Sometimes, when you try to delete, rename, or move a file or folder in Windows, you may receive a message saying the file is busy, locked, or in use by another process. The name of the program that is holding the file open is most often listed directly in the error. To unlock a file, simply close this program. However, it is possible that the required file is being used (locked) by an unknown or system process.
If a program opens a file in exclusive mode, the file system blocks other applications from performing input/output (I/O) operations on that file. If you attempt to edit or delete a locked file, a message appears indicating that the file is already in use.
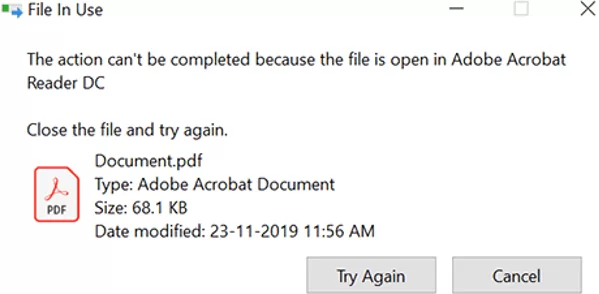
File/Folder in Use. The action can’t be completed because the file is open in another program. Close the folder or file and try again.
In this example, it is obvious which app has locked the file. To release the file, just close this program.
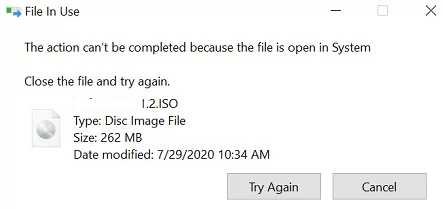
If a file is locked by the operating system or a process running with SYSTEM privileges, the “file is in use” message typically doesn’t display the specific app name responsible for the lock.
The action can’t be completed because the file is open in SYSTEM. Close the file and try again.
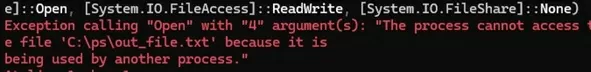
The process cannot access the file XXX because it is being used by another process.
When a Windows process opens a file, a file descriptor (handle) is assigned to its input/output (I/O) stream. The Window API allows you to send a signal to the file system to release the handle and unlock the file.
Find Out Which Process is Locking a File or Folder in Windows
There are several built-in Windows tools that allow you to identify the process (program) that is currently using a file.
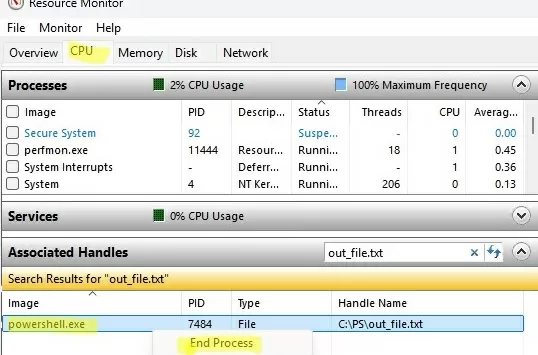
The Resource Monitor tool (resmon.exe) can be used to identify which files are open and by which processes:
- Run the
resmon.exeand go to the CPU tab - In the Associated Handles section, type the name of the locked file or folder in the search bar.
- The name of the process currently using the file will appear in the search results window.
- You can kill this process immediately by clicking on it and selecting End Process.
How to Unlock a File Using Process Explorer
It is not always possible to simply kill the process that has locked the file, especially on servers. The ProcessExplorer tool is useful for identifying the process that has locked a file and releasing it without terminating the parent process.
Download ProcessExplorer from the Microsoft website or install it using the WinGet package manager:
Winget install Microsoft.Sysinternals.ProcessExplorer
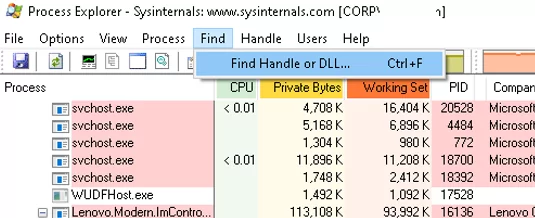
- Run the ProcessExplorer ( procexp.exe ) as an administrator.
- Select Find -> Find Handle or DLL (or press
Ctrl-F); - Specify the file name you want to unlock and click Search
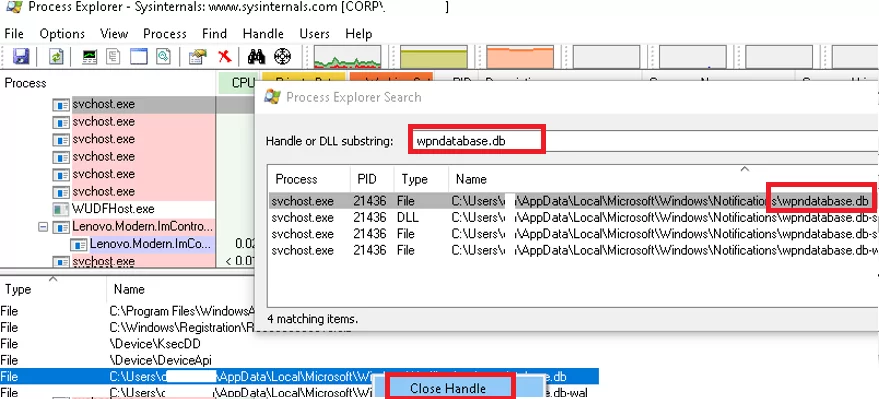
- Select the file you need. The process that opened the file will be highlighted in the process tree.
- You can stop this process by right-clicking on it and selecting Kill Process Tree.
- However, you can try to close the file handle without terminating the process. The file handle that you searched for is automatically highlighted in the bottom panel of Process Explorer
- Right-click the handle and select Close handle. Confirm closing the file.
So, you closed the file handle without terminating the parent process. You can now delete or rename the file.
How to Release a File Lock Using the Handle Tool
Handle is a Microsoft console tool that can identify the process locking your file and remove the lock by releasing the handle.
- Download or install the Handle utility using WinGet:
winget install Microsoft.Sysinternals.Handle - Open the command prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
handle64.exe > listproc.txt - This command saves the list of open handles to a text file.
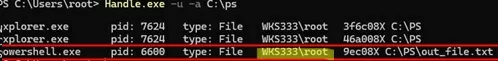
- You can list all the open file handles in a specific directory (the
-uoption shows the name of the user who ran the process):Handle.exe -u -a C:\Some\PathOr, list the open handles for a specific process (which files the process holds open):
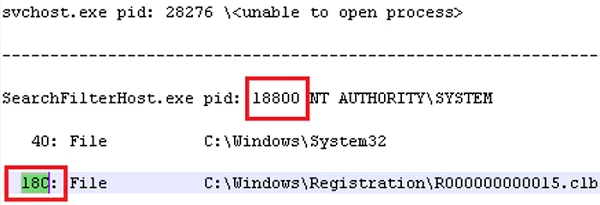
handle.exe -p winword.exe - Open listproc.txt in any text editor and find the line that contains the name of the locked file. Copy the file handle ID in hex format. Then, scroll up to the section where the process that owns the handle is shown and write down its ID. It is most likely that a process run as system will have PID 4.Handle.exe may return the following for some system processes:
wininit.exe pid: 732 \<unable to open process>. It means that you cannot get any information about these system processes (even as an administrator). To retrieve handles for files opened by such processes, run the cmd.exe with SYSTEM privileges and then list the handles again - Then, return to the command prompt and reset the file handle using its HandleID and ProcessID:
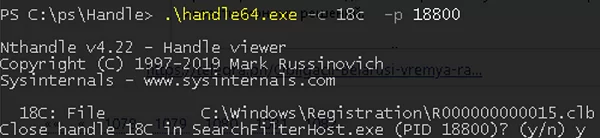
handl64e.exe -c HandleID -p ProcessIDFor example:handl64e.exe -c 18C -p 18800 - The tool will prompt you to confirm that you want to close the file description for a specific process. Confirm it by pressing
y->enter.
If Windows (or the running program) responds properly to the file closing, you can unlock your file without needing to kill the process or reboot the server/computer.
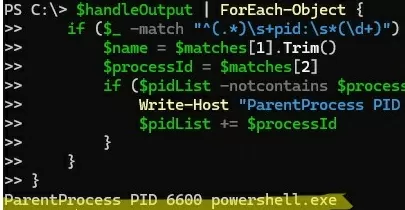
The following PowerShell script can be used to automatically identify the process that has locked the file:
$file = "C:\scripts\out_file.txt"
$handleOutput = handle.exe $file
$pidList = @()
$handleOutput | ForEach-Object {
if ($_ -match "^(.*)\s+pid:\s*(\d+)") {
$name = $matches[1].Trim()
$processId = $matches[2]
if ($pidList -notcontains $processId) {
Write-Host "ParentProcess PID $processId $name"
$pidList += $processId
}
}
}
Locked Files in a Shared Network Folder
Most of the above tools will not show who has opened a file exclusively in a shared folder on a computer if the file is being accessed over the network. This applies to both simple and admin shared folders.
Use the following command to list the files that have been opened over the network:
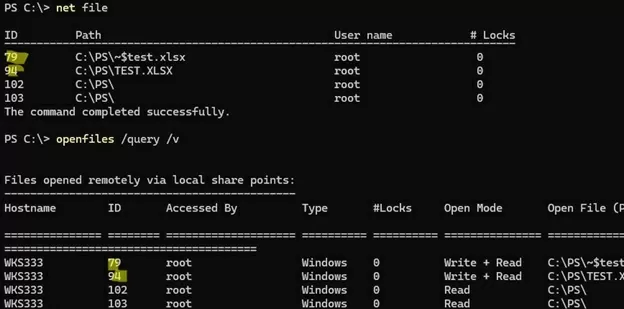
net file
or
openfiles /query /fo
To close an open (locked) file, run:
net file [id] /close
Learn more about how to find and close open files in a shared network folder.