Windows Server RDS farm administrators are often faced with the problem of running out of space on a system drive due to a large amount of user data. This article shows you how to use PowerShell and Group Policies to automatically clean up the Recycle Bin, Downloads, Temp, and Cache folders in the user profiles on Windows.
Automatically Cleanup Temp and Download Folders with Windows Storage Space
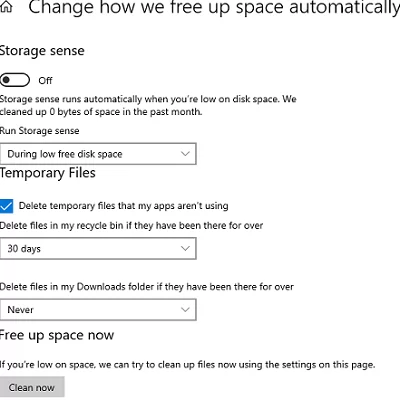
You can use the built-in Storage Sense feature to automatically delete old and temporary files on Windows Server 2019/2022 and Windows 10/11. It has special GPO options that allow you to clean up Temp and Downloads folders.
How to Empty the Recycle Bin for Windows Users?
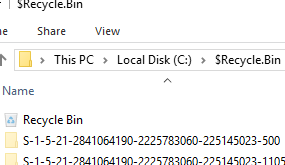
By default, the Recycle Bin folder ($Recycle.Bin) for deleted files is enabled on a Windows host. An individual Recycle Bin folder is created for each user in this directory (with the user’s SID as the name) on the RDS server. Over time, you will find that the total file size in the recycle bins of all users will take up a significant amount of disk space on the RDS host.
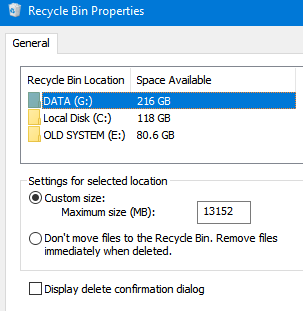
The default size of the Recycle Bin in Windows is about 5% of the disk size. You can change the maximum size of the Recycle Bin on each drive in its properties. Here you can also disable the Recycle Bin completely using the Don’t move files to the Recycle Bin option. However, this will only change the recycle bin settings for the current user.
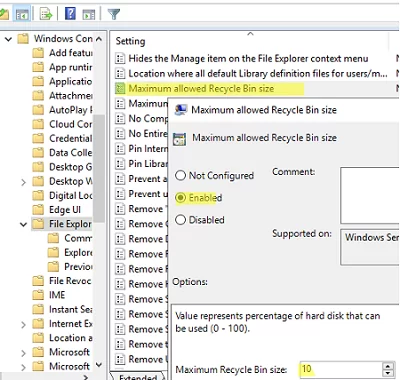
You may set the maximum Recycle Bin size for users with the Maximum allowed recycle bin size GPO option under User Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> File Explorer. The maximum Recycle Bin size is set as a percentage of your disk size. Setting this to 0 disables the recycle bin on all drives.
To clear the Recycle bin in Windows, you can use the Clear-RecycleBin cmdlet (available in PowerShell 5.1 and newer on Windows 10). In order to empty the Recycle Bin without prompting, run the following command:
Clear-RecycleBin -Force
If you run this command as a common user on an RDS host, only the recycle bin of the current user will be cleared. You can add this command to your GPO logoff scripts to clear the recycle bin when a user signs out:
%windir%\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -NoProfile -Command Clear-RecycleBin -Confirm:$false
$Shell = New-Object -ComObject Shell.Application
$RecycleBin = $Shell.Namespace(0xA)
$RecycleBin.Items() | %{Remove-Item $_.Path -Recurse -Confirm:$false}
Clear Cache, Temp, and Downloads Folders in the User Profile with PowerShell
Let’s consider a PowerShell script to clean up Temp, Downloads, and some other temporary folders in a user profile on a Windows Server RDS or a desktop computer running Windows 10/11.
Script comments:
- In this example, we will delete files older than 14 days in the Downloads folder (you can change this option). Other folders with cache and temporary files will be completely empty;
- The script runs in the current user context (the script deletes old files when a user logs out from Windows and runs as a GPO logoff script);If used in an RDS environment, ensure that users click the Logout/Login button to end their sessions. We also recommend configuring RDS session timeouts to end sessions after a period of inactivity automatically.
- All information about deleted files will be saved to a text log file (you can disable this after debugging the script on test users);
- It will also clean up the RDP connection history and cache;
- The Windows Error Reporting (WER) folder in a user profile is cleaned;
- The lines that clear the Google Chrome cache are commented out in the script. If your users use it and the Chrome cache takes up a lot of space, uncomment the lines with the paths;
- You can add an extra operation to check the current size of the user profile folder before and after the cleanup (it allows you to get more accurate information, but takes some time). Or you can simply check the free disk space before and after (it is done quickly).
# You can use this script to clean folders in a user profile (cache, temp, downloads, google chrome cache) on RDS hosts, VDIs, or workstations
# Run the PowerShell script under a commaon user account (no administrator privileges are required). Only temporary files and the current user's cache are deleted.
# You can run this script via GPO (logoff script) or with the Task Scheduler
# Test the script in your environment and then remove the WhatIf option to permanently delete files
$Logfile = "$env:USERPROFILE\cleanup_profile_script.log"
$OldFilesData = (Get-Date).AddDays(-14)
# Complete cleanup of cache folders
[array] $clear_paths = (
'AppData\Local\Temp',
'AppData\Local\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Cache',
'AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\WER',
'AppData\Local\Microsoft\Windows\AppCache',
'AppData\Local\CrashDumps'
#'AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache',
#'AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache2\entries',
#'AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cookies',
#'AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Media Cache',
#'AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cookies-Journal'
)
# Folders where only old files should be removed
[array] $clear_old_paths = (
'Downloads'
)
function WriteLog {
Param ([string]$LogString)
$Stamp = (Get-Date).ToString("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss")
$LogMessage = "$Stamp $LogString"
Add-content $LogFile -value $LogMessage
}
WriteLog "Starting profile cleanup script"
# If you want to clear the Google Chrome cache folder, stop the chrome.exe process
$currentuser = $env:UserDomain + "\"+ $env:UserName
WriteLog "Stopping Chrome.exe Process for $currentuser"
Get-Process -Name chrome -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where-Object {$_.SI -eq (Get-Process -PID $PID).SessionId} | Stop-Process
Start-Sleep -Seconds 5
# Clean up cache folders
ForEach ($path In $clear_paths) {
If ((Test-Path -Path "$env:USERPROFILE\$path") -eq $true) {
WriteLog "Clearing $env:USERPROFILE\$path"
Remove-Item -Path "$env:USERPROFILE\$path" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -WhatIf -Verbose 4>&1 | Add-Content $Logfile
}
}
# Delete old files
ForEach ($path_old In $clear_old_paths) {
If ((Test-Path -Path "$env:USERPROFILE\$path_old") -eq $true) {
WriteLog "Clearing $env:USERPROFILE\$path_old"
Get-ChildItem -Path "$env:USERPROFILE\$path_old" -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Where-Object {($_.LastWriteTime -lt $OldFilesData)} | Remove-Item -Recurse -Force -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -WhatIf -Verbose 4>&1 | Add-Content $Logfile
}
}
WriteLog "End profile cleanup script"
Similarly, you can add other folders you want to clear in a user profile to $clear_paths .
This PowerShell script can run when the user’s RDP server session ends. The easiest way to assign a script is to use the logoff GPO policy.
- Create a new GPO and assign it to the Organization Unit (OU) in which your RDS hosts are located;
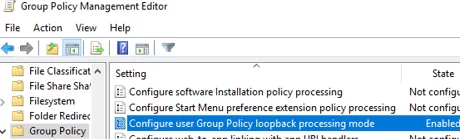
- Enable the option Configure user Group Policy Loopback Processing mode. This is necessary to apply the settings from the Users section to the computer; See Why Group Policy is not being applied to a computer/user for more information.
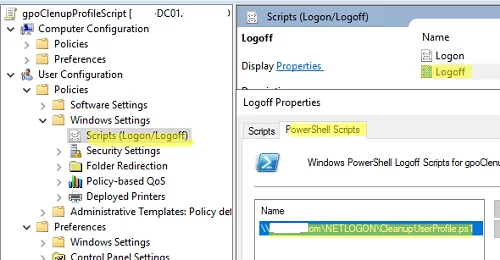
- Copy the PowerShell script file to the Net logon folder on your domain controller (
\\woshub.com\netlogon\CleanupUserProfile.ps1);You can sign the PowerShell script code with a certificate to protect it from unauthorized modification. - Go to the GPO section User Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Scripts -> Logoff. Open the PowerShell Scripts tab and add a UNC path to the PS1 file in Netlogon;
Log off the user from Windows to apply the new GPO settings;
- When ending a user session on an RDS server, the specified folders will be cleared automatically. You can view a list of deleted files and folders in a text log file in a user profile.
The user folder cleanup methods discussed here can be applied to both locally stored user profiles and User Profile Disks or FSlogix profile containers on Windows Server RDSH.
 Log off the user from Windows
Log off the user from Windows 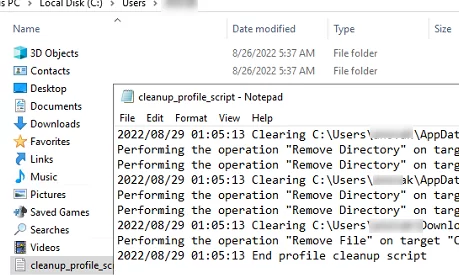
6 comments
Thank you for the great script. Works like a charm 😉
This is a great script; we plan to use it throughout our domain via GP. I do have one question, is there a way to append to the ‘cleanup_profile_script.log’?
After running the script manually a couple times, I noticed that it does append so scratch the question above.
Would it be possible to add in the Clear-RecycleBin cmdlet to the script or do they need to be run separately?
Of course, you can add the
Clear-RecycleBincommand to the CleanupUserProfile.ps1 script.It will only empty the recycle bin of the current user.
If you want to append information to the log file, you can simply send it via pipe:
"your info" | Add-Content $LogfileI notice it takes 2-3 mins of signing out.