Administrators should occasionally delete old user profiles (retired or inactive users, etc.) from C:\Users on Windows workstations and servers. The Windows user profile cleanup task is most commonly performed on Remote Desktop Services (RDS) terminal servers.
The main problem with RDS servers is the constant growth in the size of the user profile directories on the hard disk. This problem is partially solved by user profile size quotas using FSRM or NTFS quotas, roaming profiles such as FSLogix or User Profile Disk, redirected folders, etc. However, if you have a large number of RDS users, over time the C:\Users folder will contain a large number of directories with old (unused) user profiles.
How to Delete a User Profile in Windows Manually?
In Windows, you can delete a profile manually from the Control Panel:
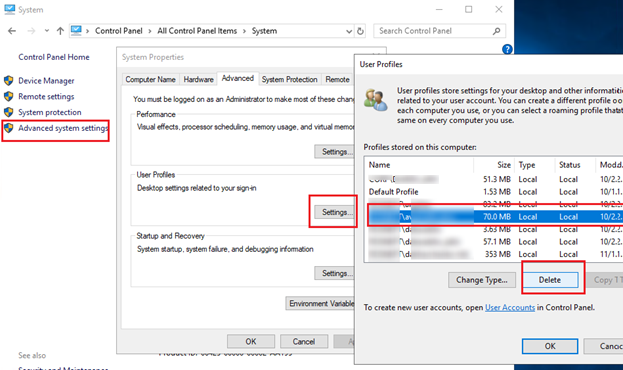
- Open the Advanced System Settings (run the command
SystemPropertiesAdvanced) and go to User Profiles -> Settings; - This window lists all the user profiles (local, domain, and Microsoft accounts) stored on this computer. The size of each user profile on disk is listed in the Size column;
- Select the user whose profile you want to delete and click the Delete button.
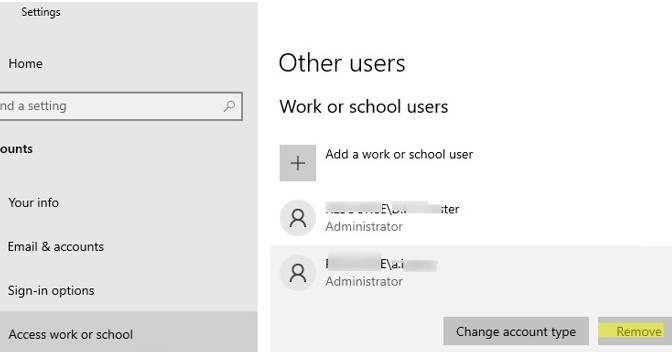
On Windows 11/10 and Windows Server 2022/2019, you can delete user profiles from disk through the Settings app. Go to Accounts -> Access work and school (or run the URI shortcut ms-settings:otherusers ). Select a user and click Remove to delete their profile data from the computer.
When a user profile is properly deleted in Windows, the profile directory in C:\Users and the user entry in the registry are deleted.
Many novice administrators try to manually remove the user profile directory from the C:\Users folder. In this case, you will need to manually delete the profile reference from the Windows registry:
- Run the Registry Editor (
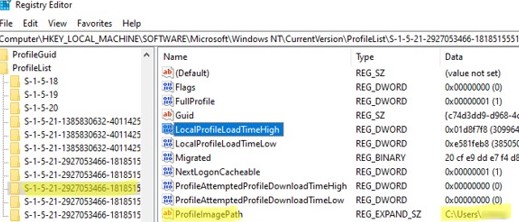
regedit.exe); - Go to the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList;
- For each user logged in locally (this login method must be allowed for the user by the Allow log on locally GPO option), a separate sub-key is created with the user’s SID as the name;
- You can find the registry key corresponding to the user by its SID, or you can manually browse the contents of all subkeys until you find a key in which the ProfileImagePath value points to the directory with the user profile on disk (for example,
C:\Users\j.smith); - Delete this registry key to complete the correct removal of the profile.
You can also delete a specific user’s profile using PowerShell:
Get-CimInstance -Class Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.LocalPath.split(‘\’)[-1] -eq 'j.smith' } | Remove-CimInstance
This command removes both the hard drive directory and the j.smith user profile reference under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList registry.
You can remove a user profile on a remote computer using PowerShell Remoting and the Invoke-Command cmdlet:
$compname="mun-wks92s3"
$user = "j.smith"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $compname -ScriptBlock {
param($user)
Get-CimInstance -Class Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.LocalPath.split(‘\’)[-1] -eq $user } | Remove-CimInstance
} -ArgumentList $user
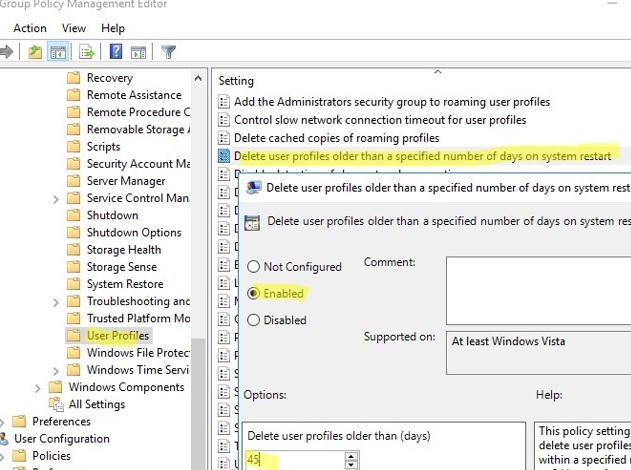
GPO: Delete User Profiles Older Than a Specified Number of Days
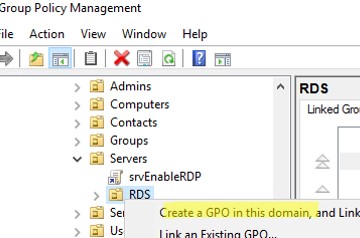
In Windows, there is a built-in Group Policy option to automatically delete user profiles older than xx days. You can enable this option using the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) or with the domain GPO management console (gpmc.msc). In this example, we are going to apply an automatic profile cleanup policy to hosts in the RDS farm that are in a separate container (Organizational Unit, OU) in Active Directory.
- Locate the OU containing the computers/servers to which you want to apply the user profile cleanup policy. Right-click on the OU and select Create a GPO in this domain and Link it here;
- Specify the policy name and edit the GPO;
- Navigate to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> User Profiles;
- Open the option Delete user profiles older than a specified number of days on system restart;
- Enable the policy and specify the number of days a user profile is considered active. When this period is over, Windows User Profile Service will automatically delete the profile at the next restart. It is recommended to specify 45-90 days here;
- After you apply the new Group Policy settings, the User Profile Service on your Windows Server will automatically delete the old user profiles. User profiles will be deleted at the next server reboot.
Another disadvantage is that you cannot prevent certain profiles from being removed, such as local accounts, administrators, etc.
This policy didn’t work correctly in versions before Windows 11/10 and Windows Server 2022/2019. Previously, user profile inactivity was determined by the date the NTUSER.dat file was modified. When installing Windows updates, the Trusted Installer service can change the modification date of the NTUSER.dat file in each user’s profile. As a result, the Win32_UserProfile service thinks that the profile has been used recently.
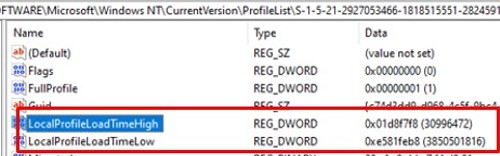
In modern versions of Windows, this Group Policy option checks for user profile activity against the values of the LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow and LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh parameters under in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList\<USER_SID>
You can use the following script to get the LocalProfileLoadTimeLow and LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh registry values in normal time format:
$profilelist = Get-ChildItem "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList"
foreach ($p in $profilelist) {
try {
$objUser = (New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier($p.PSChildName)).Translate([System.Security.Principal.NTAccount]).value
} catch {
$objUser = "[UNKNOWN]"
}
Remove-Variable -Force LTH,LTL,UTH,UTL -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$LTH = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileLoadTimeHigh -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileLoadTimeHigh
$LTL = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileLoadTimeLow -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileLoadTimeLow
$UTH = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh
$UTL = '{0:X8}' -f (Get-ItemProperty -Path $p.PSPath -Name LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue).LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow
$LoadTime = if ($LTH -and $LTL) {
[datetime]::FromFileTime("0x$LTH$LTL")
} else {
$null
}
$UnloadTime = if ($UTH -and $UTL) {
[datetime]::FromFileTime("0x$UTH$UTL")
} else {
$null
}
[pscustomobject][ordered]@{
User = $objUser
SID = $p.PSChildName
Loadtime = $LoadTime
UnloadTime = $UnloadTime
}
}
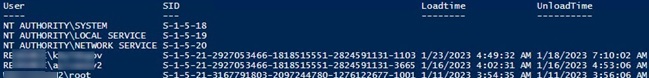
This list contains the last load time for each user profile.
Delete Old User Profiles with PowerShell Script
Instead of using the automatic profile cleanup policy described above, you can use a simple PowerShell script to find and remove the profiles of disabled or inactive users.
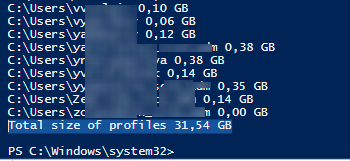
First, let’s try to calculate the size of each user’s profile in C:\Users using a simple script from the article Getting Folder Size with PowerShell
gci -force ‘C:\Users\’-ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where { !($_.Attributes -match " ReparsePoint") }| ? { $_ -is [io.directoryinfo] } | % {
$len = 0
gci -recurse -force $_.fullname -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | % { $len += $_.length }
$_.fullname, ‘{0:N2} GB’ -f ($len / 1Gb)
$sum = $sum + $len
}
"Total size of profiles",'{0:N2} GB' -f ($sum / 1Gb)
The total size of all user profiles in C:\Users is about 32 GB.
Let’s see the list of users whose profiles have not been used for more than 60 days. You can use the value in the LastUseTime field of the profile to find them.
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}| Measure-Object
It turned out that I had 127 inactive user accounts on my RDS host (with profiles total size of about 18 GB).
The following PowerShell script lists the details of user profiles that have not been updated for more than 60 days. The script converts the user’s SID to a name, calculates the size of each user’s profile, and displays a resulting table:
$allprofilesinfo = @()
$OldProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}
Foreach ($OldProfile in $OldProfiles)
{$objSID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier ($OldProfile.SID)
$objUser = $objSID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$userinfo = New-Object PSObject -Property @{
userName = $objUser.Value
ProfilePath = $OldProfile.localpath
LastUsedDate = $OldProfile.ConvertToDateTime($OldProfile.LastUseTime)
FolderSize = "{0:N2} GB" -f ((gci –force $OldProfile.localpath –Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue| measure Length -s).sum / 1Gb)
}
$allprofilesinfo += $userinfo
}
$allprofilesinfoTo remove all these user profiles, it is sufficient to pipe the list of users to the Remove-WmiObject command (it is recommended that you check the output of the script with the -WhatIf parameter before running it):
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-30))} | Remove-WmiObject –WhatIf
The screenshot above shows that all profiles were changed at about the same time. Check the date of the last updates installed in Windows:
gwmi win32_quickfixengineering |sort installedon |select InstalledOn -Last 1
Or using the PSWindowsUpdate module:
Get-WUHistory | Select-Object -First 10
It will most likely coincide with the date the profiles were changed. Therefore, on earlier versions of Windows, you can get a list of inactive profiles using another script that checks the lastwritetime attribute of the user’s profile directory:
$USERS= (Get-ChildItem -directory -force 'C:\Users' | Where { ((Get-Date) — $_.lastwritetime).days -ge 60 } | % {'c:\users\' + $_.Name})
foreach ($User in $USERS) {
Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.LocalPath -eq $User)} | Remove-WmiObject WhatIf }
To avoid deleting the profiles of some users (such as System and Network Service accounts, a local administrator account, accounts of users having active sessions, and other accounts from the exception list), you can modify the script as follows:
#The list of accounts, which profiles must not be deleted
$ExcludedUsers ="Public","zabbix_agent","svc",”user_1”,”user_2”
$LocalProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}
foreach ($LocalProfile in $LocalProfiles)
{
if (!($ExcludedUsers -like $LocalProfile.LocalPath.Replace("C:\Users\","")))
{
$LocalProfile | Remove-WmiObject
Write-host $LocalProfile.LocalPath, "profile deleted” -ForegroundColor Magenta
}
}
You can run this PowerShell script via a GPO at shutdown or with a PowerShell script in Task Scheduler.
You can modify the script to automatically delete all user profiles added to the specific AD group. For example, you want to delete the profiles of users who have quit. Just add these accounts to the DisabledUsers group and run the script on the target host:
$users = Get-ADGroupMember -Identity DisabledUsers | Foreach {$_.Sid.Value}
$profiles = Get-WmiObject Win32_UserProfile
$profiles | Where {$users -eq $_.Sid} | Foreach {$_.Delete()}

38 comments
Using Remove-WmiObject to get rid of the Win32_UserProfile sets only clears out the user home folders. I found that users can still sign in with their old locally-cached Windows Hello (for Business) PINs; is there a way to flush those credentials out of the TPM too?
This article shows how to clear user profiles that have not been logged in for a long time. After deleting the profile, users can log in again and a new profiles directory will be created for them.
Amazing! Thanks a lot for this!
This is going to save me so much time.. and its so clearly explained.. Fantastisch!
Thank you for the very detailed article. However, what is the right command to delete only a specific user profile?
I use the below command STE.
Get-CimInstance -Class Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.LocalPath.split(‘\’)[-1] -eq ‘UserA’ } | Remove-CimInstance
Hi. I tried run the script to delete old profiles in my Windows Server 2016 but the message was showed:
Exception calling “ConvertToDateTime” with “1” argument(s): “Exception calling “ToDateTime” with “1” argument(s): “Specified argument was out of the range of
valid values.
Parameter name: dmtfDate””
At line:3 char:64
+ … le | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTim …
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [], MethodInvocationException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : ScriptMethodRuntimeException
Were you able to figure out how to fix this error? I am getting it as well
yeah commun error, due to an update. i am looking for the solution as well for a fair amount of time
Instead of « $_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) » just use « $_.LastUseTime »
i applied this policy and it ended up deleting 2 profiles that werent older than the setting in the GPO was set to. Now trying to use data recovery software on the drives and that’s only pulling corrupted files now. Wish i would of never even used the GPO. Not sure what the hell happened.
Using an untested GPO on a live System? Are you nuts?
At least you took a learning from this.
I started a few computers and none of the user profiles are older that one day. The computers has been shutdown over a month and at least 10 user profiles are older than two years.
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-1))}| Measure-Object
Count : 0
Average :
Sum :
Maximum :
Minimum :
Property :
That GPO doesn’t work either because Windows updates modifies NTUSER.DAT file in every user profile. New modified times are also show in Advanced System Settings -> User Profiles -> Settings.
[…] to work around the issue The PowerShell script in the Windows OSHub post “How to Delete Old User Profiles Using GPO and PowerShell?” looks […]
Update: July 2021
Reportedly, the group policy setting now checks the LocalProfileUnloadTimeLow & LocalProfileUnloadTimeHigh keys within HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList\, to determine when to delete a profile. Hi Gents, I have a question with regard to the scripts above. I have an environment running RDS sessions and want to create a script too clear all inactive user profiles older that 60days. Now my problem is I dont want to delete the profiles like Public and Remote User and Admin and cscsa user profiles. How do I go about altering this script to work for me. I am not a powershell guru so any assistance would be appreciated.
Hi Valentino,
Please check the following line in this script:
$ExcludedUsers =”Public”,”zabbix_agent”,”svc”,”user_1”,”user_2”
It contains accounts that the script will not delete. Just add your accounts to it.
Hello,
Is there a way that I use the built-in Group Policy to automatically delete user profiles older than xx days but at the same time create an exception rule to exclude certain machines ex. local computer profiles?
Cannot for the life of me get this working on Windows 10 21H2. It tells me it’s deleting profiles and that they have been deleted but they are still on the C drive. I test the script on a machine running the file from the desktop. This is what the output is:
C:\Users\deployment$ profile deleted
Remove-WmiObject :
At C:\Users\ygg-itco\Desktop\RemoveUserProfiles.ps1:8 char:17
+ $LocalProfile | Remove-WmiObject
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidOperation: (:) [Remove-WmiObject], COMException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : RemoveWMICOMException,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.RemoveWmiObject
Any help appreciated.
Gareth
Hi Gareth, without knowing the full extent of what you’re trying to achieve based on that limited exposure to your script (as in, enumerating all profiles that meet a set criteria, or just trying to single out a specific user), you should find this works (it gets you the LastUseTime in proper format from the outset, so no additional conversions necessary):
((Get-CimInstance -ClassName win32_userprofile).Where{!$_.Special -and ($_.LastUseTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}).ForEach{$_ | Remove-CimInstance}
(The .ForEach part shouldn’t really be necessary, as the Remove-CimInstance should accept an array input, but you can attempt to throw it in there if you find it bugs without it.)
If you already know the user you want to remove, you can use:
(Get-CimInstance -ClassName win32_userprofile).Where{$_.LocalPath -like “*UsernameHere”} | Remove-CimInstance
You could also make a variable out of it, and then use that in conjunction with other cmdlets to help clear anything Remove-CimInstance may not have removed (I’ve never used it myself, so I am unclear on if it gets every last shred, or if it leaves behind the user folder, but removes all the data within it and the registry key):
$prof = (Get-CimInstance -ClassName win32_userprofile).Where{$_.LocalPath -like “*UsernameHere”}
$prof | Remove-CimInstance
Remove-LocalUser -SID $prof.SID
Again, I’ve never used these methods, I always just use the built-in Windows method within ‘Advanced System Settings’ whenever the rare occasion calls for me to need to remove a user profile. But I do build scripts for me and my Service Desk colleagues to use to help with everyday SD life, so I’m not a complete novice.
Let me know how you get along 🙂
Doesnt work, scrap this article
Even if you can’t get the PowerShell WMI/CIM part to work because your system hasn’t been properly configured for it, the rest of the article still explains other ways to do it, and the comments explain other variations.
There is a difference between something not working and not being able to get something to work.
It would be useful if you could provide some sort of data to backup your claim that the method is fundamentally broken, and it isn’t just that LastUseTime sometimes is blank or whatever.
Worked for me today on my 21H2 image except instead of “-60” for the “AddDays” part, I had to do “60”
Glad to read it!
If you’re doing it like that though, it will get all the accounts on the machine, and you can just get rid of the .AddDays(60) because you’re essentially telling it to get profiles where the LastUseTime is less than 60 days from the current date. Removing that part and just using ‘.. -lt Get-Date’ to tell it to get profiles with the LastUseTime less than the current date would return the same results.
Equally, if you didn’t wanna get scoop up any of the more recently used profiles you could set the 60 (or -60) to something a little more reasonable like -15 or -30, so it’ll pick up any profiles on that machine that haven’t been used in the last 15 or 30 days rather than 60 (which is no doubt why -60 returned no results for you… I have a feeling if you lower the number to between -10 and -30 you’ll pick up some waste profiles).
Feel free to let me know how the change works out for you, but if nothing else, make sure you remove the AddDays(60) because for this particular script in question, anything that isn’t a negative number is just the same as not using the AddDays at all, so removing it will keep the code more efficient 🙂
I agree, Completely!
What needs to be understood is that, these are just examples. More often than not, it is up to you, to perform the necessary research & testing, in regard to your own environment, etc.
It should also be noted that Microsoft is in the process of decommissioning the WMI Architecture. As a result, the WMIObject Cmdlets may or may not work, in your Environment. If this is the case, in your environment, you are going to want to utilize the CimInstance Cmdlets, in particular.
Hi,
How can include delete user profile size more than 2gb to this script instead of number of days
#The list of accounts, which profiles must not be deleted
$ExcludedUsers =”Public”,”zabbix_agent”,”svc”,”user_1”,”user_2”
$LocalProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}
foreach ($LocalProfile in $LocalProfiles)
{
if (!($ExcludedUsers -like $LocalProfile.LocalPath.Replace(“C:\Users\”,””)))
{
$LocalProfile | Remove-WmiObject
Write-host $LocalProfile.LocalPath, “profile deleted” -ForegroundColor Magenta
}
}
Please advise
$ExcludedUsers ="Public","zabbix_agent","svc","user_1","user_2"$LocalProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special) -and (!$_.Loaded) -and ($_.ConvertToDateTime($_.LastUseTime) -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}
foreach ($LocalProfile in $LocalProfiles)
{
# Get the total size of the profile directory
$ProfileDirectory = Join-Path $env:SystemDrive 'Users' $LocalProfile.LocalPath.Split("\")[-1]
$ProfileDirectorySize = (Get-ChildItem $ProfileDirectory -Recurse | Measure-Object -Property Length -Sum).Sum / 1GB
if (!($ExcludedUsers -like $LocalProfile.LocalPath.Replace("C:\Users\","")) -and ($ProfileDirectorySize -gt 1))
{
$LocalProfile | Remove-WmiObject
Write-host $LocalProfile.LocalPath, "profile deleted" -ForegroundColor Magenta
}
}
Hi folks, is there a way to exclude the local admin profile or exclude certain other profiles?
To remove user profiles, use the PowerShell script from the article.
#The list of accounts, which profiles must not be deleted$ExcludedUsers ="Public","zabbix_agent","svc","user_1","user_2","administrator"
This line contains a list of user profiles to exclude from deletion.
Also, my comment up above has a code example that will exclude any profiles classified as ‘Special’ – this would be all of the default, built in Windows ones, administrative and the like. Pasted again below for your convenience, with the addition of excluding a predefined list of profiles;
((Get-CimInstance -ClassName win32_userprofile).Where{(!$_.Special -or $_.LocalPath -notlike ”$($ExcUsers)”) -and ($_.LastUseTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-60))}).ForEach{$_ | Remove-CimInstance}
If you read up just a little bit you’ll see my original comment with more of an explainer, plus more details from the admin.
nice to meet you
With reference to the script that lists the details of user profiles on this site that have not been updated in 60 days or more, I ran the following script that removes only the condition part that has not been updated in 60 days or more, but nothing is displayed. not.
What on earth is causing this?
$allprofilesinfo = @()
$OldProfiles=Get-WMIObject -class Win32_UserProfile | Where {(!$_.Special)}
Foreach ($OldProfile in $OldProfiles)
{$objSID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier ($OldProfile.SID)
$objUser = $objSID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$userinfo = New-Object PSObject -Property @{
userName = $objUser.Value
ProfilePath = $OldProfile.localpath
LastUsedDate = $OldProfile.ConvertToDateTime($OldProfile.LastUseTime)
FolderSize = “{0:N2} GB” -f ((gci -force $OldProfile.localpath -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue| measure Length -s).sum / 1Gb)
}
$allprofilesinfo += $userinfo
}
$allprofilesinfo
my misunderstanding.
I will withdraw the question. Please delete it.
Thanks a lot for this article! Helped me a lot, thank you!
that the policy no longer works in Windows 8 and later. This is because it checks for a file which is updated by Windows no matter if the user logs into their account on the machine
The Group Policy method was broken in Windows Server 2016 and is working again, as of Windows Server 2019 and up.
The script doesn’t work:
Method invocation failed because [Deserialized.System.Management.ManagementObject#root\cimv2\Win32_UserProfile] does not contain a method named
| ‘ConvertToDateTime’.
As said in the article LastUseTime is modified by Windows updates and cannot be used. If you use LastWriteTime, actively used profiles are deleted. For example my own profile shows LastWriteTime 2024.2.6 and my last login date is 2024.5.20.
I don’t understand why the article starts out saying that the NTUSER.dat last used date is not accurate since NTUSER.dat gets updated with system updates. An example script is given to list profiles from the registry with last used dates, but then then a script example is given using the last used date of NTUSER.dat. What am I missing?