP banner:
portqry -n mx.woshub.com -p tcp -e 25
PortQuery GUI Version
Originally, the PortQry was exclusively a console (CLI) tool. To make it more convenient for the users who don’t like to use the command prompt, Microsoft has developed a simple graphic interface for portqry – PortQueryUI. You can download PortQueryUI from the official Microsoft download website: PortQueryUI.
Actually, PortQueryUI is a graphic add-on for portqry to generate a command and return the result in the graphic window.
In addition, the PortQueryUI contains several predefined set of queries to check the availability of the popular Microsoft services:
- Domain and trusts (checking ADDS services on an Active Directory domain controller)
- Exchange Server
- SQL Server
- Networking
- IP Sec
- Web Server
- Net Meeting
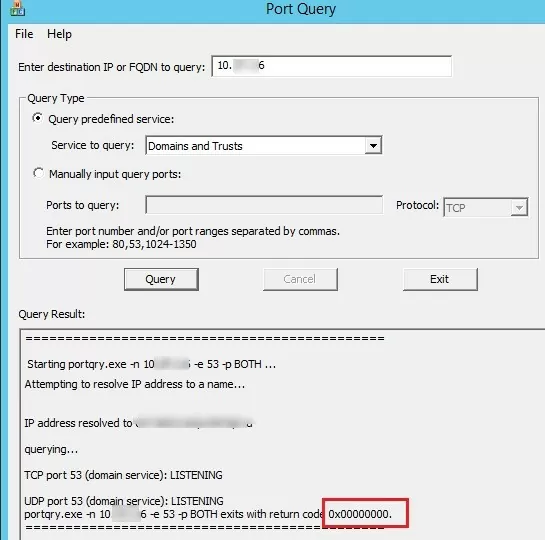
I think PortQueryUI doesn’t need any special comments. It should be clear if you look at the screenshot below. Enter the DNS name or IP address of the remote server, select one of the predefined services (Query predefined service), or specify the port numbers for manual port check (Manually input query ports) and click the Query button.
Possible return codes in PortQueryUI (highlighted in the screenshot):
- 0 (0x00000000) – the connection has been established successfully and the port is available;
- 1 (0x00000001) – the specified port is unavailable or filtered;
- 2 (0x00000002 – a normal return code when checking the availability of a UDP connection, since ACK response is not returned.
1 comment
Hi, very usefulll! Thanks for your time and effort to write such an article!