Windows Group Policy allows you to run various script files at a computer startup/shutdown or during user logon/logoff. You can use GPOs not only to run classic batch logon scripts on domain computers (.bat, .cmd, .vbs), but also to execute PowerShell scripts (.ps1) during Startup/Shutdown/Logon/Logoff.
In modern versions of Windows, you can directly run logon/logoff PowerShell scripts from a GPO editor (previously it was necessary to call the .ps1 file from the .bat batch file as a parameter of the powershell.exe executable).
Run the Domain Group Policy Management console (GPMC.msc), create a new policy (GPO), and assign it to the target Active Directory container (OU) with users or computers (you can use WMI GPO filters for fine policy targeting). Switch to policy Edit mode.
You must select a GPO section to run the PowerShell script, depending on when you want to execute your PS1 script:
- If you want to run a PS script when a user logon (logoff) to a computer (to configure the user’s environment settings, or programs: for example, you want to automatically generate an Outlook signature based on the AD user properties, customize screensaver or Start screen settings), you need to go to the GPO section: User Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Scripts (Logon / Logoff);
- If you want to run the PowerShell script at a computer startup (to disable legacy protocols: NetBIOS and LLMNR, SMBv1, configure computer security settings, etc.) or prior to the computer shutdown, you need to go to the GPO section with the computer settings: Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Scripts (Startup / Shutdown).
How to Run PowerShell Scripts on Windows Startup with Group Policy?
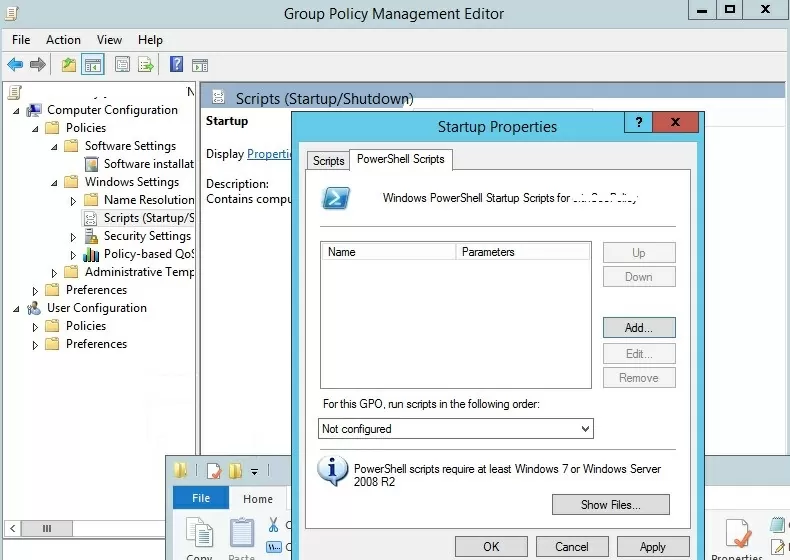
Suppose, we have to run the PowerShell script at a computer startup. Select the Startup policy, and go to the PowerShell Scripts tab.
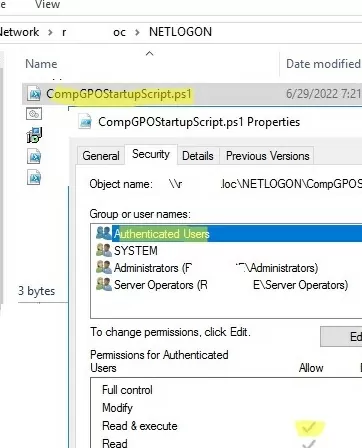
Now you need to copy the file with your PowerShell script to the domain controller. Copy your ps1 file to the Netlogon directory on the domain controller (for example, \\woshub.com\netlogon).
Since we configure the Startup PowerShell script, you need to check the NTFS “Read&Execute” permissions for the Domain Computers and/or Authenticated Users groups in the ps1 file permissions.
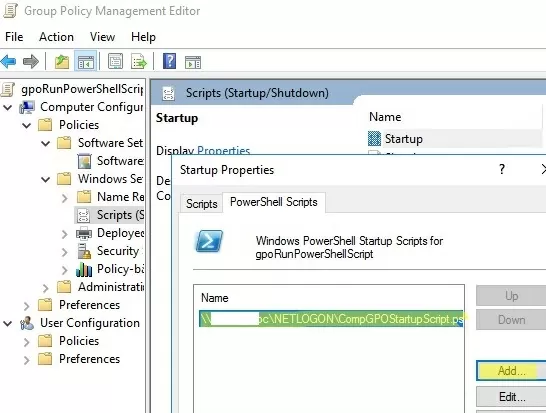
Now click Add and specify the UNC path to your ps1 script file in Netlogon.
If you run multiple PowerShell scripts through a GPO, you can control the order in which the scripts are executed using the Up/Down buttons.
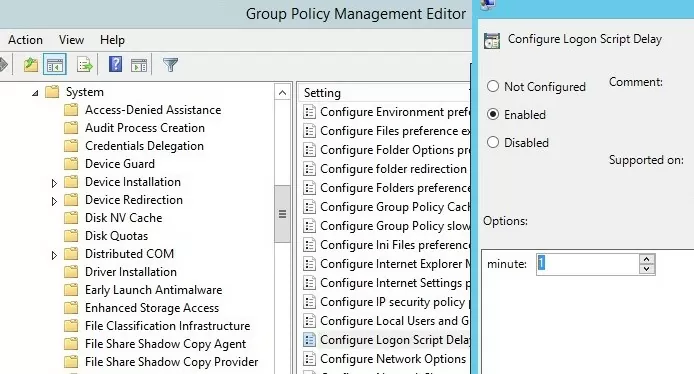
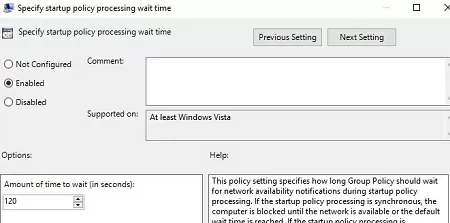
To correctly run PowerShell scripts during computer startup, you need to configure the delay time before scripts launch using the policy in the Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Group Policy section. Enable the “Configure Logon Script Delay” policy and specify a delay in minutes before starting the logon scripts (sufficient to complete the initialization and load all necessary services). Usually, it is enough to put here 1 or 2 minutes.
On Windows Server 2012R2 and Windows 8.1 and newer, PowerShell scripts in GPO are run from the NetLogon directory in the Bypass mode. This means that PowerShell Script Execution Policy settings are ignored. If you want to run a script from a different shared folder, or if you still have Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008R2 clients on your network, you need to configure the PowerShell script execution policy.
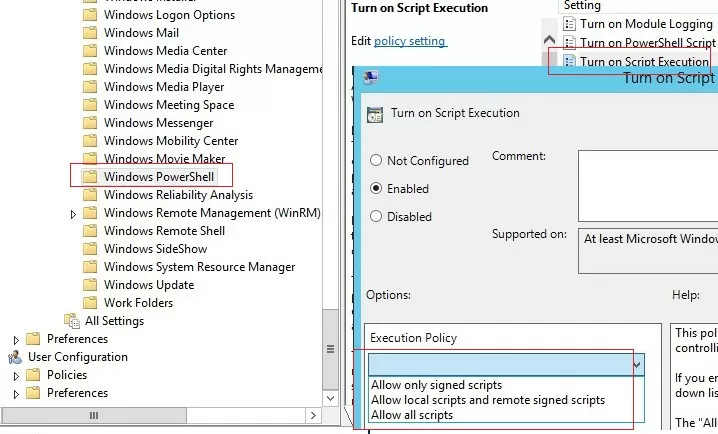
By default, Windows security settings do not allow running PowerShell scripts. The current value of the PowerShell script execution policy setting can be obtained using the Get-ExecutionPolicy cmdlet. If the policy is not configured, the command will return Restricted (any scripts are blocked). The security settings for running the PowerShell script can be configured via the “Turn On Script Execution” policy (in the GPO Computer Configuration section -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell). Possible policy values:
- Allow only signed scripts (AllSigned) – you can run only signed PowerShell scripts (“How to digitally sign a PowerShell script?”) — this is the best option from a security perspective;
- Allow local scripts and remote signed scripts (RemoteSigned) – you can run any local and signed remote scripts;
- Allow all scripts (unrestricted) – the most insecure option, because allows running any PowerShell scripts.
If not one of the settings of the PowerShell scripts execution policy is suitable for you, you can run PowerShell scripts in the Bypass mode (scripts are not blocked, and warnings do not appear).
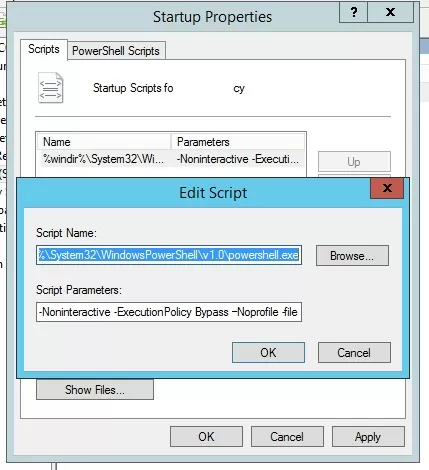
To do this, run the PowerShell script from the Startup -> Scripts section. In this section, you can run your PS1 script by calling the powershell.exe executable (similar to the script described in the article). Set:
- Script Name:
%windir%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe - Script Parameters:
-Noninteractive -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Noprofile -file %~dp0MyPSScript.ps1
%~dp0 is an environment variable that is automatically converted to a UNC path to the script directory (in this case, NETLOGON).In this case, you are forced to allow any (even untrusted) PowerShell script to run using the Bypass parameter.
Reboot your computer to update the GPO settings and check that your PowerShell script runs after Windows boots.
Run Windows PowerShell Script at User Logon/Logoff
Let’s look at how to automatically run a PowerShell script when a user logs into (or logs out) Windows.
If you need to run the script not at computer startup, but after the user logs into Windows (for each user on the computer), you need to link the GPO to the Active Directory OU with users. In this case, the PowerShell script needs to be configured in the User Configuration section of your GPO.
In this example, I will use a simple PowerShell script that writes the user’s login time to a text log file.
- Copy your PowerShell script file to the
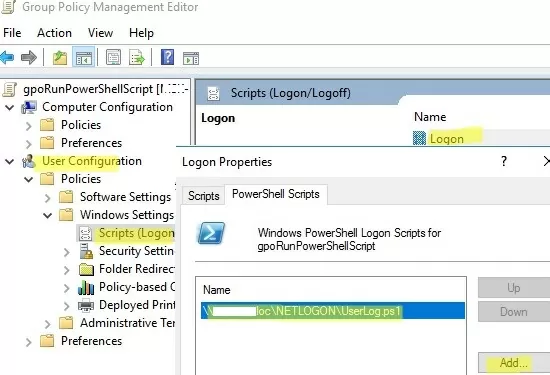
\\woshub.com\NETLOGON\folder on the Active Directory domain controller; - Go to User Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Scripts -> Logon;
- Go to the PowerShell Scripts tab and add your PS1 script file (use the UNC path, for example
\\woshub.com\NETLOGON\UserLog.ps1); - Re-login the user on the target computer;
- Your PowerShell script will be launched automatically via GPO when the user logs in;
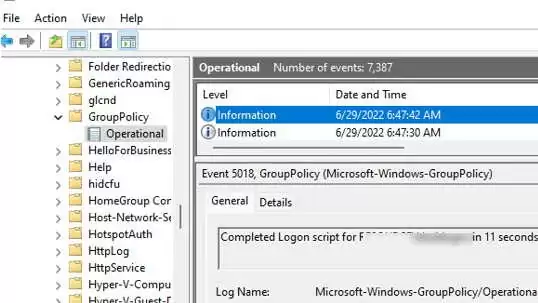
- You can verify that the user logon script was executed successfully by the Event ID 5018u nder Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy/Operational section of Event Viewer:
Completed Logon script for woshub\jsmith in 11 seconds.
If you want the user not to be able to access his desktop until the script is finished, you must enable the GPO parameter Run logon scripts synchronously (Computer Configuration –> Administrative Templates -> System -> Logon). In this case, the explorer.exe process will not start until all policies and logon scripts have been completed (this increases the user logon time!).
Note that the script runs with the current user permissions. If the user has administrative privileges on the computer and the User Account Control (UAC) settings are enabled, the PowerShell script cannot make changes that require elevated privileges.
In order to run PowerShell logon scripts with elevated user permissions, you can use the Scheduler Tasks.
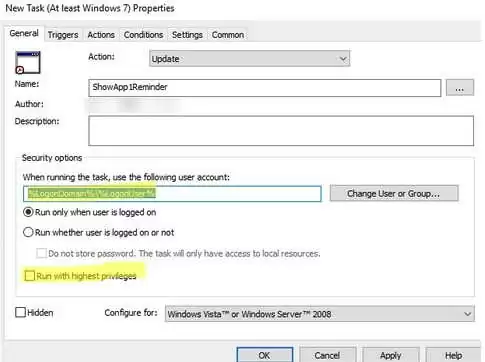
- Create a new Task Scheduler job under User Configuration -> Preferences -> Control Panel Settings -> Scheduled Task;
- On the General tab, specify that the task will be started on behalf of the current user
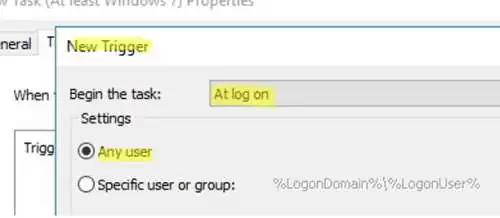
%LogonDomain%\%LogonUserand enable theRun with highest privilegesoption; - On the Trigger tab, specify that the task should be started At log on;
- Specify the path to your PowerShell script file on the Actions tab:
Action: Start a program
Program/Script: C:\WINDOWS\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
Add Arguments (optional): -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -command "& \\woshub.com\Netlogon\Your_PS_Script.ps1"
Such a PowerShell script will run as an administrator (if the domain user is added to the local Administrators group).
Some logon scripts need to be run for each user only once at the first login to the computer (initialization of the working environment, copying folders or configuration files, creating shortcuts, etc.). Here is a simple trick that allows you to run a script only once using GPO.
12 comments
How would you specify -NoProfile in your first GPO example?
Fashionably late as always.
Regardless, you could simply create a .BAT Script, with the following Commands, to accompany your PowerShell Script.
@echo off
%windir%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -Noninteractive -ExecutionPolicy Bypass –Noprofile -file %~dp0MyPSScript.ps1
exit
Script runs fine locally with elevated powershell, however, in testing by \\ to sysvol I am getting an access is not allow and permissiondenied on the registry key. Full error message below:
Set-ItemProperty : Requested registry access is not allowed.
At \\ts-dc02\SYSVOL\thirdsecurity.com\Policies\{16088BE5-A9DA-4A1C-A4A2-9B52C8B9714D}\Machine\Scripts\Startup\DisableNB
NS.ps1:2 char:34
+ … |foreach { Set-ItemProperty -Path “$regkey\$($_.pschildname)” -Name …
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : PermissionDenied: (HKEY_LOCAL_MACH…7-d2d2f7c2680f}:String) [Set-ItemProperty], Securit
yException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : System.Security.SecurityException,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.SetItemPropertyCommand
Hello regarding the section on “Configure Logon Script Delay”. I think you really wanted to “Specify startup policy processing wait time” as you are setup up a Start up Script not a logon script. You want the the network stack to fully load before attempt to run the startup scripts.
Thanks for your post it pointed me in the right direction
I could do an article explaining step by step more using user configuration.
It was not well explained how to do this process.
Please do! I am trying to get the logon script to work and it’s not working.
[…] end up just running a bat file to run the ps file, as it's easier, but you can also do it this way Running PowerShell Startup (Logon) Scripts Using GPO | Windows OS Hub Better way is to sign your scripts […]
For the “Logon script ByPass” solution:
1. The posted code contains mixed hyphens and dashes. So @all, don’t just copy&paste 😉
2. The “%~dp0” won’t expand this way. Fortunately, you don’t need the absolute path to the script file. Just “-ExecutionPolicy ByPass -NoProfile -NonInteractive -File MyPSScript.ps1” will do it already.
Could you please provide the PowerShell way to do the same i.e. to add the shut down script in automated way instead of doing it manually.
if my script is in a shared folder
\\fs01\temp\script\MyPSScript.ps1
then I need to run like this?
Script Parameters: -Noninteractive -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Noprofile -file \\fs01\temp\script\MyPSScript.ps1
It will be right?
It’s true.