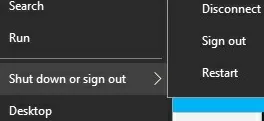
In this article, we will look at several ways to manage non-admin user permissions to restart or shutdown Windows workstations or servers. By default, non-privileged users can only reboot and shut down desktop versions of Windows, and cannot restart a Windows Server host (shutdown and restart buttons are not available in the Start Menu). Is it possible to allow a user without local administrator privileges to restart Windows Server? There is also a reverse task – how to prevent users from restarting a computer with Windows 10 or 11, which is used as an information kiosk, dispatch console, etc.
How to Allow or Prevent Shutdown/Reboot Options in Windows via GPO
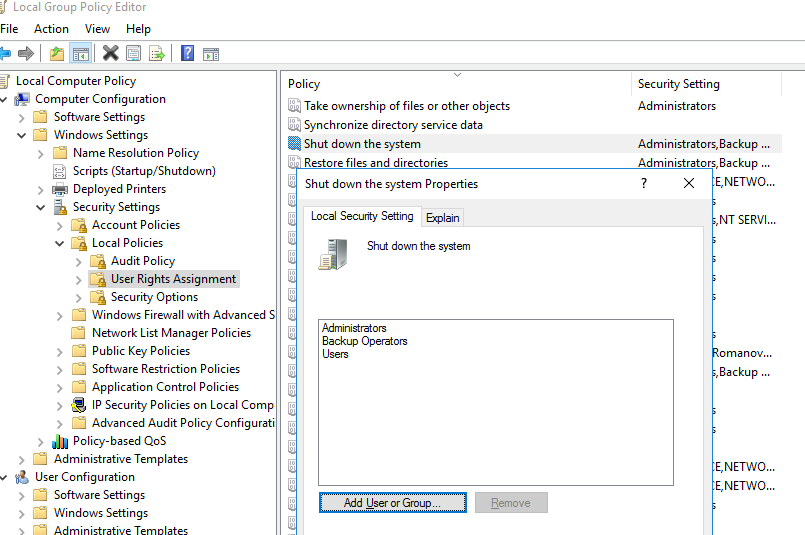
You can set the permissions to restart or shutdown Windows using the Shut down the system parameter in the GPO section Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> User Rights Assignment. This GPO option allows you to specify which locally logged-on users can shut down an operating system.
Please note that the default restart/shutdown permissions for desktop versions of Windows 10/11 and Windows Server editions are different.
Open the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) and navigate to the section specified above. As you can see, the members of local groups Administrators, Users and Backup Operators have the permission to shutdown/reboot a computer running Windows 10 or 11.
On Windows Server 2022/2019/2016, only Administrators or Backup Operators can shut down or restart the server. It is reasonable, since in most cases a non-admin user must not have the privileges to shutdown a server (even accidentally). Just imagine an RDS farm host that is often shuts down since users accidentally click on the “Shutdown” button in the Start menu…
On Active Directory domain controllers, the rights to shut down Windows are delegated to:
- Administrators
- Backup Operators
- Server Operators
- Print Operators
If the user does not have permission to restart/shutdown the operating system, then an error will appear when running the following command:
shutdown –r –t 0
Access is denied.(5)
If you want to allow a specific user (without administrator rights) to restart your Windows Server, you need to add their account to this policy and update the GPO settings on the computer.
ntrights +r SeShutdownPrivilege -u woshub\j.smith
To prevent a user from shutting down or restarting Windows:
ntrights -r SeShutdownPrivilege -u woshub\j.smith
Or, vice versa, you can prevent users of workstations running the desktop Windows 10/11 edition from restarting the computer that performs some kind of server function. In this case, just remove Users group from the local policy Shut down the system.
In the same way, you can prevent (or allow) shutdown/reboot operations for non-admin users on all computers in a specific Organizational Unit (OU) of an Active Directory domain using a domain GPO.
- Create the grpAllowRestartComputers user group in AD, to whom you want to grant the permissions to restart computers. You can create a new group using the ADUC snap-in (
dsa.msc) or theNew-ADGroupPowerShell cmdlet. Add users to the group; - Open the domain Group Policy Management Console (
gpmc.msc). Select the OU with the computers you want to apply the policy to and select Create a GPO in this domain and Link it here; - Set the GPO name (gpoAllowReboot) and edit it;
- Navigate to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> User Rights Assignment;
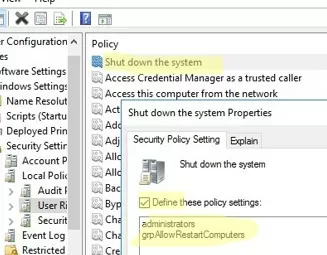
- Open the Shut down option, enable the policy, and add your target group (
grpAllowRestartComputers) and the built-inAdministratorsgroup; - Update the GPO settings on the target computers and check the resulting GPO settings with the
rsop.mscsnap-in. Users in your group can now shut down or reboot this host; - The options to shutdown and restart the operating system will appear in the user’s Start Menu.
Allow Remote Shutdown/Restart without Admin Permissions
You can allow some non-admin users to restart your Windows Server remotely using the shutdown command without granting them local administrator privileges, permission to log on through Remote Desktop (RDP), or local logon permissions (if this sign-in method is not allowed)
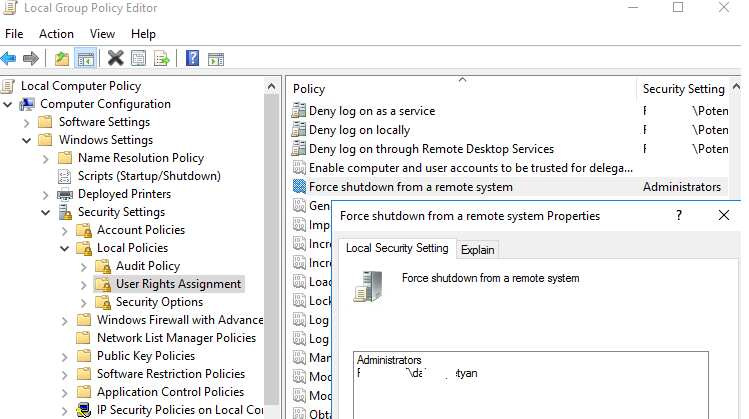
To do it, add a user account to the Force shutdown from a remote system Group Policy option in the same GPO section (User Rights Assignment).
By default, only administrators can shutdown/restart the server remotely. Add a user account to the policy.
ntrights +r SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege -u woshub\j.smith
After that, the user will get the SeRemoteShutdown privilege and will be able to restart the server remotely using the command:
shutdown -m \\hamb-rds01 -r -f -t 0
Or using the Restart-Computer PowerShell cmdlet:
Restart-Computer –ComputerName hamb-rds01 –Force
VERBOSE: Performing the operation "Enable the Remote shutdown access rights and restart the computer." on target ...
If WinRM (Windows Remote Management) is enabled on the remote computer, you can use WSman instead of WMI to connect:
Restart-Computer -ComputerName hamb-rds01 -Protocol WSMan
If the user does not have permission to connect to the WMI namespace, an error will appear:
Restart-Computer : Failed to restart the computer srv-rds1 with the following error message: The WS-Management servicecannot process the request. The WMI service returned an 'access denied' error. .
Disable (Hide) Shutdown or Restart Options From Windows?
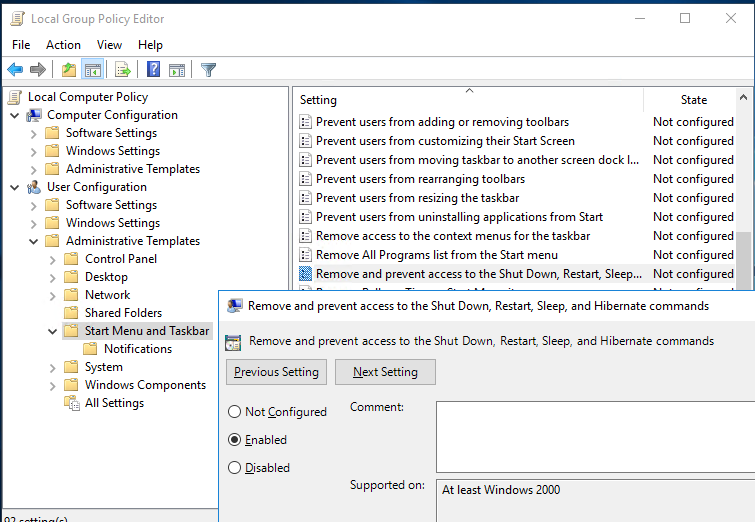
You can use Group Policy to hide the Shutdown, Restart, Sleep and Hibernate options from the sign-in screen and Start Menu. This GPO option is called Remove and Prevent Access to the Shut Down, Restart, Sleep, and Hibernate commands and is located under User Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Start Menu and Taskbar
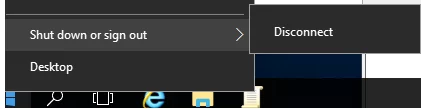
After you enable this policy, a user will be able only to disconnect the current session or use the logoff command. The Shutdown, Sleep and Restart buttons will become unavailable.
You can use some registry tweaks to hide only a specific item from the Power/Shutdown menu in Windows. For example, you want to hide only the “Shut down” option in the Start menu, but keep “Restart”.
- Open the Registry Editor (
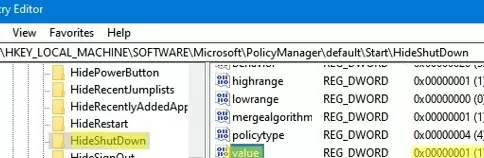
regedit.exe); - Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideShutDown;
- Change the Value option to 1;
- This will hide only the “Shut down” option from the Windows Start Menu.
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideShutDown" /v "value" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
Or using PowerShell:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideShutDown" -Name "value" -Value 1
Also, you can hide other options in the Start Menu and Windows sign-in screen:
- Hide only thr Restart option in Windows:
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideRestart " /v "value" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f - Hide Hibernate option from Start Menu in Windows: R
EG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideHibernate" /v "value" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f - Hide Sleep from the Start Menu:
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideSleep" /v "value" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f - To completely disable the Power button and remove the “Shut down or sign out” option from WinX menu:
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HidePowerButton" /v "value" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
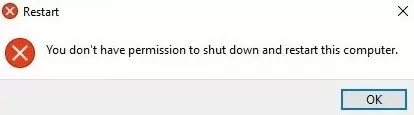
Please note that in Windows Server 2019/2022, after assigning restart permission to a user, an error may appear:
You don’t have permission to shutdown or restart this computer.
In this case, you need to enable the UAC parameter “User Account Control: Run all administrators in Admin Approval Mode” in the GPO:
How to Find Out Who Restarted/Shutdown a Windows Server
If you have granted permission to reboot a computer for a non-admin user, you may want to know who restarted a Windows Server: a user or one of the administrators.
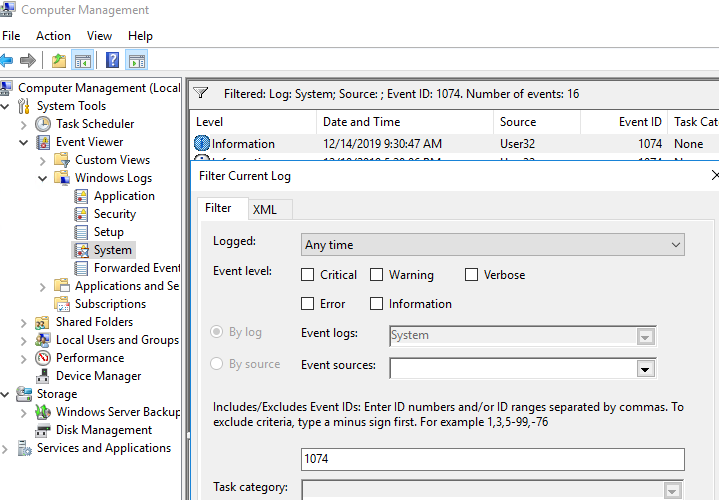
Use the Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc) to search for shutdown logs in Windows. Go to Windows Logs -> System and filter the current log by the Event ID 1074.
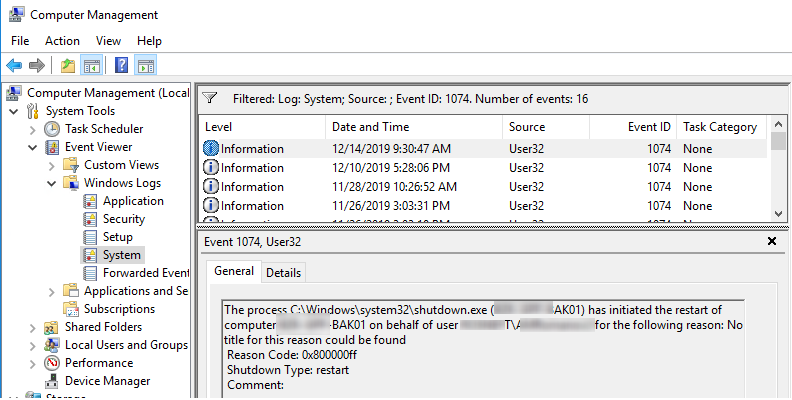
As you can see, there are server restart events in the log in chronological order. The event description includes the restart time, the reason, and the user account that restarted the host.
Log Name:SystemSource: User32 EventID: 1074 The process C:\Windows\system32\shutdown.exe (BE-BAK01) has initiated the restart of computer MUN-BAK01 on behalf of user corp\jsmith for the following reason: No title for this reason could be foundReason Code: 0x800000ff Reason Code: 0x500ff Shutdown Type: restart Comment:
You can get information about recent Windows shutdown events using the same Event ID 1076:
The process C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\vmtoolsd.exe (MUN-BAK1) has initiated the shutdown of computer MUN-BAK1 on behalf of user NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM for the following reason: Legacy API shutdown Reason Code: 0x80070000 Shutdown Type: shutdown Comment:
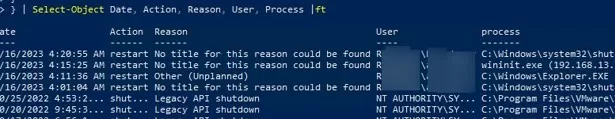
Use the following simple PowerShell script to list the last ten computer restart and shutdown events. This list contains the names of the users and processes from which the reboot was initiated.
Get-EventLog -LogName System |
where {$_.EventId -eq 1074} |select-object -first 10 |
ForEach-Object {
$rv = New-Object PSObject | Select-Object Date, User, Action, process, Reason, ReasonCode
if ($_.ReplacementStrings[4]) {
$rv.Date = $_.TimeGenerated
$rv.User = $_.ReplacementStrings[6]
$rv.Process = $_.ReplacementStrings[0]
$rv.Action = $_.ReplacementStrings[4]
$rv.Reason = $_.ReplacementStrings[2]
$rv
}
} | Select-Object Date, Action, Reason, User, Process |ft
7 comments
So sad that there’s no option to disable only shutdown. I have a need to allow user to restart their machines but not shutdown.
FYI you can hide shutdown from the start menu using HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PolicyManager\default\Start\HideShutDown
Thanks, but even so an advanced user would know to turn it off using other ways.
Thank you MT.. this helped..
Me too!
On Windows 11, this did work, however, a user who is blocked from restarting/shutting down in this way, can still press Control-Alt-Delete and has the restart/shutdown option in the lower right hand corner. Is there a way to remove that, too?
I just actually tried it from a “non-privileged” account. The good news is that although the options appear, they don’t actually work. 🙃