Microsoft FSLogix technology is used to manage user profiles and allows you to replace Roaming Profiles and User Profile Disks (UPD) in RDS, VDI, and Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD) deployments. FSLogix allows you to dynamically connect user profile containers from shared network folders. It can be used both in on-premises environments and in Azure (you can use Azure Files as profile storage). In this article, we’ll look at how to use FSLogix user profile containers instead of User Profile Disks (UPD) in RDS deployments on Windows Server 2019/2022.
What are FSLogix Containers?
The FSLogix concept is similar to RDS User Profile Disks (UPD) when user profiles are stored as virtual (VHDX) disks and connected via the network when a user logs on to Windows. However, FSLogix allows us to get rid of many UPD disadvantages in RDS environments:
- Allows loading a user profile over the network much faster. It reduces login/logout time for a user;
- Optimized for Office 365 (Microsoft 365 for Enterprise) apps;
- The same profile may be used in different RDS collections, RDS/VDI farms, and even physical computers;
- FSLogix profile may be connected to multiple sessions at once (in read-only mode);
- In UPD, the Windows search index is cleared when a user logs out and must be regenerated at the next logon. FSLogix allows saving the search index to a user profile container;
- Provides the availability of Outlook cache files (OST, Outlook Cached Mode), Outlook search index, cache and MS Teams data, etc.;
- FSLogix roaming profile containers can be used even on standalone RDS hosts.
The FSLogix is free to use in on-premises RDS deployments provided that you have purchased RDS CALs and they are installed on an RDS license server.
How to Install and Configure FSLogix for User Profiles on Windows Server RDS
Let’s see how to install and configure FSLogix on a terminal RDS farm running Windows Server 2019.
- Download FSLogix (https://aka.ms/fslogix/download, about 180 MB). The tool is free;
- Extract the archive and install the FSLogix
\FSLogix_Apps\x64\Release\FSLogixAppsSetup.exeagent on the RDSH server; - Then copy FSLogix administrative policy files to the Central Store of administrative GPO templates on your domain controller (fslogix.admx to \PolicyDefinitions, and fslogix.adml to \PolicyDefinitions\en-US).Learn more about how to install and update ADMX GPO templates.
Create a shared network folder on your file server to store containers with FSLogix user profiles. For example, \\mun-fs01\Share\Profiles.
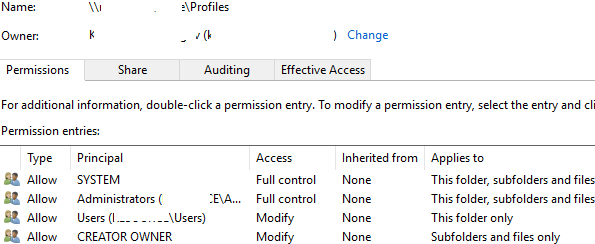
Set the following NTFS permissions on the folder:
| User Account | Folder | Permissions |
|---|---|---|
| Users | This Folder Only | Modify |
| Creator / Owner | Subfolders and Files Only | Modify |
Now you can create a GPO to configure FSLogix options for RDS hosts.
Open the domain GPO management console (gpmc.msc), create a new policy, and assign it to the Organizational Unit (OU) with your RDSH servers. Expand the GPO section Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> FSLogix. Configure the following GPO options:
- Profile Containers -> Enabled – enable FSLogix profiles;
- Profile Containers -> VHD Location – specify the UNC path to the profile shared folder (
\\mun-fs01\Share\Profiles); - Profile Containers -> Delete local profile when FSLogix Profile should apply – delete a local user profile when FSLogix enabled;
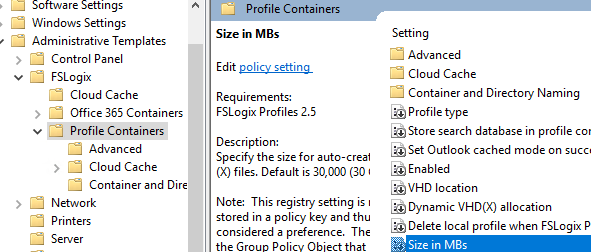
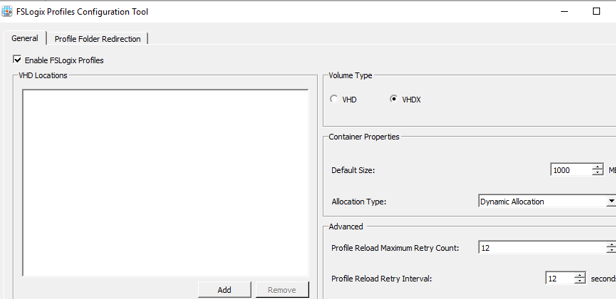
- Profile Containers -> Size in MB – to set the maximum size of a profile file (30,000 MB by default);
- Profile Containers -> Dynamic VHD(X) allocation = Enabled. If you do not enable the policy, the VHD/VHDX disks of user profiles will be created with their maximum size;
- Profile Containers -> Advanced -> Prevent login with temporary profile –prevent creating temporary user profiles;
- Profile Containers -> Advanced -> Prevent login with failure –prevent log on in case of any FSLogix failures;
- Profile Containers -> Advanced -> Locked VHD retry count = 3, specify the number of attempts to access a VHD(X) file if it is locked by another process;
- Profile Containers -> Container and Directory Naming -> Virtual disk type –use VHDX disk type for a profile instead of the default VHD;
- Profile Containers -> Container and Directory Naming -> Swap directory name components –use
%username%_SIDas a format for user profile folders (instead of SID_%username%); - Profile Containers -> Store search database in profile container = Disabled – don’t store Windows Search index database in a profile container;
- Enable logging = All logs enabled —enable FSLogix logs;
- Path to logging files –set a path to FSLogix logs (
\\mun-fs01\Share\FSLogixLogs\%COMPUTERNAME%); - Days to keep log files – 7 days are enough.
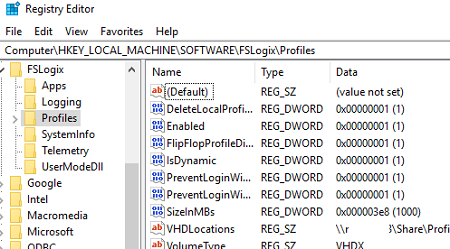
Restart Windows Server to apply new GPO settings. System settings of FSLogix profiles are located under the HKLM\SOFTWARE\FSLogix\Profiles registry key.
Now, when a remote user logs in through the RDP, a notification should appear on the Welcome Screen:
Please wait for the FSLogix Apps Services
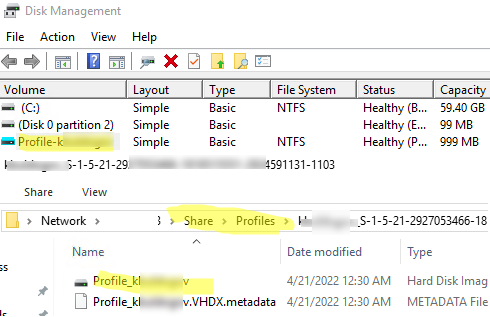
Once logging in, you can open the Disk Management console and make sure that the FSLogix user profile container is mounted as a VHDX disk. A new folder for the user profile has appeared in the share you specified.
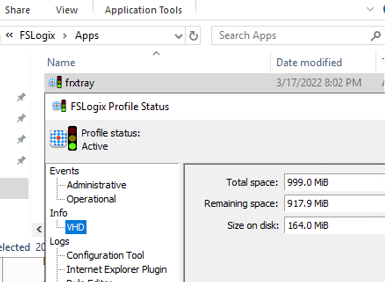
The FSlogix administrative tools are located at C:\Program Files\FSLogix\Apps:
frxtray.exe– this tool displays the FSLogix window in the system tray and allows you to check if a user is logged in with an FSLogix profile;ConfigurationTool.exe– FSLogix profiles GUI configuration tool.
Advanced FSLogix Profile Configuration on Windows Server RDS
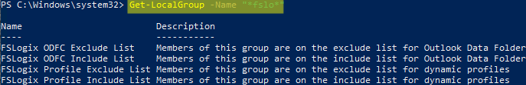
When you install the FSLogixAppsSetup agent on the server, several additional local groups appear. You can display these groups using Get-LocalGroup cmdlet:
Get-LocalGroup -Name "*fslo*"
FSLogix ODFC Exclude List— Members of this group are on the exclude list for Outlook Data Folder ContainersFSLogix ODFC Include List— Members of this group are on the include list for Outlook Data Folder ContainersFSLogix Profile Exclude List— Members of this group are on the exclude list for dynamic profilesFSLogix Profile Include List— Members of this group are on the include list for dynamic profiles
These groups allow set users or groups having FSLogix profiles enabled or disabled.
By default, roaming FSLogix profile containers are created for all users. To allow the members of the local Administrators group to log on to the server locally in case of any FSLogix failures, add the Administrators group to the FSLogix Profile Exclude List.
You can add users to the local group using the Restricted Group policy (Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Restricted Groups -> Add Group -> FSLogix Profile Exclude List) or Group Policy Preferences (Computer Configuration –> Preferences –> Control Panel Settings –> Local Users and Group –> New -> Local Group -> FSLogix Profile Exclude List).
To exclude some folders from an FSLogix roaming profile, you can use the redirection.xml file. Folders in the file are redirected to the local folders on the server’s local drive (local profile folders).
The path to the XML file with the settings is specified in FSLogix -> Profile Containers -> Advanced -> Provide RedirXML file to customize redirections GPO option. You can exclude Temp folders, IE/Edge/Chrome cache directories, etc.
Here is an example of such a file:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <FrxProfileFolderRedirection ExcludeCommonFolders="0"> <Excludes> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\LocalLow\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Packages\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Temporary Internet Files\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\WebCache\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Temp\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Diagnostics\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Comms\</Exclude> <Exclude Copy="0">AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache\</Exclude> </Excludes> </FrxProfileFolderRedirection>
Analyze user profiles, and installed programs and add additional exceptions to the file.
Add FSLogix executable files to your antivirus exclusions (frxdrv.sys, frxdrvvt.sys, frxccd.sys, frxccd.exe, frxccds.exe, frxsvc.exe).
26 comments
Hello,
Sorry to bother you i configured rdp high avalibility wwith broker, so in have two rdp server, can i use this tutorial to set fslogic policies on domain controller and after install fslogic on the 2 rdp servers?
i dont understand what order should i do
What i want is the 2 rdp servers install fslogic and the servers will get the polices from AD about fslogic and apply is this possible?
Yes, you can use the fslogic profile in RDS with Broker HA.
1) Deploy your RDS farm with RDS Connection Broker HA https://woshub.com/configure-rds-connection-broker-high-availability-windows-server/
2) Then install fslogic on the RDS hosts and configure the fslogic settings via GPO.
Hello,
I’m thinking about implementing FSLogix Containers.
I see that no collection is created as in the case of UPD. Will it be possible to connect to shadow session after implementation ?
Of course you can do it. Shadow RD session is a built-in Windows feature and dosn’t depend on the type of user profile used (fslogix, UPD or local)
Hi,
Quick question, is it possible to convert existing UPDs to FSLogix user profile containers?
You can use this Github script to migrate UPD profiles to FSLogix.
_https://github.com/andif888/convert-udp-fslogix
Thank you.
Hello, is threre a way to migrate vom Roaming Profil to FSLogix?
Thanks
Boris
Hi again,
i want to ask again. Are there some clues to move from an roaming enviorment in to an FSLogix?
Thanks
Boris
Great article! Does it make sense to use FSLogix in case of a TS RemoteApp?
Considering that the RemoteApp will run from 3-4 different RDS Session Hosts and doesn’t need to save anything in the user profile, which profile strategy is more appropriate?
Thanks!
It depends on the apps running in the RemoteApp mode. If they store some settings in the user profile folder, is advisable to use a roaming profile concept so that users have the same application settings on any RDSH. This can be FSlogix or UPD.
If there isnothing to save to the user profile, then you can stay with the local RDS profiles. But in a large RDS deployment, the total size of the user profiles that are stored on each host can be quite large.
Thanks for your prompt reply, appreciated!
Good article!
Do you know if it is possible to use FSlogix profile that are created under Windows 2016 RDP server can be used under a new Windows 2022 RDP server?
I haven’t tested this, but I think they should be compatible because Windows Server 2016 and 2022 have the same user profile version (v6).
Good morning.
Could you please explain how to update FSLogix? If you have a procedure available, I would greatly appreciate it if you could share it with me.
Thank you in advance for your help.
Just install the new FSLogix version on the top of the older version. This requires a reboot.
If you are running an RDS farm with multiple RDSH hosts, you should update them during the same maintenance window. Put the hosts in maintenance mode (RDS drain mode), log off users, update FSlogix on the first host, test that users can log in after the update, verify that the login process works, and then install the new version on the next host.
Thank you for this! was thinking about it how we can do fslogix with rds server, I see that you doing it with a local disk, is it possible to do this with a storage account? I know now we can do flsogix for avd for entra join only with a couple of scripts, and was wondering if we can use the same method to do this rds setup with storage account instead of local disk? thanks!
Yes, the FSLogix containers can be stored on any file shares that support the SMB protocol, including Azure Storage Account Blob.
Store FSLogix profile containers on Azure Files and Active Directory Domain Services or Microsoft Entra Domain Services
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fslogix/how-to-configure-profile-container-azure-files-active-directory?tabs=adds
In terms of solidity/reliability of the solutions, with a scratch new RDS deplyment, would you recommend to stay on UPD or adopt FSLogix? Thank you.
Of course, it’s preferable to use FSLogix for new installations.
In fact, I think FSLogix Profiles is even easier to support than UPD.
I asked because it seems to me that MS does not push FSLogix that much, despite that solution has been around for several years now. Thank you for the feedback.
Hello,
I’m in the process of setting up an RDS farm following your tutorial.
I have a question regarding the recommended FSLogix version.
On the following page: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/fslogix/how-to-install-fslogix, two versions are available for download:
https://aka.ms/fslogix-latest → FSLogix_Apps_2.9.8884.27471.zip (approximately 173 MB)
https://aka.ms/fslogix_download → FSLogix_25.02.zip (approximately 90 MB)
I don’t quite understand the difference between the two.
Thank you in advance for your valuable advice! 😊
In most cases, you should use the latest version from https://aka.ms/fslogix-latest.
For legacy scenarios with compatibility concerns, use FSLogix_25.02
Bonjour
S’il vous plaît, savez-vous comment supprimer les profils utilisateurs qui ne se sont pas connectés depuis 30 jours ou qui ont déjà quitté l’entreprise ? Est-il normal que mon partage de profils continue d’augmenter ? Avant, j’avais 50 Go et j’ai dû ajouter un stockage supplémentaire de 100 Go. Quelles sont les recommandations pour la gestion des profils
Merci pour votre aide.
Hello,Please, do you know how to delete user profiles that haven't logged in for 30 days or have already left the company? Is it normal for my profile sharing to continue increasing? I used to have 50 GB and had to add an additional 100 GB of storage. What are the recommendations for profile management?
Thank you for your help.
Check the post How to find and delete old (unused) user profiles in Windows
In the case of the FSLogix profile, you can find unused user profiles by the modification date of the VHDX files.
Thank you for your feedback.
How often should I clean up user VHDX files on my server? Additionally, how can I properly delete them while allowing their recreation? My disks keep filling up.