Disk quotas allow Windows administrators to control and limit the amount of disk space that users use on the file systems of servers and workstations. Windows Server supports two types of disk quotas: File Server Resource Manager quotas and NTFS quotas. Though FSRM quotas are more flexible and convenient, in some cases NTFS quotas can be efficiently used. For example, to limit the size of roaming profile folders (but not User Profile Disks) and redirected home folders on RDS hosts, personal user directories on FTP servers and IIS sites, etc. In this article, we’ll walk you through how to configure NTFS disk quotas for Windows users.
Understanding NTFS Disk Quotas in Windows
You can use Windows disk quotas to limit the maximum size of files and folders for each user so that they don’t consume all disk space with their data. Disk quotas are available both in server and desktop Windows versions.
The key features and limitations of NTFS quotas:
- Quotas can only be applied to an entire NTFS-formatted volume (partition). This quota type won’t work on ReFS drives;
- Quotas are applied to all users who store their data on this partition. You cannot apply a quota to a group of users or a separate folder. In this case it’s better to use FSRM;
- File and folder ownership is determined by checking the Owner record in the NTFS security descriptor;
- By default, Windows scans a partition with disk quotas enabled and calculates the total file size of each user once an hour;
- When using NTFS compression, the original file size (before compression) is taken into account.
There are the following scenarios for using NTFS disk quotas:
- Monitoring of the disk usage — viewing statistics of users’ disk space usage on the server;
- Monitoring and notification — in addition to the first scenario, when the quota is exceeded, an event is recorded in the Event Viewer with information about the username and the quota usage;
- Control of the disk usage — if the quota is exceeded, user cannot save new files
Enable Disk Quotas on Windows 10/Windows Server 2016
Let’s consider the case of NTFS quotas configuration on a disk containing user data on the Windows Server 2016. In all previous versions of Windows (starting with Windows 2003), NTFS disk quotas are configured in the same way.
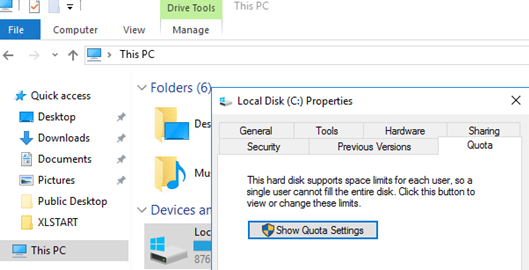
Open the disk properties window, on which you want to enable quotas, go to the Quota tab. Then click Show Quota Settings:
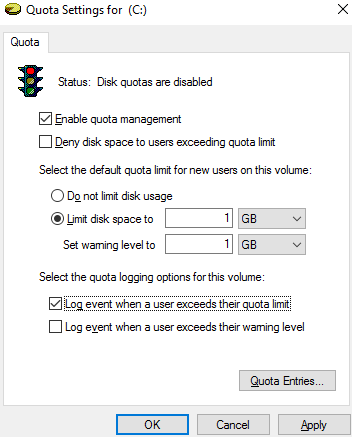
To enable the quotas for this volume, check Enable quota management.
The following options may be checked depending on the scenario of quota usage:
- Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit – prevent users who have exceeded the quota limit from writing to disk;
- Limit disk space to — set a limit on the total size of files for one user;
- Log event when a user exceeds their quota limit – logs an event in the Event Viewer if a user exceeds the quota limit;
- Log event when a user exceeds their warning level – logs an event when the quota threshold is reached.
It is not recommended to enable the option “Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit” at once. It is preferable to estimate the current utilization of disk space by your users. In our example, we want to limit each user to 1 GB of disk space on the server.
Save the changes (Apply). In some time (depending on the disk size and the number of files), Windows will count the total usage of the disk space by every user.
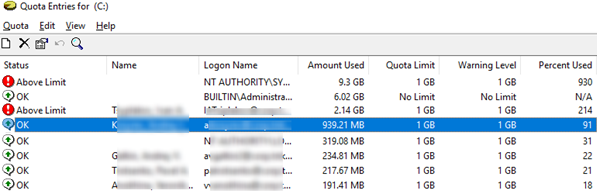
Click on the Quota Entries button. You will see a resulting table showing quotas and the current size of the space used by each user (whose files are found on file system). Here you can see at a glance which users have already exceeded their disk quotas.
By default, the same quotas are set for all users. From the Quota Entries window, you can create, increase or disable a custom quota settings for a certain user.
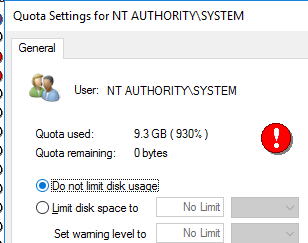
To disable NTFS disk quotas for a specific user account, open the properties (Properties) of the entry in the quota table and check “Do not limit disk usage”.
From the quota list window, you can export your quota settings and then import and apply them to another disk or computer.
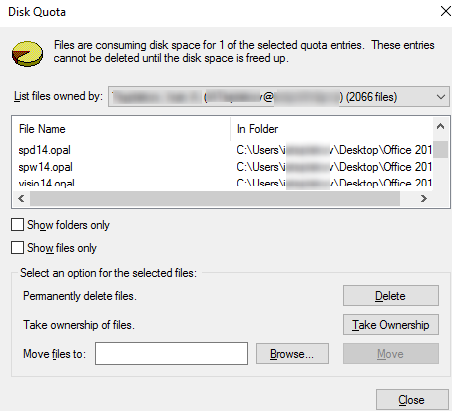
If you want to display a list of files that are counted in the quota of a specific user, you need to select the Delete menu item.
This dialog box allows to change the owner of a specific file (Take ownership), delete or move the file.
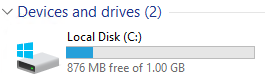
After you have arranged your soft quotas in the audit mode, you can enable the Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit option. This will enable the hard disk quotas mode. Now users won’t be able to exceed their allocated disk space. Please note that the size of the disk in the user session is now displayed according on existing disk quotas. In this example, 876 MB of the 1 GB quota is free for my account on the C:\ drive.
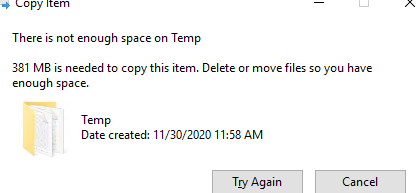
If the quota limit is exceeded, a user receives the following message:
There is not enough space on …. xx MB is needed to copy this item. Delete or move files so you have enough space.
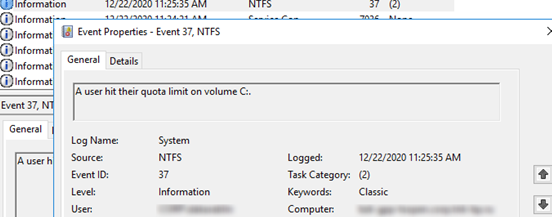
At the same time, an event with the EventID 37 and source Ntfs is logged into Event Viewer:
A user hit their quota limit on volume C:.
Configuring Disk Quotas with Group Policy Settings
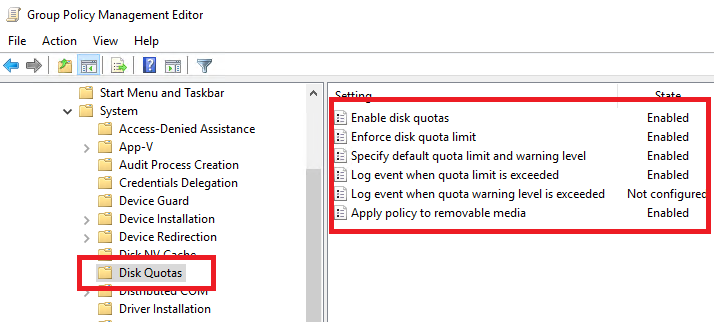
You can manage disk quota settings on computers and servers in domain using Group Policies. The quota settings are located under the GPO section: Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Disk Quotas. To enable disk quotas similar to those discussed above, set the following settings in your GPO:
- Enable Disk Quotas:
Enable - Enforce Disk Quota Limit:
Enable - Default Quota Limit And Warning Level:
Enable(Default quota limit/warning level:1 Gb) - Log Event When Quota Limit Exceeded:
Enable - Apply Policy To Removable Media:
Enable(if you need to apply quotas for removable media, including a USB flash drives)
It remains to assign this GPO to the OU with computers/servers on which you need to apply disk quotas and wait for the update of group policy setting.
Managing Disk Quotas Using Command Prompt/PowerShell
NTFS quotas can also be managed from the command prompt. To do it, the command fsutil quota is used.
To enable soft quota for a disk, use the command:
fsutil quota track E:
To enable hard NTFS quota, run:
fsutil quota enforce E:
To completely disable disk quotas, use the command:
fsutil quota disable E:
To get the current quota settings for a specified drive, run:
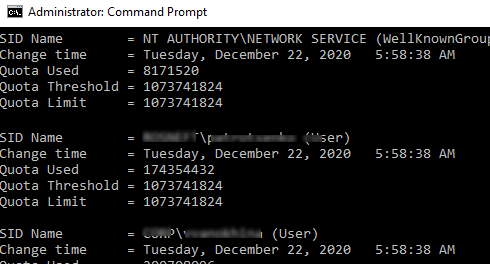
fsutil quota query e:
Get a list of users who have already exceeded their disk quotas:
fsutil quota violations
To change the quota thresholds for a specific user, use the command:
fsutil quota modify E: 2000000000 100000000 corp\aabrams
Quota sizes are specified in bytes (2 GB in this example). The first value is the maximum size of user data on the disk (hard quota), the second is the limit at which warnings appear (warning level).
Find out the frequency of updating disk quotas (in seconds):
fsutil behavior query quotanotify
By default, quotas are updated once an hour.
There are no built-in PowerShell cmdlets for managing NTFS disk quotas. However, they can be managed using the Win32_DiskQuota WMI class. For example, the following PowerShell script will display information about the current user quotas.
$strCom = "."
$colItems = get-wmiobject -class "Win32_DiskQuota" -namespace "root\CIMV2" -computername $strCom
foreach ($objItem in $colItems) {
write-host "Quota usage: " $objItem.DiskSpaceUsed
write-host "Quota Hard Limit: " $objItem.Limit
write-host "Drive: " $objItem.QuotaVolume
write-host "Status: " $objItem.Status
write-host "Username: " $objItem.User
write-host "Quota Warning Limit: " $objItem.WarningLimit
}

1 comment
Very informative, accurate and useful information, thank you! It helped me to solve a wrong disk quota management on sysltem volume C: of my Windows laotop, being then unable to login in my user session properly and to do anything: I had missed to exclude TrustelInstaller and System built-in accounts for quota enforcement! So Windows was unable to work properly… Applying the command “fsutil.exe quota disable C:” in a recovery console session did the trick! Thanks to have let me resolve my issue by finding this tutorial. I believed my disk was died when seeing its size limited to 5 GB in Windows Explorer: I didn’t catch it just was my user limit quota by default! I was very confused because CHKDSK and SFC were reporting no errors, just DISM refusing to execute ScanHealth but was OK with AnalyzeComponentStore and successful with StartComponentCleanup. Thanks again!