To apply new local or domain Group Policy (GPO) settings to a Windows computer, the Group Policy Client (gpsvc) service must read the policy files and apply the setting to the environment. Group Policy settings are updated when the Windows boots, when the user logs on, and automatically in the background (within 90 to 120 minutes). Sometimes an administrator may want to force new GPO settings to apply immediately, without waiting for the above events to occur.
Refreshing Group Policy Settings on Windows
Group Policy is automatically refreshed on the client in the following cases:
- Group Policy settings specified in the Computer Configuration section are applied when Windows starts.
- GPO settings from the User Configuration section are applied when the user logs in.
- Automatic Group Policy refresh occurs in the background every 90 minutes + random time offset between 0 and 30 minutes (random delay used to reduce the load on the DC from the clients). This means that the new policy settings will be applied to the clients within 90 to 120 minutes after the GPO files have been changed on the DC.Domain controllers update GPO settings every 5 minutes.
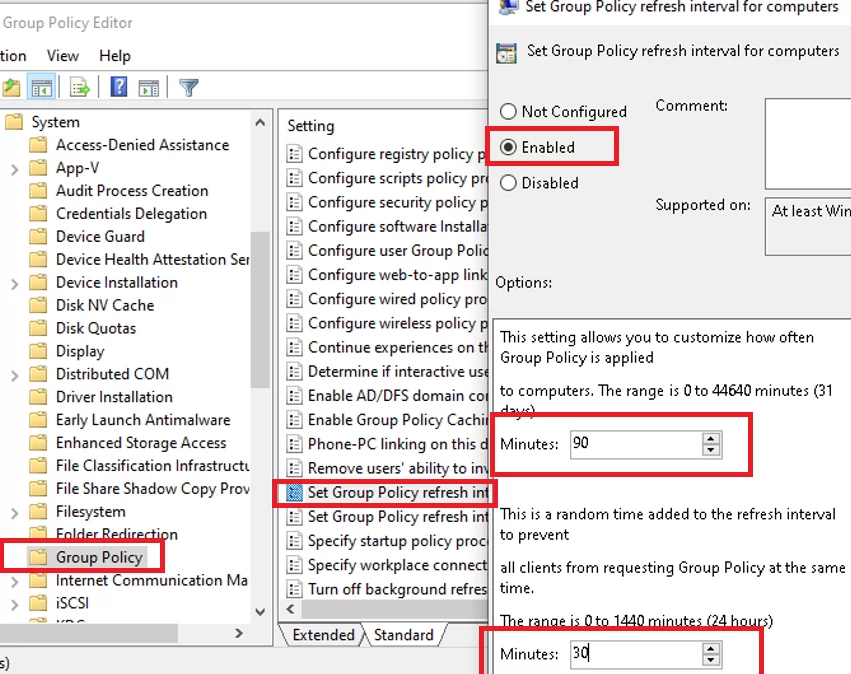
The background policy refresh settings can be changed using the GPO options in Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Group Policy:
- Set Group Policy refresh interval for computers – this parameter allows to change the refresh frequency of the GPO settings from the default 90 minutes, and edit the offset value.
- Turn off background refresh of group policy – completely disable background GPO updates
However, in most cases it is not recommended to modify the default background GPO refresh settings.
Forcing Windows to Refresh GPO Settings with GPUpdate.exe
The gpupdate command line tool is used to force update (apply) the Group Policy settings on a Windows computer.
To update the Group Policy configuration on the client machine, most administrators use the following command:
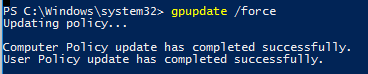
gpupdate /force
This command forces the computer to re-read all policies from the domain controller and re-apply all settings. The force key tells the client to re-download the files of ALL the GPOs targeted to it from the domain controller. This may increase the load on the network and the domain controller.
If you run the gpudate command without any parameters, this will only apply the new and changed GPO settings.
Updating policy... Computer Policy update has completed successfully. User Policy update has completed successfully.
You can update only the user’s GPO settings:
gpupdate /target:user
or only the computer’s policy settings:
gpupdate /target:computer /force
If some GPO settings policies cannot be applied in the background (usually it is the client-side GPO extensions that are processed when the user logs on), gpudate command can log off the current user:
gpupdate /target:user /logoff
Or restart a computer (some policies are only applied when Windows boots, such as software deployment via GPO or startup/logon scripts).
gpupdate /boot
How to Force a Group Policy Update on Remote Computers
There are several ways to force an update of GPO settings on remote Windows computers.
In simple cases, you can run the gpupdate command on the remote computer with any remote tool:
- Using PSexec tool:
PsExec \\manPC21 gpupdate - via PowerShell Remoting (WinRM):
Invoke-Command -computername manPC21 -Scriptblock {gpupdate /force}
If you need to bulk update GPO settings on multiple domain computers, use the Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc).
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
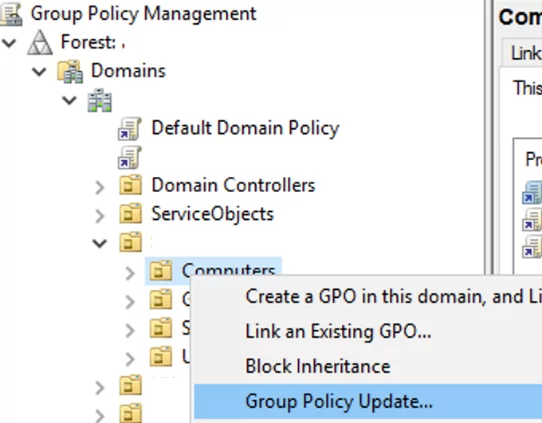
To update the policy settings on the remote computers, click on the target Organizational Unit (OU) in the GPMC console and select Group Policy Update.
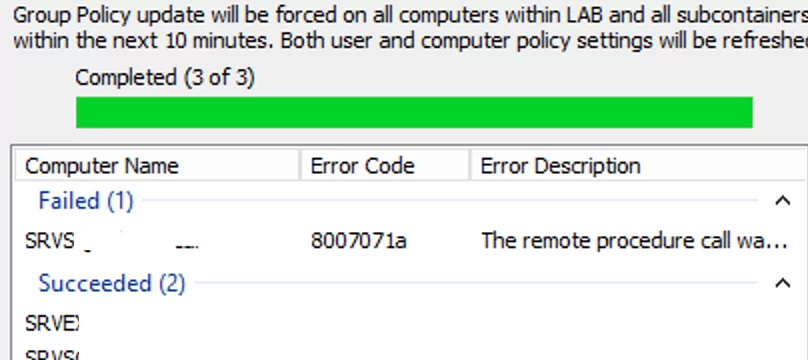
The console will connect to each computer in the OU in turn and will return the policy update status (Succeeded or Failed).
The utility creates a Task Scheduler job on a remote computer that runs the GPUpdate.exe /force command for each logged-on user. The task will start after a random time (up to 10 minutes) to reduce the network load on DC.
- Remote Scheduled Tasks Management (RPC)
- Remote Scheduled Tasks Management (RPC-ERMAP)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-IN)
If a computer is powered off or a firewall blocks access to it, the The remote procedure call was canceled. Error Code 8007071a’ error will be returned.
The Invoke-GPUpdate PowerShell can also be used to update GPO settings on remote computers. For example, to update user policies on a remote computer, run:
Invoke-GPUpdate -Computer manPC21 -Target "User"
-RandomDelayInMinutes 0 parameter.When used with the Get-ADComputer cmdlet, you can force all computers (except inactive ones) in a specified OU to update their Group Policy settings:
Get-ADComputer –filter {enabled -eq "true"} -Searchbase –"OU=Computes,OU=Mun,OU=DE,dc=woshub,dc=com" | foreach{ Invoke-GPUpdate –computer $_.name –RandomDelayInMinutes 10 -force}
When you run the Invoke-GPUpdate cmdlet remotely or update the GPO from the GPMC, a black prompt with the running gpupdate command might appear briefly on a user’s desktop.
4 comments
Amazing like always !!
Hi,
How could you update the policies of a user who is currently logged into a computer remotely?
Than kyou.
Hey Jorge, do you know psexec? This tool is very powerful for administrators, it enable you make domain computers execute CMD commands, you can open remote CMD in others computers and do all you have to do.
Hi Michel,
I know about that tool, but I haven’t been able to run a user session gpo update remotely.
I think you need rdp to the opened user session and run a gpupdate.
Thank you.