Windows administrative shared folders are used for remote access and computer management. By default, the following administrative shares are created by Windows:
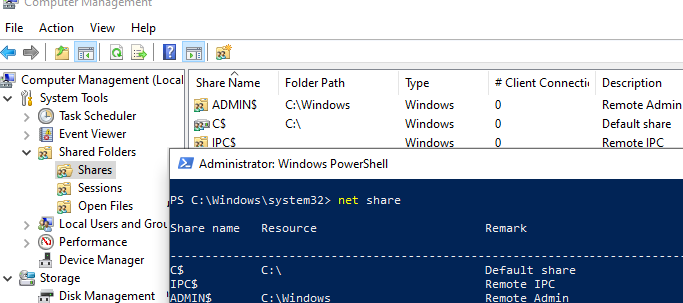
Admin$– Remote Admin (refers to%SystemRoot%directory). Used for remote computer management;IPC$– Remote IPC, used to communicate with programs via named pipes;C$– Default Share. Shared system drive. If there are any other drives on the computer that have letters assigned to them, these will also be automatically published as admin shares (D$,E$, etc.);Print$– published when you share your printer (opens access to the printer drivers directory C:\Windows\system32\spool\drivers);FAX$– for shared fax server access.
What are Hidden Administrative Shares on Windows?
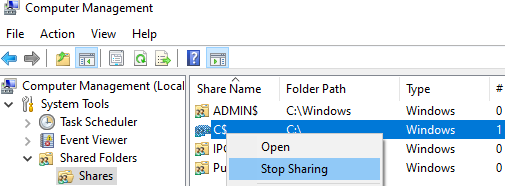
You can view a list of administrative folders on your computer in the Computer Management snap-in compmgmt.msc (System Tools -> Shared Folders -> Shares), or by running the net share command.
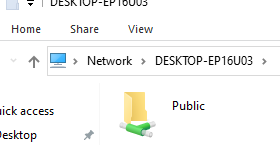
The names of the administrative shares end with a $ sign. The LanmanServer service hides shared folders with the $ symbol in the network environment. Administrative shares are not displayed when you open the list of available shared network folders on a remote computer in File Explorer (\\computername).
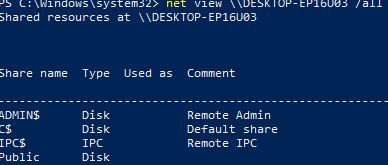
This command lists available admin shares on a remote computer:
net view \\computername /all
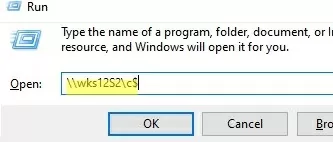
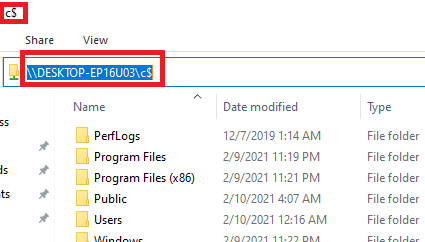
You must specify the full name of an administrative share to open its contents from File Explorer. Press Win+R and run the command \\computername\c$
This command opens the contents of the local C drive, giving you full access to the file system of the remote computer’s system drive.
Administrative shares can only be accessed by members of the computer’s local Administrators Administrators group (and the Backup Operators group), provided that you have SMB protocol enabled, turned on file and printer sharing, and access to TCP port 445 is not blocked by Windows Defender Firewall rules.
How to Remove Administrative Shares on Windows
While Windows administrative shares are convenient for managing computers remotely, they also present additional security risks. You can completely prevent Windows from creating these hidden admin shares. This will not disrupt the operation of the Windows computer used as the client but will limit its remote administration capabilities.
To remove a shared admin folder, select the Stop sharing option in the Computer Management snap-in (or use the net share Admin$ /delete command). This will remove the admin share, but Windows will automatically re-create the Admin$ share when you restart your computer.
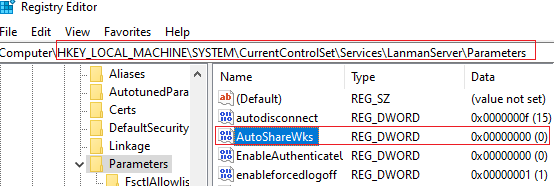
To prevent Windows from creating administrative shares, you must open the registry editor (regedit.exe), go to the registry key HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters, and add a Dword parameter named AutoShareWks (for desktop versions of Windows) or AutoShareServer (for Windows Server) with a value of 0.
You can create this registry entry manually by using the reg add command:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\lanmanserver\parameters /f /v AutoShareWks /t REG_DWORD /d 0
or with PowerShell:
New-ItemProperty -Name AutoShareWks -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters -Type DWORD -Value 0
Now after rebooting the administrative shares will not be created. In this case, remote computer management tools, including psexec, will stop working.
If you are on a domain network, you can use Group Policy to prevent the local hard drives of the computers from being published as admin shares:
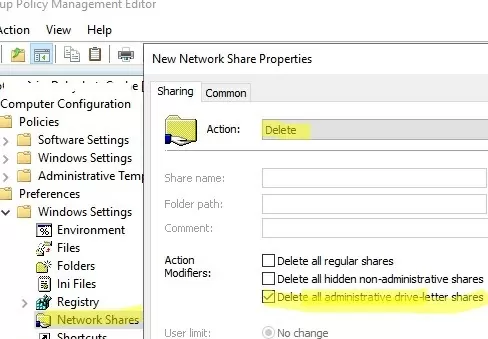
- Create a new GPO using the Group Policy Management snap-in. Go to Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Network Shares;
- Select Action: Delete and check the option Delete all administrative drive-letter shares.
Restore or Enable Admin Shares on Windows
If you want to enable admin shares on Windows, you need to change the parameter value to 1 or delete it:
Set-ItemProperty -Name AutoShareWks -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters -Value 1
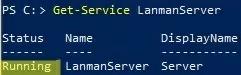
The LanmanServer service creates administrative shares on Windows. Remote users cannot access shared resources on this computer if this service is stopped.
Get-Service LanmanServer
Windows can automatically recreate the hidden admin shares, simply restart the LanmanServer service with the command:
Get-service LanmanServer | restart-service -verbose
Run the Get-SmbShare PowerShell command and check that admin shares are available.
Enable Remote Access to $Admin Shares on Windows
On computers joined to the AD domain, remote access to administrative shares is allowed to users who are members of the local Administrators group.
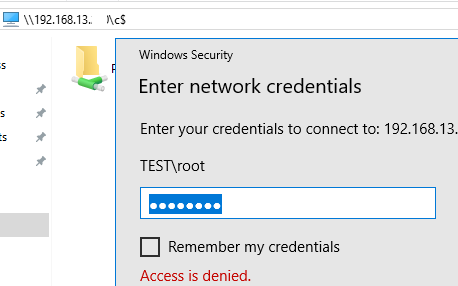
However, by default, Windows blocks remote access to administrative shares on workgroup computers. If you try to open a list of files on such a computer in the Explorer using the command \\win10_pc\C$, you will be prompted for user credentials. After entering the credentials of a local user who is in the local Administrators group, an access denied error is displayed. Only the built-in Windows Administrator account can remotely access administrative shares.
In this case, remote access to administrative shares is blocked by the Remote UAC (Remote User Account Control). Remote UAC blocks remote administrative access to folders by filtering local and Microsoft account access tokens. If you access the admin shares using a domain account, this restriction doesn’t apply.
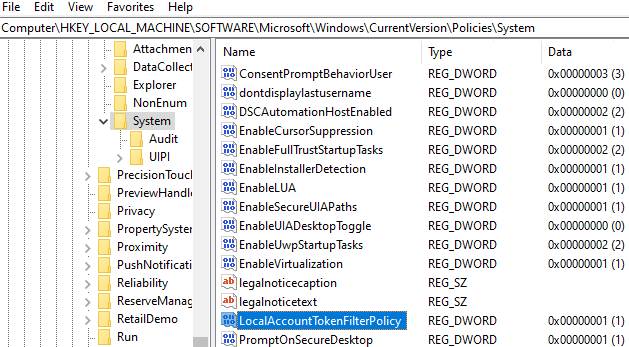
You can disable Remote UAC by creating the LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy registry parameter.
- Open the Registry Editor (regedit.exe);
- Go to the following reg key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System ;
- Create a new DWORD (32-bit) parameter with the name LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy;
- Set the LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy parameter value to 1;
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" /v "LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
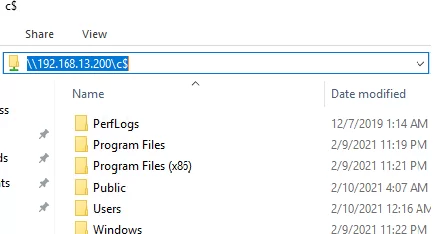
After the reboot, try to remotely open the C$ admin share on a remote computer. Log in with an account that is a member of the local Administrators group.
A File Explorer window should now display the contents of the remote drive.


10 comments
Thank you very much for this information. I have an odd circumstance, where I need to find out all the people MAC of who is remote into my computer. I was finally able to get my network to run on Private and it stay there I’m finding a second network on my computer. I have other situations that backs this up in my router settings.
check event viewer
Thank God someone had the answer.
how to change permission without deleting a share from cmd?
what the impact if we have disable c$ d$ etc on the server?
Oh do I LOVE you…let me count the ways…! Thanks xoxo!
What’s the catch? What does the built-in administrator have in the settings that a user manually added to the Administrators group does not have, so that UAC does not block them?
This is the default behavior of the built-in Windows Administrator account.
This account is not subject to UAC (User Account Control), and all programs are executed without a UAC prompt (this is an important difference from user accounts with administrator privileges).https://woshub.com/enable-built-in-administrator-account-in-windows-10/
As a local user with admin privilege’s on a workgroup computer the cmd “dir \\Win10Computer\c$” to a networked computer works fine. I get no credential requests and I already had UAC off. This wasn’t always the case. There was a time when it just wouldn’t work through the cmd window but you could map the admin share to a local drive letter using the GUI in file manager.
change this value to to effect
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters]
“AutoShareWks”=dword:00000001
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System]
“LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy”=dword:00000001