Microsoft has officially ended support for Internet Explorer (IE) in all current builds of Windows 10 and 11 since June 15, 2022 (except LTSC editions and Windows Server). The classic Internet Explorer 11 app now redirects the user to the built-in Microsoft Edge browser. Microsoft promises to completely disable the IE in modern Windows builds in the upcoming updates. In this article, we will show you how to disable or uninstall Internet Explorer on Windows 11/10/8.1 and Windows Server.
How to Uninstall Internet Explorer in Windows 10 and 11?
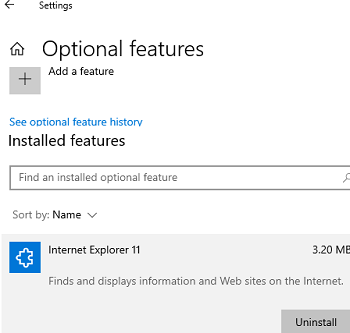
In Windows 10 and 11, Internet Explorer 11 comes as a separate feature available as a Feature on Demand/FoD (like RSAT or NetFx3). You can install or uninstall the IE through the Settings app.
- Go to Settings -> Apps -> Apps and Feature -> Optional Features or run the MS-Settings URL command:
ms-settings:appsfeatures - Find Internet Explorer 11 in the list and click Uninstall.
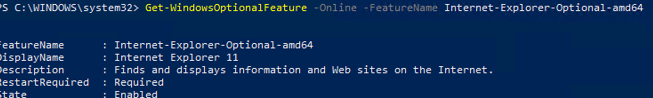
You can also use PowerShell to verify that IE is installed on a computer:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online –FeatureName Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64
FeatureName : Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64 DisplayName : Internet Explorer 11 Description : Finds and displays information and Web sites on the Internet. RestartRequired : Required State : Enabled CustomProperties : \ SoftBlockLink : http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=142507
In this example, the IE11 feature is installed. Uninstall IE11 by running the following command:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64 –Online
Restart your computer.
After you uninstall Internet Explorer, .html files are no longer associated with IE. Note that the Windows Store and other built-in apps will continue to work even if you don’t have a web browser installed on your computer.
Use the following PowerShell script to uninstall IE from a computer:
RemoveIE.ps1
#PowerShell script to remove Internet Explorer
#Check If IE is Installed
$check = Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online | Where-Object {$_.FeatureName -eq "Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64"}
If ($check.State -ne "Disabled")
{
#Remove Internet Explorer
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64 -Online -NoRestart | Out-Null
}
You may use the Invoke-Command cmdlet to uninstall the Internet Explorer on remote computers (requires configured WinRM/PowerShell Remoting):
Invoke-Command -ComputerName PC01,PC02,PC03 -FilePath C:\PS\RemoveIE.ps1
Removing Internet Explorer from Windows Server
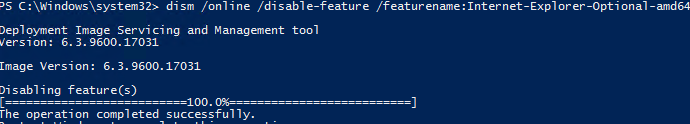
There is no IE in Windows in Windows Server 2022. You can use DISM to uninstall Internet Explorer 11 on previous versions of Windows Server (2019/2016/2012R2):
dism /online /disable-feature /featurename:Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64
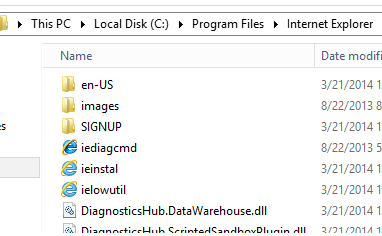
Start the Windows Server and verify that the iexplore.exe executable file has been successfully removed from the C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer folder.
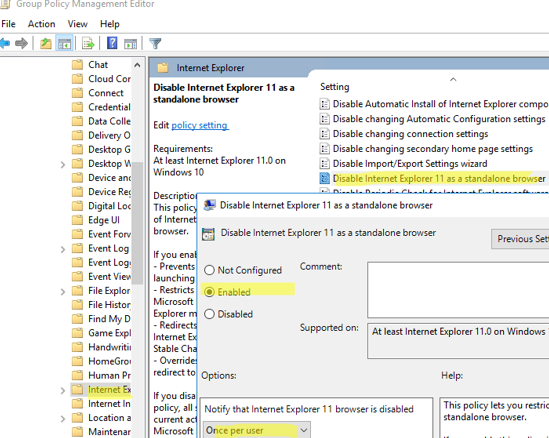
Disable Internet Explorer 11 Using Group Policy
If you don’t want to completely uninstall IE on Windows (for example, if you want to use the IE Mode in Microsoft Edge), you can use Group Policy to prevent Internet Explorer 11 from running on your computer:
- Create a new domain GPO and assign it to an OU with computers/servers using the
GPMC.mscconsole or use the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc); - Go to Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Internet Explorer;
- Find the Disable Internet Explorer 11 as a standalone browser GPO option, enable it and choose how you want to notify users that IE is disabled: Never – users will not be notified about disabling IE 11;
Always – each time IE starts, users will be notified that Internet Explorer 11 is disabled and redirected to the Microsoft Edge browser;
Once per user – users will be notified only once (recommended). - Update group policy settings on your computers.
This policy denies Internet Explorer 11 from running (using Windows file associations or by running the iexplore.exe app directly) and runs Microsoft Edge instead (with fully functional IE mode in Edge). IE icons are removed from the Start Menu and taskbar.
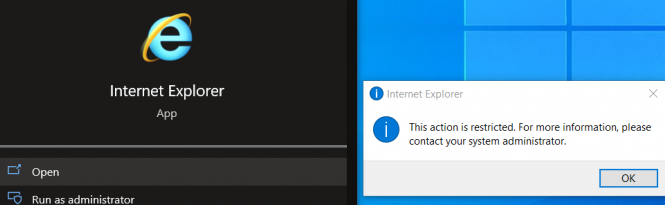
If you try to start IE manually, the following notification will appear:
Internet Explorer This action is restricted. For more information, please contact your system administrator.
2 comments
MS365 v2301 still uses IE11 components. How will this affect it?
How did you find this out and what are your concerns? If IE11 is disabled and not removed, does the problem still occur?