This guide explains how to install free Let’s Encrypt TLS/SSL on a Windows host. We’ll cover how to issue, bind, and renew a certificate for an IIS website, and how to use a Let’s Encrypt certificate to secure connections to RDS services.
Let’s Encrypt is an open Certificate Authority (CA) that allows to automatically issue free trusted X.509 cryptographic certificates for TLS (HTTPS) encryption. Only Domain Validation (DV) certificates can be issued with a validity period of 90 days with the option to renew on a scheduled basis.
The Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME) API is the open Let’s Encrypt API interface that enables automated certificate issuance. The WACS (Windows ACME Simple) tool is the most popular ACME API client implementation for a Windows environment.
How to Generate and Install a Let’s Encrypt Certificate on Windows IIS
If you want to automate installing the Let’s Encrypt TLS certificate on Windows, use the Windows ACME Simple (WACS) command line tool. WACS is a simple command-line wizard that lets you select an IIS site and automatically issue and bind a Let’s Encrypt SSL Certificate.
So, I have a Windows Server 2022 host running an IIS web server and a simple website. The task is to install a TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt to enable the site to use the HTTPS protocol.
Download the latest WACS client for your architecture from GitHub https://github.com/PKISharp/win-acme/releases. In my case it is win-acme.v2.2.9.1701.x64.pluggable.zip. Extract the archive to a local folder.
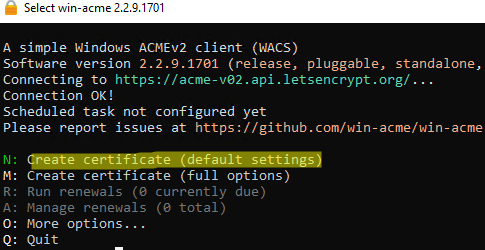
Run the wacs.exe as an administrator.
An interactive wizard will start to help you generate a Let’s Encrypt certificate and bind it to the IIS site. To quickly create a new certificate, select N: — Create certificate (default settings) .
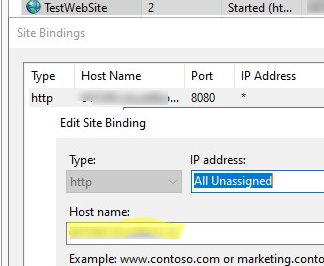
No websites with host bindings have been configured in IIS. Add one in the IIS Manager or choose the plugin 'Manual input' instead. Source plugin IIS was unable to generate options.
In this case, open the IIS Management console (inetmgr), open the Site Bindings settings, and verify that the site has a Host Name set. See “How to run multiple sites in IIS with the same port or IP address” for more information about this parameter.
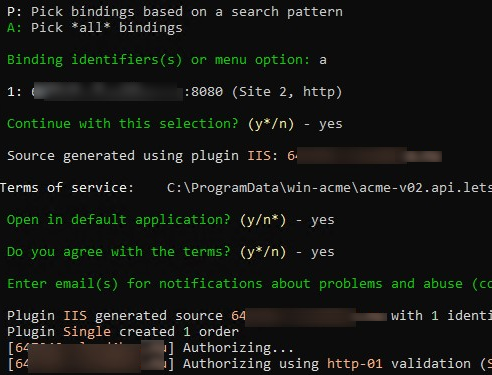
Select the site number to which you want to issue a certificate.
Then press A to select all site bindings and y to continue.
Press y to accept the terms of the user agreement.
Specify the email address of the person who will be notified if there are problems with certificate renewal and other notifications (or enter multiple emails separated by commas).
At this stage, Let’s Encrypt Web Services needs to verify that you are the owner of a domain for which the certificate is being issued. By default, HTTP validation is used (http-01 validation, SelfHosting). This is done by launching a small HTTP Challenge Server on the TCP/80 port (if this port is busy, then IIS will be used). Inbound HTTP port 80 must be open in the firewall. The response file will be written to the web server folder \.well-known\acme-challenge\<random_filename> .
The entire process of enrolling and installing a Let’s Encrypt TLS certificate on IIS is fully automated.
- The certificate’s private key (*.pem) and the certificate itself (*.pfx) are saved to folder
C:\ProgramData\win-acme\acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org\Certificates\ - WACS tool writes detailed logs of all actions to the folder
C:\ProgramData\win-acme\acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org\Log\
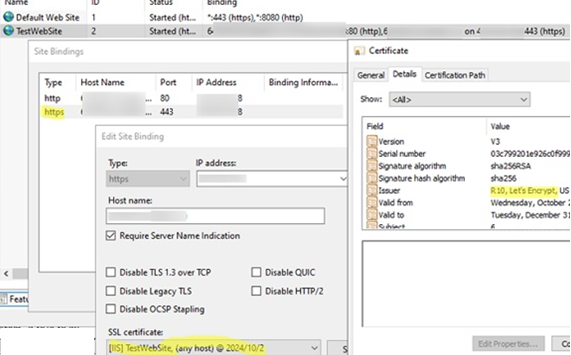
If the domain validation is successful, the tool will retrieve a certificate from the CA, install it in the certificate store, and bind it as an SSL certificate for the target IIS website. If the site already has an SSL certificate installed (for example, a self-signed certificate), it will be replaced with a new one.
Open IIS Manager and navigate to your site’s Bindings settings. Make sure it uses a certificate from R10, Let’s Encrypt Authority.
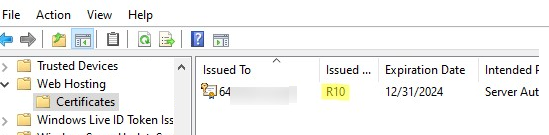
The Let’s Encrypt certificate for IIS is installed in the Web Hosting -> Certificates section of the computer’s certificate store (certlm.msc).
wacs.exe --target manual --host sample.woshub.com --store certificatestore --validation selfhosting --siteid "MyTestWebSite"
Renewing Let’s Encrypt Certificates on Windows
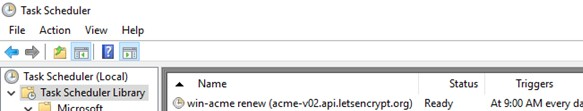
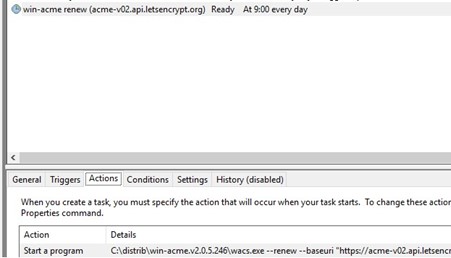
Because Let’s Encrypt certificates expire after 90 days of validity, they need to be renewed regularly. When a new certificate is generated and installed, the WACS tool creates a separate automatic certificate renewal task in the Windows Task Scheduler.
As you can see, it has a win-acme renew (acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org) task that runs a command once a day to check the certificate’s expiration date and renew it:
wacs.exe --renew --baseuri "https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/"
The Let’s Encrypt certificate can be renewed after 60 days from the date of issue.
Enable HTTP to HTTPS Redirect with IIS URL Rewrite
Once your IIS site has a TLS certificate installed, you can stop using the insecure HTTP protocol and switch to HTTPS. All HTTP requests to a site can be automatically redirected to an HTTPS URL address using the Microsoft URL Rewrite Module.
Using Let’s Encrypt Certificates for RDS Gateway and RD Web Access
If you’re using Remote Desktop Gateway or RD Web Access to connect external users to the corporate network, you can install a trusted Let’s Encrypt certificate instead of a default self-signed certificate. Let’s look at how to properly install a Let’s Encrypt certificate to protect Remote Desktop Services connections.
Issue a Let’s Encrypt certificate for the Default Web Site in IIS using the wacs.exe client on the RD Gateway host as described above. This certificate can be manually exported and bound to the RDS services via SSL Binding. But, you’ll have to perform these steps manually every 60 days after your Let’s Encrypt certificate is renewed.
The ACME project provides a PowerShell script to automatically import the Let’s Encrypt cert into the RD Gateway configuration (…\Scripts\ImportRDGateway.ps1). The main disadvantage of this script is that you have to specify the new certificate fingerprint manually:
ImportRDGateway.ps1 <certThumbprint>
To automatically get the certificate thumbprint from a specified IIS site, use the modified ImportRDGateway_Cert_From_IIS.ps1 script (based on the ImportRDGateway.ps1).
You can run this script manually:
powershell -File ImportRDGateway_Cert_From_IIS.ps1
If you have RDS Gateway running on the ‘Default Web Site’ with an index 0, you can use the script as is.
Import-Module WebAdministration
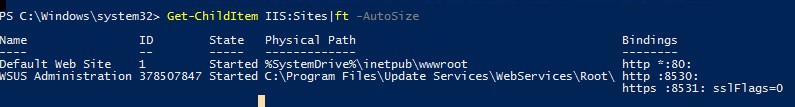
Get-ChildItem IIS:Sites|ft -AutoSize
The ID column shows the index of your IIS site, subtract one from it. In line 27 of the PowerShell script, type the index value that you have instead of 0:
$NewCertThumbprint = (Get-ChildItem IIS:SSLBindings)[0].Thumbprint
Now open the win-acme-renew (acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org) task properties in the Task Scheduler. On the Actions tab, add a new task to run the PowerShell script (ImportRDGateway_Cert_From_IIS.ps1) after the Let’s Encrypt certificate has been renewed.
To avoid changing the PowerShell execution policy settings, you can run the script with the command:
PowerShell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File c:\ps\wacs\scripts\ImportRDGateway_Cert_From_IIS.ps1
Now, immediately after the Let’s Encrypt certificate is renewed, the script will bind the SSL certificate to the RDS services and will restart the RD Gateway service:
Restart-Service TSGateway
When the TSGateway service is restarted, all current RDS user sessions are disconnected, so it is recommended that the frequency of the certificate renewal task be changed to once every 60 days.

10 comments
Hello,
Where would web.config be located? I know I can search for it, I just think it should be mentioned (it’s default location anyway) Thanks great little tutorial.
Default is in the root of the web directory.
Anywhere else is done by design.
I am hoping you can help me out. Please email me.
Scenario:
The issue we are facing is that clients would setup domains in an A record or CNAME like app.customerdomain.com pointed to our domain. That’s on our server like custom.elevatie.com which is binded.
We generate a certificate but where do we bind it because the certificate generated is for client domain which isn’t binded on our system because they have their CNAME/A Record pointed to our custom.elevatie.com to handle all the requests.
But if we were to physically bind the domain on the server and apply the certificate then yes we are able to obtain SSL. But this isn’t the case.
Is there any way to renew the SSL automatic, 30 days before and not 60 days?
Thanks for the guide,
Do you know if the URL Rewrite will break the ACME automated renewal?
I have not encountered such cases. Check your IIS and ACME log files.
Great post
most of free SSLs are 3 months
At Windows Server 2016 Essentials
$NewCertThumbprint = (Get-ChildItem IIS:SSLBindings\0.0.0.0!443)[0].Thumbprintand
$RdsSslCertThumbprint = (Get-Item -Path RDS:\GatewayServer\SSLCertificate\Thumbprint).CurrentValueif ($RdsSslCertThumbprint -ne $CertInStore.Thumbprint)
{
Set-Item -Path RDS:\GatewayServer\SSLCertificate\Thumbprint -Value $CertInStore.Thumbprint -ErrorAction Stop
Restart-Service TSGateway -Force -ErrorAction Stop
"Cert thumbprint set to RD Gateway listener and service restarted"
}
I have been getting a error now with the renewals.
Cert thumbprint was not set successfully
Error: Access to the object at RDS:\GatewayServer\SSLCertificate\Thumbprint is denied for the cmdlet Set-Item.The certificate is not valid or you do not have sufficient permissions to perform this operation.
Any ideas what can be causing it?
[…] un certificat émis par une autorité de confiance. On peut obtenir un certificat gratuit avec Let’s Encrypt ou bien le faire soi-même en PowerShell. C’est la voie que je vais […]