Remote users can connect to their Windows 10 and 11 computers through the Remote Desktop Services (RDP). All you need to do is enable Remote Desktop, grant the user RDP access permissions, and connect to the computer using any remote desktop client. However, the number of concurrent RDP sessions is limited in desktop versions of Windows. Only one active Remote Desktop user session is allowed.
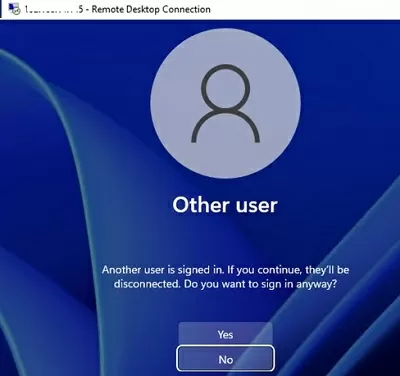
A warning will appear asking you to disconnect the first user’s session if you try to establish a second RDP connection.
Another user is signed in. If you continue, they’ll be disconnected. Do you want to sign in anyway?
Number of Concurrent RDP Connections on Windows
There are several restrictions on the use of Remote Desktop Services in all desktop versions of Windows 10 and 11:
- Only Windows Professional and Enterprise editions can accept remote desktop connections. RDP access is not allowed to Home/Single Language Windows editions;
- Only one simultaneous RDP connection is available. Attempting to start a second RDP session will prompt the user to end the active session;
- If the user is working at the computer console (locally), their local session is disconnected (locked) when they make a remote RDP connection. The remote RDP session will also be terminated if the user logs into Windows from the computer’s console.
The number of concurrent RDP connections on Windows is a license limitation. Microsoft prohibits the creation of a workstation-based Terminal RDP server for multiple users to work simultaneously.
If your tasks require the deployment of a terminal server, Microsoft suggests purchasing a Windows Server (allows two simultaneous RDP connections by default). If you need more concurrent user sessions, you will need to purchase RDS CALs, install, and configure the Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH) role, or deploy an RDS farm.
Technically, any version of Windows with sufficient RAM and CPU resources can support dozens of remote user sessions simultaneously. On average, an RDP user session requires 150-200MB of memory (excluding running apps). This means that the maximum number of concurrent RDP sessions is limited only by the available resources of the computer.
In this article, we are going to show you three ways to remove the limit on the number of concurrent RDP connections in Windows 10 and 11:
- RDP Wrapper
- Modifying the termsrv.dll file
- Upgrading Windows 10/11 edition to Enterprise for virtual desktops (multi-session)
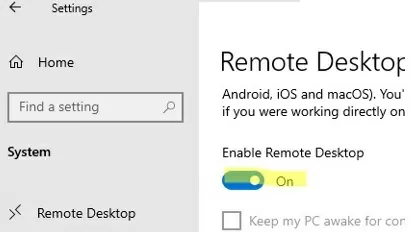
Before you proceed, make sure that the Remote Desktop protocol is enabled in Windows.
- Go to Settings -> System —> Remote Desktop -> Enable Remote Desktop;
- Or use the classic Control Panel: run the command
SystemPropertiesRemoteand check the option Allow remote connection to this computer.
RDP Wrapper: Enable Multiple RDP Sessions on Windows
The RDP Wrapper Library OpenSource project allows you to enable multiple RDP sessions on Windows 10/11 without replacing the termsrv.dll file. This tool acts as a layer between SCM (Service Control Manager) and the Remote Desktop Services. The RDP wrapper doesn’t make any changes to the termsrv.dll file, it simply loads the termsrv with the modified settings.
Thus, the RDPWrap will work even in the case of termsrv.dll file update. It allows you not to be afraid of Windows updates.
You can download the RDP Wrapper from the GitHub repository https://github.com/binarymaster/rdpwrap/releases (the latest available version of the RDP Wrapper Library is v1.6.2). The project hasn’t been updated since 2017, but it can be used in all new builds of Windows 10 and 11. To use the wrapper on modern versions of Windows, simply update the rdpwrap.ini configuration file.
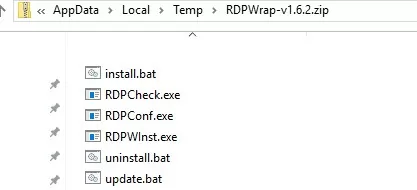
The RDPWrap-v1.6.2.zip archive contains some files:
- RDPWinst.exe — used to install/uninstall an RDP wrapper library;
- RDPConf.exe — RDP Wrapper configuration tool;
- RDPCheck.exe —an RDP check tool (Local RDP Checker);
- install.bat, uninstall.bat, update.bat — batch files to install, uninstall, and update RDP Wrapper.
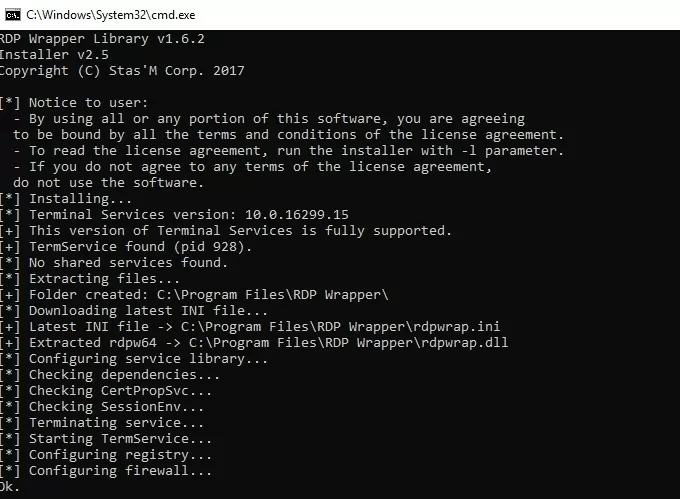
To install RDPWrap, run the install.bat file as an administrator. The program is installed in the C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper directory.
Run RDPConfig.exe when the installation is complete.
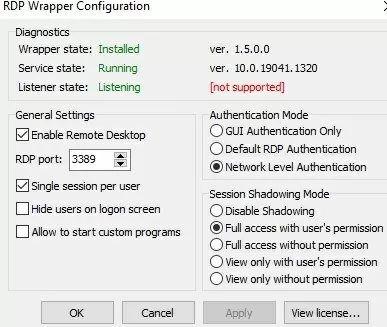
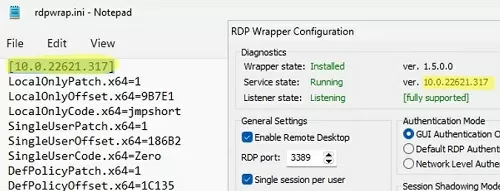
Most likely, immediately after installation, the tool will show that the RDP wrapper is running (Installed, Running, Listening), but not working. Note the red [not supported] warning. It reports that this version of Windows 10 22H2 (ver. 10.0.19041.1949) is not supported by the RDPWrapper.
This is because the rdpwrap.ini configuration file does not contain settings for your Windows version (build). +
✅ Download the latest version of rdpwrap.ini here https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sebaxakerhtc/rdpwrap.ini/master/rdpwrap.ini
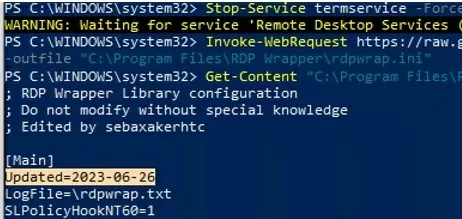
Manually copy the contents of this page into the C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper\rdpwrap.ini file. Or download the INI file using the PowerShell cmdlet Invoke-WebRequest (you must first stop the Remote Desktop service):
Stop-Service termservice -Force
Invoke-WebRequest https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sebaxakerhtc/rdpwrap.ini/master/rdpwrap.ini -outfile "C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper\rdpwrap.ini"
This screenshot shows that the latest version of the rdpwrap.ini file (Updated=2023-06-26) is used on the computer.
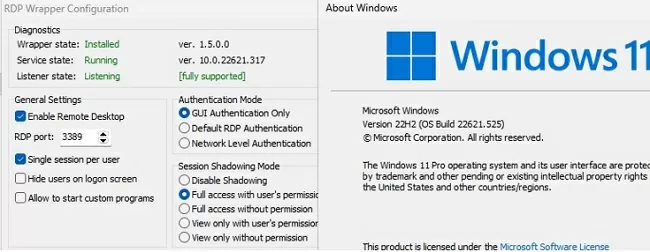
Restart your computer and run the RDPConfig.exe tool. Check that all items in the Diagnostics section are green and that the [Fully supported] message is displayed. The RDP wrapper started successfully on Windows 11 22H2 in my case.
Now try to establish several concurrent RDP sessions with this computer under different user accounts (use your favorite RDP client: mstsc.exe, RDCMan, mRemoteNG, etc).
You can check that two (or more) RDP sessions are active on the computer at the same time by using the command:
qwinsta
rdp-tcp#0 user1 1 Active rdp-tcp#1 user2 2 Active
The RDPWrap tool is supported in all Windows editions, so you can build your own terminal (RDS) server on any Windows device. So you can turn any version of Windows client into a full-featured terminal server.
The following options are available in the RDP Wrapper:
- Enable Remote Desktop
- RDP Port —change the default remote desktop port number (TCP 3389)
- Hide users on logon screen – allow hiding the list of users from the Windows Logon Screen;
- Single session per user — allow several concurrent RDP sessions under the same user account. This option sets the fSingleSessionPerUser registry value to 0 (
HKLM\SYSTEM\ CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\fSingleSessionPerUser). This parameter is also configured through the GPO option Restrict Remote Desktop Services to a single Remote Desktop Services session under Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections; - The Session Shadowing Mode allows you to configure the remote control (shadow) connection mode to the RDP users’ desktops
RDP Wrapper Not Working on Windows
In some cases, the RDP Wrapper may not work as you expect it to and you may not be able to use more than one RDP connection on Windows.
The termsrv.dll file version can be updated during Windows Updates installation. If the description for your version of Windows is missing from the rdpwrap.ini file, then the RDP Wrapper will not be able to apply the necessary settings. In this case, the status [not supported]. will be displayed in the RDP Wrapper Configuration window.
✅ In this case, you must update the rdpwrap.ini file as described above.
If RDP Wrapper does not work after updating the rdpwrap.ini file, try to open the rdpwrap.ini file and look for the section for your version of Windows.
How to understand if your Windows version is supported in rdpwrapper config?
The screenshot below shows that for my version of Windows 11 (10.0.22621.317) there are two sections of settings:
[10.0.22621.317] ... [10.0.22621.317-SLInit] ...
If there is no section in the rdpwrap configuration file for your version of Windows, try searching the web for the rdpwrap.ini file. Add the configuration settings you found to the end of the file.
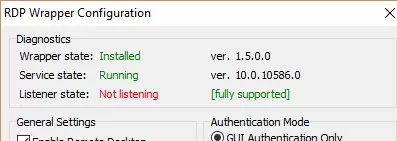
If the RDP Wrapper does not work after you install security updates or upgrade the Windows build, check that there is no Listener state: Not listening warning in the RDPWrap Diagnostics section.
Try updating the rdpwrap.ini file, and then reinstalling the rdpwrapper service:
rdpwinst.exe -u
rdpwinst.exe -i
It can happen that when you try to make a second RDP connection as a different user, you will get an error message:
The number of connections to this computer is limited and all connections are in use right now. Try connecting later or contact your system administrator.
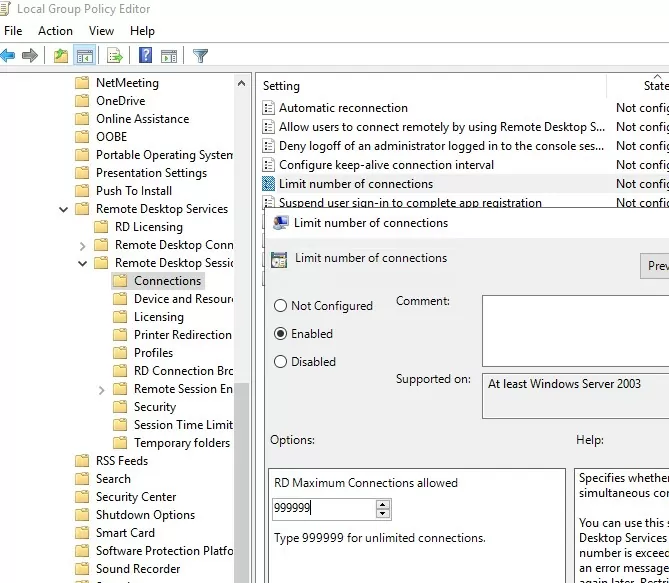
In this case, you can use the local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) to enable the “Limit number of connections” option under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections section. Increase the ‘RD maximum connection allowed’ value to 999999.
Restart your computer to update the local Group Policy and apply the settings.
Patch the Termsrv.dll to Enable Multiple Remote Desktop Sessions
To remove the limit on the number of concurrent RDP user connections in Windows without using rdpwrapper, you can replace the original termsrv.dll file. This is the main library file used by the Remote Desktop Service. The file is located in the C:\Windows\System32 directory.
It is advisable to make a backup copy of the termsrv.dll file before editing or replacing it. This will help you to revert to the original version of the file if necessary. Open an elevated command prompt and run the command:
copy c:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll termsrv.dll_backup
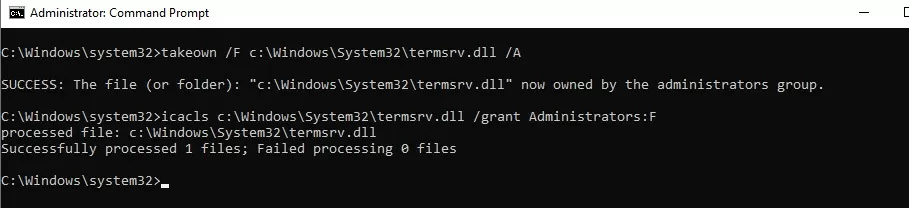
Then you need to take ownership of the termsrv.dll file. To change a file’s owner from TrustedInstaller to the local Administrators group, use the command:
takeown /F c:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll /A
SUCCESS: The file (or folder): c:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll now owned by the administrators group
Now use the icacls.exe tool to grant Full Control permissions to the termsrv.dll file for the local Administrators group:
icacls c:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll /grant Administrators:F
processed file: c:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll Successfully processed 1 files; Failed processing 0 files.
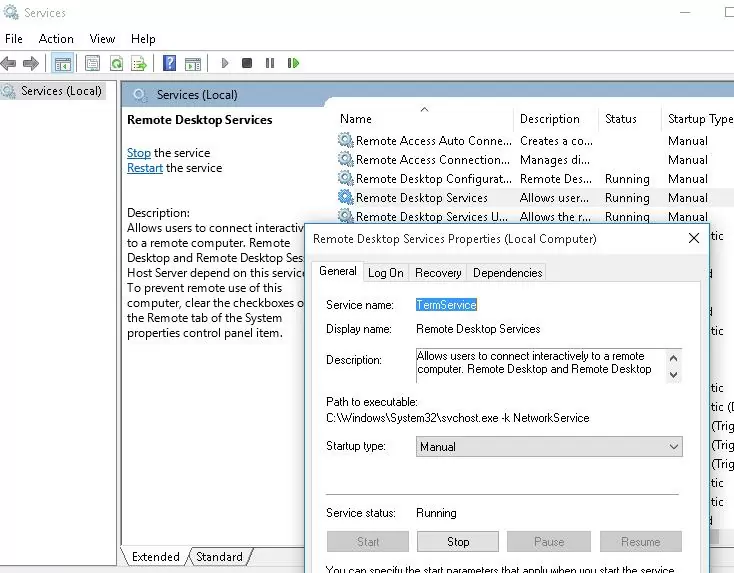
Now you need to stop the Remote Desktop service (TermService) using the services.msc console or with the command:
net stop TermService
It also stops the Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector service.
Run the winver command or the following PowerShell command to find your Windows build number:
Get-ComputerInfo | select WindowsProductName, WindowsVersion
Then open the termsrv.dll file using any HEX editor (for example, Tiny Hexer). Depending on the build of Windows you are using, you will need to find and replace the string according to the table below:
| Windows build | Find the string | Replace with |
| Windows 11 22H2 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 75 7A 01 00 |
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
|
| Windows 10 22H2 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 85 45 01 00 | |
| Windows 11 21H2 (RTM) | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 4F 68 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 21H2 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 DB 61 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 21H1 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 2B 5F 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 20H2 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 21 68 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 2004 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 D9 51 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 1909 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 5D 61 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 1903 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 5D 61 01 00 | |
| Windows 10 x64 1809 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 3B 2B 01 00
| |
| Windows 10 x64 1803 | 8B 99 3C 06 00 00 8B B9 38 06 00 00
| |
| Windows 10 x64 1709 | 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 B1 7D 02 00
|
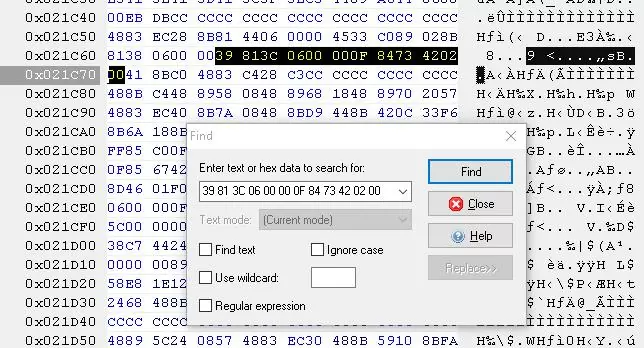
For example, my build of Windows 10 x64 is 22H2 19045.2006 (termsrv.dll file version is 10.0.19041.1949). Open the termsrv.dll file in Tiny Hexer, then find the text:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 75 7A 01 00
and replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Save the file and start the TermService.
If something goes wrong and you experience some problems with the Remote Desktop service, stop the service and replace the modified termsrv.dll file with the original version:
copy termsrv.dll_backup c:\Windows\System32\termsrv.dll
https://github.com/maxbakhub/winposh/blob/main/termsrv_rdp_patch.ps1
This script was written for the Windows PowerShell version and does not work in modern PowerShell Core.
👍 The advantage of the method of enabling multiple RDP sessions in Windows 10 or 11 by replacing the termsrv.dll file is that antivirus software will not react to it (unlike RDPWrap, which is detected by many antivirus products as a malware/hack tool/trojan).
👎The disadvantage of this is that you will have to manually edit the file each time you update the Windows build (or if the monthly cumulative patches update the version of termsrv.dll).
Multiple Concurrent RDP Connections in Windows 10 Enterprise Multi-session
Microsoft has recently released a special edition of the operating system called Windows Enterprise Multi-Session (Previously known as Windows 10 Enterprise for Remote Sessions and Windows 10 Enterprise for Virtual Desktops)
The key feature of this edition is that it supports multiple concurrent RDP user sessions out of the box. Although the Windows multi-session edition is only allowed to be run in Azure VMs, you can install this edition on an on-premises network and use that computer as a terminal server (even though this would be against Microsoft’s licensing policies).
Next up, we’re going to show you how to upgrade a Windows 10 Pro edition to Windows 10 Enterprise for Virtual Desktop and use it for multiple RDP users simultaneously.
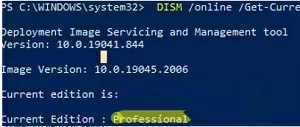
Open a command prompt and check your current edition of Windows (Professional in this example):
DISM /online /Get-CurrentEdition
Upgrade your edition of Windows 10 from Pro to Enterprise with the command:
changepk.exe /ProductKey NPPR9-FWDCX-D2C8J-H872K-2YT43
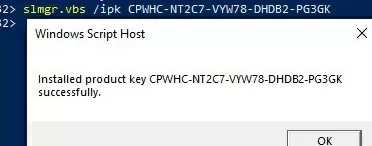
Now install the GVLK key for Windows 10 Enterprise for Remote Sessions:
slmgr.vbs /ipk CPWHC-NT2C7-VYW78-DHDB2-PG3GK
Check that your edition of Windows 10 has now changed to ServerRdsh (Windows 10 Enterprise for Virtual Desktops).
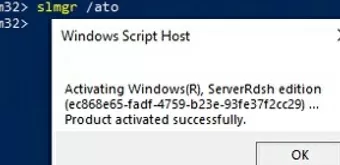
Activate your copy of Windows 10 Enterprise Multi-Session edition on your KMS server:
slmgr /skms kms-srv.woshub.local:1688
slmgr /ato
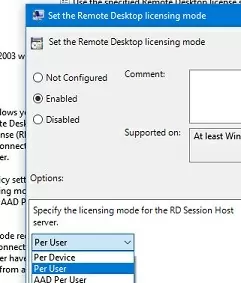
Open the Local GPO Editor (gpedit.msc) and enable Per-User licensing mode in the Set the Remote Desktop licensing mode (Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Licensing).
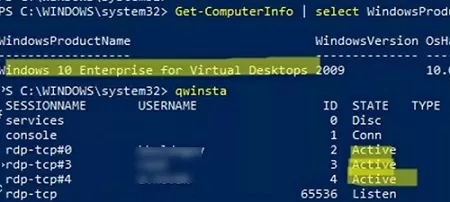
You must restart Windows after activation. Now try connecting to the computer using RDP with different user accounts. As you can see, Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session supports simultaneous RDP connections right out of the box.
Get-ComputerInfo | select WindowsProductName, WindowsVersion, OsHardwareAbstractionLayer
Windows 10 Enterprise for Virtual Desktops 2009 10.0.19041.2728
qwinsta
In this article, we have looked at a number of ways to get rid of the limit on the number of concurrent RDP user connections and run a free terminal server on desktop versions of Windows 10/11. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Which one you choose is up to you.



302 comments
This isnt working
The listening state is not working
Run the update.bat with administrator privileges
“Important. Before installing RDP Wrapper, it is important to make that you are using the original (unpatched) version of the termsrv.dll file. Otherwise, RDP Wrapper may become unstable or not start at all.”
How could you possibly confirm this? So this can’t be done on existing machines that have been in service for more than a few months or year? We patch every month with Patch Tuesday.
ummm, by using what’s called a “test” or “development” environment before going live? Grab a VM or 2, and run both instances and see.
Hi Ben
I tried after update.bat file and still its not supporting for Listening.
On GitHub there is no archive with .exe’s anymore, only source code. Anyone have the already compiled version?
I cant find it either any help would be appreciate email to [email protected]
Apparently, the link in the article leads to an old or somewhat different fork of the project which contains only source codes.
The .exe’s are in the Release section over here: https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/releases
Hi I am also getting same problem like Listener state [not supported ] and I have ran the update.bat file then I am getting error as Failed to Download latest INI from GitHub.
A mi me ha funcionado correctamente tras ejecutar el archivo .bat. Comprabado en un Windows 10 Pro 64bits
Perdón me refería al ejecutar el ACTUALIZADOR.BAT
Thanks. The link to rdpwrap is stale and it’s confusing because there are downloads available but none of them contain binaries. The link should be https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/releases.
I’m running Windows 10 Home and installed RDP Wrapper from the following binary listed above: “https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/releases”
A fix for the listener state when running RDPConf.exe or if you get a error in Update.bat about a serive not starting is to enable “Routing and Remote Access” in services.
Change it from disabled to automatic, then right click the service and start it. This worked for me I hope it helps.
I found a site with the zip file containing the wininst.exe file.
https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/releases
I installed RDP Wrap and ran the Config. Everything was Green.
However, when I try to run a second user remotely, it removes the first user.
Everything looks good. On the host pc I am allowing all connections.
Any help would be appreciated.
Hello,
If a User is connected through RDP to Windows 10 via USER1, How to prevent other users from other PCs to connect remotely to the same PC with Widows 10 using USER1.
In Other Words if there is a live RDP connection, I want to prevent other users to connect remotely at the same time forcing the live connection to break?
Hi
You can’t prevent such behavior.
Perhaps it will be easier to create a separate account for each remote user or allow multiple Remote Desktop sessions per user (registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer-> fSingleSessionPerUser = 0 )
You would prevent them from doing so with a password.
If you only want a connection from a specific computer, set up firewall rules for port 3389 to only allow a certain mac address in
By default each user is restricted to a single Remote Desktop session. You can allow multiple Remote Desktop sessions per user by changing a registry key:
Create (or edit) the follwoing registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer
Create a new DWORD value with name fSingleSessionPerUser
The possible values for this setting :
0×0 Allow multiple sessions per user
0×1 Force each user to a single session
fSingleSessionPerUser only works for Windows Server versions.
termsrv.dll version 10.0.10586.0 is not supported in version 1.6 (output from RDPWInst.exe):
[*] Installing…
[*] Terminal Services version: 10.0.10586.0
[-] This version of Terminal Services is not supported.
Send your termsrv.dll to project developer for support.
…
<Now, our Windows 10 allows two users to start RDP sessions simultaneously…>
Not interested in only two, how about 10 or so?
Did you ever find out if this is possible? I have a client that wants to do this for about 20 users.
Windows 10 Anniversary Update change code anyone now fix ?
new version
termsrv.dll
10.0.14393.0
16.07.2016
Since build 14393 is rumored to be the RTM Anniversary Update, here is the hex required to allow multiple RDP sessions on the 64 bit version of this build:
Replace
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 D3 DE 02 00
with
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
I’ve patched the Anniversary Update (version 1607 / build 14393):
https://ufile.io/cb5ee
From today i recive not spported on Win 10,mybe after some win update….Any solution??
Hi. I am also getting same problem on Windows 10 Pro 32 Bits.
Stop working. Any Help?
After installing latest updates on Windows, RDP Wrapper Library has stopped normal functioning
To fix this issue, try to run update.bat from release package
Hi. Is is possible, that RDP Wrapper still does not work?
Hi,
You have tried to update using a update.bat file?
Hi, yes I have. After deinstalling and installing again the first log-in works sometimes, but then RDP only says “connecting…” for a few seconds and just stops without doing anything. The problem started after Windows 10 updated to 1607 (Build 14393.xxx) a couple of days ago.
Try to install RDP Wrapper Library v1.6.1 (_https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/releases). According to the developers, support of Windovs 10.0.14931.1000 and 10.0.14936.1000 was added to the ini file (_https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/168)
Hi, thanks for the replay. Sadly I am using 1.6.1, it is not working. Only optionI found so far is uninstalling, setting windows settings back to allowing RDP (after every uninstall it is set to no) and reinstalling. Then I have about 30 seconds to one minute to log every external user into windows.
I will try uninstalling the windows update, maybe that will help until windows forces the update back in.
I am back to 1511, that works without a problem.
Obrigado, me ajudou muito…
have you logined 50 users at the same time?I can only login 28 users.Is there any limit by Windows 10?
Thanks . It is working . I use RDP Wrapper library
Thanks for this article! Works perfectly. This, in combination with Hamachi (paid version so the service stays alive after logout), is a great!
what is the maximum number of concurrent logged in users that it will support?
Is it possible to have 1 local user (physically at the PC) and 1 remote simultaneously)? I’m on Windows 10 Pro.
Is it possible to use a computer with rdpwrapper local and with one or two remote connections?
How to configure?
If I am logged-in locally on my computer and work and a remote connection tries to get in then my local account must be closed otherwise the remote connecrion can be placed.
Is that normal??
Can I not use the computer local and remote (with another user account? – of course) at the same time?
83/5000
Hi, thanks for the tutoring. Is there any way to have sound on the client pc? Thank you!
Open connection options in mstsc.exe and go to the tab Local Resources. Find Remote audio section and press Settings button. Select the option Remote audio playback -> Play on this computer.
It’s working perfectly 🙂
today my windows 10 machine rebooted and it stopped working. maby there is a new update or something? Anyone having the same issue?
I have the same problem. Last update W10 and this stop working.
windows 10 build 16299 – ran the program , works in the config and testmode ! but i get remote desktop error in that it says remote desktop isnt working ??? for one of 3 reasons , 1, 2, 3, typical windows error message, is this still working or have i totally stuffed the remote desktop now ? please help asap
It stop working after last update 1803 🙁
I will answer myself, if you overwrite termsrv.dll from older version 10.0.16299.15 for example you will be able to install correctly and works correctly with last version 1803
– Windows 10 April 2018 Update 17134 RTM x64 build
– Find: 8B 99 3C 06 00 00 8B B9 38 06 00 00
– Replace With: B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
I cant do the hex editing, because the hex editor is not willing to open the dll. I did the ownership change on the dll, I gave full access to it, but still no luck. I used RDP Wrapper earlier, but it doesnt support build 17134. Can somebody upload please the updated ini for RDP wrapper OR the patched dll (for build 17134)?
Replace the file in the :\Windows\system32\termsrv.dll directory with the old version of C:\Windows.old\system32\termsrv.dll, and restart the computer. After that, rdp wrapper starts working again! Tested on Windows 10 1803 Spring Update!
Avira says this is malware. Chrome says it’s dangerous. Comments about that?
Microsoft has the power to have any software that mods Windows listed as “malware” to scare people away from using it.
My current version of termsrv.dll is 17741 and my prior version is 17738. I notice that the size of termsrv has changed dramatically from 339k to 992k. Both of these releases also control an additional service called Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector, I don’t know if the older versions controlled that service or not. Bottom line, I can’t modify termsrv because the hex string to search for is no longer in the module, rdpwrapper does not work with the updated termsrv. I downloaded the patched version of termsrv.dll but haven’t tried using it yet. that will be my next adventure. Somehow I think it may not work only because it appears the code has been redesigned to function differently than was originally designed. However, I’m going to give it a try.
Tried the downloaded version of termsrv, it just crashed when starting. put 17741 back in place. Anyone have any ideas here?
Just realized, my email address is wrong, s/b gpkerr not gkerr
– Windows 10 April 2018 Update 17134.254 RTM x64 build
I try these :
– Find: 8B 99 3C 06 00 00 8B B9 38 06 00 00
– Replace With: B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Can’t have more than 1 user in RDP at a time … any solution to this ?
THanks for your help
this worked for me
Thank you VERY much for the information. I managed to get it working with the RDP Wrapper Library. I tried to edit the DLL but it was impossible to find the reference to 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 73 42 02 00
while downloading RDPWrap-v1.6.2.zip, my anti-virus programs is saying the file contains a virus or malware.
Has anyone else seen this? I’m using firefox also.
Windows 10 October 2018 Update 17763.1 x64 build, tested today and working OK:
– Search: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 7F 2C 01 00
– Replace: B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Enjoy it!
Thank you very much
The download from GitHub may trigger your virusscanner: see https://www.virustotal.com/#/file/4f9ea0c2ef2e6df72c42e47abcf591dde2f59716a2bc48c353697261c1462e53/detection
Ok, i figured that this doesnt work very well. So i clicked on uninstall.bat. Now i cannot contact my server anymore. Not via Putty, RDP… help?
Very funny, It looks like no one is using antivirus here…
The file RDPConf.exe contains a virus that gives access to external people to your PC (RemAdmin)
The point of the software is to modify Windows to allow multiple remote connections. It’s expected behaviour to have antivirus software flag it as a risk that allows remote connections.
I also installed
17763.107.101029-1455.rs5_release_svc_refresh_CLIENTENTERPRISEEVAL_OEMRET_x64FRE_en-us
4518890KB
windows enterprise 1809 evaluation 90 days & applied patch. It was working perfectly.
It was working as single user with many multisession at a time, (multi login single user RDP as it is normal with windows server 2016/2008)
It was also working as different terminal services users with multisession to a single machine.
I see there updates on machine were installed and then single user with multiple session is no longer working. I don’t cause the issue. Update KB4487044 / KB4470755 / KB4483452 installed on 13-Feb-2019.
Later i uninstalled those two KB but still the multi login/ simultaneously single user with terminal services for different sessions didn’t worked. (the kb4470788 was not removable)
I used two things to make it happened
1.) HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server fSingleSessionPerUser key Change the key value from 1 to 0
2.) RDPWrap-v1.6.2.zip 1.52MB
Can some one assist to make again windows 10 pro or entp 1809 multi-logging same user with differnt concurrent sessions to single host locally or remotely as I done previously so that I get updates as well.
https://www.virustotal.com/es-ar/file/35a9481ddbed5177431a9ea4bd09468fe987797d7b1231d64942d17eb54ec269/analysis/1550152290/
On Win 10 Pro i had to set via gpeditor
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections.
From here, first set the Restrict Remote Desktop Services user to a single Remote Desktop Services session parameter to Disabled.
Next, double-click on Limit number of connections and then set the RD Maximum Connections allowed to 999999.
I have Win Pro and I have only 1 option there “Set rules for remote….”
on:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections.
getting the following error: another user is signed in if you continue, they’ll be disconnected do you want to sign in anyway
I have two Windows 10 Pro x64 systems that no longer allow multiple users at the same time.
Thank you so much, i found this and solve all of my problems 👌
Ver 1.5.0.0 service ver. 10.0.17763.292 is showing not supported no matter what I try. This will not allow multiple people to use the machine. I continue to get “another user is signed in if you continue, they’ll be disconnected do you want to sign in anyway”.
What am I missing here? The updated .ini is there. Everything appears to be correct but it will not work.
Use an updated INI file that supports 1809 and it will work as expected… read the thread here for details:
https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/699
Suddenly a restrictionon 2 rdp sessions appeared in Windows 7.
When reinstalling rdpwrapper:
[!] This version of Terminal Services is supported partially.
It means you may have some limitations such as only 2 concurrent sessions.
Try running “update.bat” or “RDPWInst -w” to download latest INI file.
If it doesn’t help, send your termsrv.dll to project developer for support.
After removing KB4489878 everything is OK.
The rdpwrapper stopped working in my Windows 10.0.17134.706 (windows 10 1803 x 64) after installing new updates on April 11, 2019.
I upgraded my Windows 10 to 1809 (the file was updated to 10.0.17763.437), then I edited the rdpwrap.ini file and add the following section:
[10.0.17763.437-SLInit]
bInitialized.x86 =CD798
bServerSku.x86 =CD79C
lMaxUserSessions.x86 =CD7A0
bAppServerAllowed.x86 =CD7A8
bRemoteConnAllowed.x86=CD7AC
bMultimonAllowed.x86 =CD7B0
ulMaxDebugSessions.x86=CD7B4
bFUSEnabled.x86 =CD7B8
bInitialized.x64 =ECAB0
bServerSku.x64 =ECAB4
lMaxUserSessions.x64 =ECAB8
bAppServerAllowed.x64 =ECAC0
bRemoteConnAllowed.x64=ECAC4
bMultimonAllowed.x64 =ECAC8
ulMaxDebugSessions.x64=ECACC
bFUSEnabled.x64 =ECAD0
[10.0.17763.437]
LocalOnlyPatch.x64=1
LocalOnlyOffset.x64=77A41
LocalOnlyCode.x64=jmpshort
SingleUserPatch.x64=1
SingleUserOffset.x64=3E520
SingleUserCode.x64=Zero
DefPolicyPatch.x64=1
DefPolicyOffset.x64=18025
DefPolicyCode.x64=CDefPolicy_Query_eax_rcx
SLInitHook.x64=1
SLInitOffset.x64=1ACDC
SLInitFunc.x64=New_CSLQuery_Initialize
bInitialized.x64 =ECAB0
bServerSku.x64 =ECAB4
lMaxUserSessions.x64 =ECAB8
bAppServerAllowed.x64 =ECAC0
bRemoteConnAllowed.x64=ECAC4
bMultimonAllowed.x64 =ECAC8
ulMaxDebugSessions.x64=ECACC
bFUSEnabled.x64 =ECAD0
Or you can download the rdpwrapper with the integrate patch. Follow the link https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/729
Thanks, I’m going to give that a shot on my machine that updated to 1809.
Hello folks
File version: 10.0.17763.437
search: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 3B 2B 01 00
replace with: B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Hey,
I got the latest rdpwrap.ini:
https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/files/3062713/rdpwrap.zip
to replace the existing one, I had to first stop the Remote Desktop Services windows service.
(which will also stop another service: Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector)
The file is now editable/replaceable.
Then replace C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper\rdpwrap.ini (in my case I just copy paste the extra section but I needed to run my text editor in Administrator privilege mode)
restart the 2 windows service (also make sure they are in automatic start mode)
And bingo, I now see [fully supported]
Wow! Its working.. Thanks for the info i have been searched a solution for hours.
Are you Tamil
contrary to what I’ve read, there is no need to restart the computer, start and stop the Remote Desktop Services is enough
(running windows 10 pro N 64 bits 10.0.17763.437)
Johnny done what you said but still can’t get it to work 🙁 any ideas anyone
Johnny needed reboot and it’s working fine thank you
Just tested on Windows 10 x64 1809. I chose to restart the PC tho. Concurrent Remote Desktop sessions is functional.
What I did: installed RDPWrap 2.6.2.
That’s all.
RDPWRAPPER works fine for me on 1809 but I noticed that the printer redirection has stopped working, anyone else have this problem
Hi. Is the Wrapper use illegal?
Remote access. No more than once every 90 days, you may designate a single user who physically uses the licensed device as the licensed user. The licensed user may access the licensed device from another device using remote access technologies. Other users, at different times, may access the licensed device from another device using remote access technologies, but only on devices separately licensed to run the same or higher edition of this software.
From https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/Useterms/Retail/Windows/10/UseTerms_Retail_Windows_10_English.htm
Yes, this is violation of the Microsoft licensing agreement.
By mistake I click on rdpcheck file and now my system not login after the restart.
It showing username and password and after putting the credentials, login error.
I think you need to reset the local administrator password using a boot, rescue or install disk.
Hello,
we did a security update on windows 10 Pro, today 7/24/19, and after it we can connect only one RDP at a time. So we changed the termsrv.dll, did all as instructed, and now we can’t connect even one RDP, we get Access Denied error. Any suggestions how we may solve this?
also worth to note that I disconnected the windows auto-updater, and for some reason it still told one of the users (administrators) that there is an update that has to be made.
Cannot get concurrent session to work on Win 10 Pro version 1903 OS build 18362.356. All green in RDPConf, except still shows “not supported”. Followed all possible instructions in correct order including replacing INI file and restarting appropriate services and/or restarting computer – nothing works. All was good 1 week ago. Any ideas? Will appreciate any suggestions, impacting my work big time.
If you updated to version 1903 less than 10 days ago you can go to settins > updates > recovery and use the go back to the previous version of Windows 10 option. Version 1903 was recently released and not sure if there is a fix for it yet.
edit termsvr.dll for win ver 18362.267 1903
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 5D 61 01 00
to
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
HI IM AFTER PATCH FOR THE NEW WIN 10 20HD2 , FOR TERMSERV.DLL
I TRIED THEONE FOR VER 20HD1 AND IT WONT WORK WITH THE NEW 20HD2. HAVE LOOKED EVERYWHERE .DO YOU KNOW WHERE I CAN GET IT. THANKS IN ADVANCE
Thank you Rob. I actually when back to previous build and it worked. I also found updated INI here https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/pull/859 that supposed to work for newest build.
Thanks, Rob. That worked for me on 1903.
Does this permit the console session at the same time as the RDP session?
putatively
Windows 10×32 vercion 1903
os-build: 18362.356
All green in RDPConf, except still shows “not supported”.
help for windows 10 November 2019 (1909)
Any update for 18363.476?
1909 win 10 pro x64 Works for me, same ROB solution for 1903:
Rob
September 21, 2019 – 9:03 pm
edit termsvr.dll for win ver 18362.267 1903
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 5D 61 01 00
to
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Thank You ROB!
Hi there, it worked for me aswell (after a few hours digging).
1903 Win 10 Pro with Rob’s solution. (Thanks Rob from Robb)
I previously installed RDP Wrapper and got all green but didn’t work till I did the termsvr.dll change, so I’m not sure what is really doing the trick LOL.
Hi, I’m having one issue with this, one remote connection get suddenly close and I have to connect again, it doesn’t show me any error or something, it just close the session, any idea why this Is happening?
Hi there, maybe somebody has logged in. Have you checked that more than one session are allowed?
Great and detailed instructions, obviously written by a real pro. However…
1. The RDP Wrapper software gets marked as malware, both by Malwarebytes and Trend Micro antivirus apps. In comes up relatively clean on the VirusTotal site, but I didn’t dare ignore my antivirus app warnings and opted instead for editing the termsvr.dll file as per instructions. The result works fine, but the instructions about editing it appear to be missing a small but crucial item…
2. The Tiny Hexer editor app refused to edit termsvr.dll while in was inside the system32 folder and gave an error message. I intuitively copied it out to another, non-system folder and the edit went fine. I then copied the edited file back into the system32 folder and all was well.
Please keep up the great work and add updates as regards the edits required to termsvr.dll in future updates of W10.
Yep a few people are saying RDP Wrapper is infected. Is there any other software?
You can use the modified termsrv.dll file instead of RDP Wrapper.
Still get ‘listener not supported’ on Windows 10 Home v1909 with RDP Wrapper v1.6.2, latest version of rdpwrap.ini and patching termsrv.dll as described by Rob and the hex editing table you had provided. I also tried enabling Routing and Remote Access in services. I had run update.bat and even tried the RDPWinst commands with no success. I guess there’s no way to get RDP to work with Windows 10 Home.
With Windows 10 x64 1909, the listening state is no supported, even with the latest ini file
Hei is there somewhere info about rdp patch 20h1 (19041) insider? The patchted rdp file from 1903 do not work.
Thanks
I just moded my termsrv.dll and it worked, 2 users at the same time. Was a pain with the admin rights for system 32 folder but got there in the end. Excellent work and thank you
For Version 10.0.18362.657
Do the following 3 replacements
Find Hex
39813C0600000F845D610100
Replace with
B80001000089813806000090
Find Hex
047411488D1577
Replace With
04EB11488D1577
Find Hex
58010000FF15F7
Replace With
58000000FF15F7
It worked for me by modified termsrv.dll. Thank you.
Hi,
So I think I’d like to use the code modification method – changing the termsrv.dll file – and Not use RDP Wrapper. It sounds straightforward. I don’t want to install software that might set off virus warning bells. And all I really care about is being able to allow a 2nd user (RDP or local) without bumping an existing user (RDP or local) off.
However, it seems RDP Wrapper tool provides for numerous parameters:
– specifying a different RDP port
– type of Authentication Mode
– type of Session Shadowing Mode
– etc.
Does anybody know What the termsrv.dll code changes above actually does ?
What settings/configuration is being setup ?
For instance, I specifically do Not want to use the default port (3389). But does the termsrv.dll code changes above allow for a port other than 3389 ?
Thanks, appreciate any helpful responses/comments.
fyi – I already have my RDP setup with a different port #
You can change the RDP listening port number on your computer in accordance with the article https://woshub.com/change-rdp-port-3389-windows/
Thanks for the response, but I already have my RDP connection setup with a different port #. The gist of my question is, what does the code change method actually do ?? For example, one of my concerns is, if I change the termsrv.dll file…. does that code (those parameters) override my port # setup…. and ‘that’ code relies on using the default of 3389 ? How about Authentication Mode or Session Shadowing Mode, etc.
Hi
I tried using RDP wraper but I could not fix the error not supported.
Then I tried editing termsrv.dll and it worked great. Thank you So much
hi Bharath, how did you edit termsrv.dll and what to edit in the file? need help, tnx
tengo la versio win 10 pro 1903 pero no me funciona
Microsoft Windows [Versión 10.0.18362.30]
hello i have 1809 17763.1158 can you halp me \?cannot download rdpwrap from sourse , i tryed to update termsrv but it dont works
On Windows 10 x64 2004 you should replace 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 D9 51 01 00 to B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 in the termsrv.dll file.
Hello KROX – I tested it on x64 2004 – but after that, the service did not start, I made 2 restarts – what could be wrong? thanks
Thanks KROX,
It worked for me. Awesome!
worked for me as well.
I see this topic a lot. Why doesn’t MS create a multi-user desktop OS and just charge more for it to account for the multiple users? I think a lot of people would go for it for the convenience. I know I would.
Windows server!
Latest Windows 10 version Build 19041 (either came out in May or June 2020) updates termsrv.dll, can no longer find the binary code.
Patch for termsrv.dll [10.0.19041.84] – Windows Professional (x64) – version 2004 (OS build 19041.264)
007444833D46BA 00EB44833D46BA
C706010000008BDF C706000000008BDF
39813C0600000F84D9510100 B80001000089813806000090
I have OS build 19041.329. I replaced the first string, but could not find the other two strings. It did not work, I get bumped by a new remote user. Thank you.
GREG, try to to search from the beginning again.
Must the second and third strings be found and replaced before this will work? In the past there was only one string that had to be replaced, and then it worked.
Did not see your answer, sorry. That was my problem. Thank you!
Works great, thank you! I actually have Server 2016, but do not want to install it just to allow one other person to share my computer.
Glad it works. Another drawback for using server OS is its incompatible with many applications.
Version 2004
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 D9 51 01 00
replaced with
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Different version of 1909:
Search for 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 5D 61 01 00
replace with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
NOT ALL 1909 versions are the same. My build is: Version 10.0.18363.836
I also edited the INI file in Program Files\RDP Wrapper to include that version at the end. Just copied the latest 10.0.1836* version groups and added the current version.
Just a heads up everyone: In THIS instance, RDPCheck.exe still told me “Not Supported” but it DOES work.
Curious whether the same revision to the wrapper could be done for 18363.997?
Could someone share the information How to extract the code on our own on every windows update version?
Win10 build 1904: i write the termsrv.dll and worked. but the string wan’t exactly match. it was 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 xx xx xx xx that i replaced with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90.
Thank you! I done option 1
What is the hex code on Windows 10 20H1? Does this method work on Enterprise Image?
i was upgrade windows 10 home to pro, and i installed rdp wrap.
its say ok. listening and fully supported, but i still cant using remote desktop with multiple sesion.
HI. need the rdp edit for window 10 version 2004 which they keep updating.
i edited termsrv.dll and rebooted .. service started ok.. but no mulitiple logins.
so msn has done some thing else or the hex edis for version 1909 does not work on 2004.
i have not tried rdp wrapper becuse it wont down load under virus protection. i may
turn that off and down load.
I tried to install this and now I can’t resolve any DNS. Pinging IP’s works, but not names. This looks like a virus to me.
Everyone, Thanks to the great work by the author and everyone who has posted to assist everyone. I have the new version 2004 and have used tiny Hexer, just as the author says and got everything working fine. Here is the needed data for the new version and how I found the area to make the change. Using Tiny Hexor I used a backup to mod first (follow the directions on ownership and icals and making backup) Use tiny hexer to find
Windows 10 x64 2004 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 D9 51 01 00
Replace with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
In the future search for just 39 81 3C 06 00 00 as that never appears to change and replace the full hex (12 pairs starting with 39 81 3C 06 00 00 ) and replace with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Hopes this helps everyone and stay safe and healthy.
Thank you very much
Regards, sorry me for my bad english.
I used your procedure using the RDPWrap-v1.6.2.zip.
It works but if I try to log in from another PC, in the same account I log off the account of the PC I connect to.
How can I solve?
Thank you.
Regards, sorry me for my bad english.
I used your procedure using the RDPWrap-v1.6.2.zip.
It works but if I try to log in from another PC, in the same account I log off the account of the PC I connect to.
How can I solve?
Thank you.
Use the latest version which is 1.6.2 (https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/releases) Follow the procedure on that page and then download the update for the .ini file for the latest version of Windows on this page:
https://github.com/asmtron/rdpwrap/blob/master/binary-download.md
Again read and follow the procedures.
I did everything they say and it is working for Windoes Version 10.0.19041.84
Hello
Thanks man this works Great for Window 10 Pro Build 1903 but can you help for Window 10 Pro Build 2009 which code i need to change.
Thanks
Read Kubat mes … In the future search for just 39 81 3C 06 00 00 as that never appears to change and replace the full hex (12 pairs starting with 39 81 3C 06 00 00 ) and replace with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
I have Windows 10 Version 1909 (OS Build 18363.1256). Using TinyHexer and HxD, I am having trouble finding 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 5D 61 01 00 to replace with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90. When I do a find for the value it states “No Results”. Even if i just search for 39, I get the same results so I know I am doing something wrong. I am not very familiar with Hex Editing software. Can anyone provide more details in how to change the termsvr.dll file with TinyHexer? I have tried using RDP Wrapper and although everything appears as if it should work, I cannot get multiple RDP sessions to work. By the way, EXCELLENTLY written by the Author and great feedback as well!!
Just found windows build 2004 on my machine after auto update. Not finding the code strings in the termsrv.dll anymore. Has the hex editing instruction here no longer effective with this latest build?
Same here! Las windows update has modified termsrv.dll and can’t find the string anymore.
Someone can tell what is the new string to search for ?
Thanks.
i done have a step “group policy”, thanks bro
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.19041.746]
For this version what code should be looked up for and replaced with.
Microsoft has been updated very quick recently.
Computer has just updated to latest version windows 10 pro version 2004, OS 19041.264
recheck termsrv.dll
It has been overwrote by the latest update.
It is
39 81 3c 06 00 00 0F 84 D9 51 01 00
Replace to
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
This solution runs without additional software RDP Wrapper or RD Plus.
It is successful allowed multiple users access at same time simultaneously。
Used this on 20H2 build 19041.746
searched for
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 01 5E 01 00
replaced with
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Works without RDPWrapper .. of course backup termsrv.dll before editing.
Hmmm, for me didn’t work – Win 10 Pro ver. 2004 – fileversion 10.0.19041.746 – TermService wont start… Any suggestions? Thank You very much.
Seconadry it worked ;o)
I’m on build 20H2 and termsrv 10.0.19041.746
I’m searching for: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 01 5E 01 00 and not finding.
Any help?
Thanks in Advance.
Thanks Kalandor – that worked for 20H2! FYI – can’t use Tiny Hexer to patch termsrv.dll in \windows\system32, even after taking ownership and setting full access (it would never find the file, probably due to inherited permissions). Had to copy termsrv.dll to another directory (i.e Downloads), use Tiny Hexer to patch that file, then copy the file back to \windows\system32
Used this on win10pro 1909 vers 18363.1316
Search at 0x01F270
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 75 61 01 00
Replace by
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
I too had to copy the termsrv.dll to a different directory to edit and then copy back but it Works like a champ – thanks All!
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 75 61 01 00
Replace by
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
WindowsProductName WindowsVersion
—————— ————–
Windows 10 Pro 2009
OS Build 19042.746
Worked for me. However, is there a sustainable way to update this string in sebsequent versions? I have 19042.844 today. Thanks
So, Windows just updated this again.
The version of the new termsrv.dll is 10.0.19041.789
I can’t find the above sequence in the file.
Anyone that could shine a light on this would be great!
Thanks you!
Never mind that, it’s the same string as .746. I have looked at it and at first I wasn’t finding that string. I was probably doing something wrong in the search. Tried again after a good night of sleep and, well, it’s working now. Tested!
Agradezco publicaran la linea para Windows 10 Enterprise Compilación 2009
they can leave the line of win 10 Enterprise Compilation 2009
If you’ll need patched termsrv for Windows 10 x64 Build 20H2_v2 look for it in the comments here https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/1354
Anyone knows how to do it for Windows 10 Pro 1909 Build 18363.1440?? Please help!!!
I’m trying to set up an AWS Lightsail instance and ran into a surprising trap. This instance is running Windows Server 2019 and the greedy SOB’s only allow 2 simultaneous RDP connections. Purchasing Remote Desktop Services CAL’s is ridiculously expensive at about $100/user. I’m thinking about patching termsrv.dll just like I”ve done successfully on a Windows 10 computer. The problem here, is that you have to be able to connect to the instance other than with RDP. TeamViewer is deliberately blocked by AWS (so they can sell you and expensive integration via their AWS marketplace) – only can use it when connected via RDP. SSH doesn’t appear to be possible with a Windows Server instance, only with Linux instances.
If I can get connected to the instance with anything other than RDP, I can attempt the RDP patch.
The DLL mod works great with Windows 10 20H2 / 1909 (Pro x64). Like others above have said, since the search string changes, it is best to search for “39 81 3C 06 00 00” as that part never seems to change. In my case, the whole string I had to find was actually:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 01 5E 01 00
A couple other tips:
–Make sure you are searching for a hex value, not text-string, integer, etc. In the HxD hex editor, you have to select the data type and text-string is the default.
–Make sure you open the hex editor with admin permissions or it won’t allow you to modify the DLL file. Right click the hex editor in the start menu and select “run as administrator”
Nailed it, thanks Jamie
Good morning, i have replace rdpwrap.ini and i have all green in RDPConf.exe
I have modify the Limit number of connections to 999999 and activate function but remote desktop, used in other pc, tell me “log off the current user?” and if i use RDPCheck in win 10 enterprise, used as server, the message is “The number of connections to this computer is limited…”
Do i have to perform other steps? Thank you
solved with autoupdate in this link
https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/860
universal patch
LANG=C sed ‘s/\x39\x81\x3C\x06\x00\x00[\x00-\xFF]\{6\}/\xB8\x00\x01\x00\x00\x89\x81\x38\x06\x00\x00\x90/’ termsrv.dll > termsrv_patched.dll
for termsrv.dll 10.0.19041.964
Replace
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 E1 6A 01 00
With
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember to backup
@KALANDOR (using your format)
For termsrv.dll 10.0.19041.1023
Replace
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 21 68 01 00
With
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember to backup
tanks many @KALANDOR, that’s work for me, where do you find this !!!, i search untill months :(((
i want a universal patcher for futur release !!!
Only the last 4 bytes change between updates… search for the common part 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 .. then copy it along with the next four bytes and replace with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 .. Worked for me for the last 6 updates …
I’m on build 20H2 and termsrv 10.0.19041.746 build?
I’m searching for: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 01 5E 01 00 and not finding.
Any help?
Thanks in Advance.
Hi John, a workaround working since a couple of years aften any windows update, is simple to search only for 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 the next 4 number are the specific jump adress. Only those 4 numbers changes between the updates. e.g. in 20H2 I found 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 and 21 68 01 00 , therefor replace 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 21 68 01 00 with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 , that is it. Keep in mind, this procedure may be works also after the next “surprising” update. Best Regards.
Is it free for multi sessions? Currently I use AweSun Remote Desktop for mutli-concurrent sessions for free. Free and works well.
Giving a backdoor to an unknown company with NO place of address anywhere on their site, with no indication whatsoever of who they are?
They claim all kinds of things on their site (aweray/awesun), but nothing whatsoever is verifiable.
Do you work for them?
Hello, the workaround is not working for me on version 10.0.19041.1081
For new termsrv.dll version 19041.1081
Windows Build 21H2 19042.1083
Or
Windows Build 21H1 19043.1110
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 DB 61 01 00
Replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember:
The entire string is 12 pairs.
For a different version, search for the first 8 pairs (39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84) and fill in the rest with the last 4 pairs you will find on your version.
Then replace the entire 12 pairs with the string (Replace it with)
The only solution that worked. Thank you all!
The procedure from MANNY works fine after any major update since a couple of years. Search for the 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 XX XX XX XX and replace it with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 . you can use a disassembler like IDA to see what is gone, the ask of termserv to the operating system “Are multible sessions allowed” gives with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 always the answer Yes :-). During the replacement, the termserv is stopped, but you can use anydesk to connect to the machine remotely as admin. After restarting the termserv by a reboot, everything with RDP is still working.
thanks
but we need it for Win 11
Hi all.
Please find below a script that works for all Windows 10 – Windows 11 version
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force# All thanks to https://renenyffenegger.ch/notes/Windows/Remote-Desktop-Services/patch-termsrv_dll
#
# Get status of the two services UmRdpService and TermService...
#
$svc_UmRdpService_status = (Get-Service UmRdpService).status
$svc_TermService_status = (Get-Service TermService ).status
#
# ... display them ...
#
Write-Host "Status of service UmRdpService: $svc_UmRdpService_status"
Write-Host "Status of service TermService: $svc_TermService_status"
#
# ... before stopping them ...
#
Stop-Service UmRdpService -Force
Stop-Service TermService -Force
#
# Save ACL and owner of termsrv.dll:
#
$termsrv_dll_acl = Get-Acl c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll
$termsrv_dll_owner = $termsrv_dll_acl.owner
Write-Host "Owner of termsrv.dll: $termsrv_dll_owner"
#
# Create backup of termsrv.dll, just in case:
#
Copy-Item c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll.copy
#
# Take ownership of the DLL...
#
takeown /f c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll
$new_termsrv_dll_owner = (Get-Acl c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll).owner
#
# ... and grant (/Grant) full control (:F) to myself:
#
cmd /c "icacls c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll /Grant $($new_termsrv_dll_owner):F /C"
#
# Read DLL as byte-array in order to modify the bytes.
#
# See https://stackoverflow.com/a/57342311/180275 for some details.
# NEL 2021-10-13 - The "if check" is there to differentiate between PowerShell Core and Powershell Traditional version...
if ($(Get-Content c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll -Raw -asByteStream).exitcode -eq 0) {
$dll_as_bytes = Get-Content c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll -Raw -asByteStream
}
else {
$dll_as_bytes = Get-Content c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll -Raw -Encoding byte
}
#
# Convert the byte array to a string that represents each byte's value as hexadecimal value, separated by spaces:
#
$dll_as_text = $dll_as_bytes.forEach('ToString', 'X2') -join ' '
#
# Search for byte array (which is dependent on the Windows edition) and replace them.
# See
# https://woshub.com/how-to-allow-multiple-rdp-sessions-in-windows-10/
# https://forums.mydigitallife.net/threads/discussion-windows-10-termsrv-dll-patching.57102/page-18
# for details.
#
# NEL 2021-10-13 - Automating for future version (Working for W11):
$patternsregex = ([regex]'39 81 3C 06 00 00(\s\S\S){6}', # W10 > 1809
[regex]'8B 99 3C 06 00 00(\s\S\S){6}' #W10 <1809
)
$patch = 'B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90'
Foreach ($patternregex in $patternsregex) {
If (Select-String -Pattern $patternregex -InputObject $dll_as_text) {
$dll_as_text_replaced = $dll_as_text -replace $patternregex, $patch
}
}
Elseif (Select-String -Pattern $patch -InputObject $dll_as_text) {
Write-Output 'The termsrv.dll file is already patch, exitting'
Exit
}
else { # Opens a url with probably new regex in comments
Write-Output "You need to search the new pattern bytes for the regex, try the last comments in : $(Start-Process https://woshub.com/how-to-allow-multiple-rdp-sessions-in-windows-10/)"
}
#
# Use the replaced string to create a byte array again
#
[byte[]] $dll_as_bytes_replaced = -split $dll_as_text_replaced -replace '^', '0x'
#
# Create termsrv.dll.patched from byte array:
#
if ($(Get-Content c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll -Raw -asByteStream).exitcode -eq 0) {
Set-Content c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll.patched -asByteStream -Value $dll_as_bytes_replaced
}
else {
Set-Content c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll.patched -Encoding Byte -Value $dll_as_bytes_replaced
}
#
# Compare patched and original DLL (/b: binary comparison)
#
fc.exe /b c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll.patched c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll
#
# Expected output something like:
#
# 0001F215: B8 39
# 0001F216: 00 81
# 0001F217: 01 3C
# 0001F218: 00 06
# 0001F21A: 89 00
# 0001F21B: 81 0F
# 0001F21C: 38 84
# 0001F21D: 06 5D
# 0001F21E: 00 61
# 0001F21F: 00 01
# 0001F220: 90 00
#
#
# Overwrite original DLL with patched version:
#
Copy-Item c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll.patched c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll -Force
#
# Restore original ACL:
#
Set-Acl c:\windows\system32\termsrv.dll $termsrv_dll_acl
#
# Start services again:
#
Start-Service UmRdpService
Start-Service TermService
Heavy inspiration from https://renenyffenegger.ch/notes/Windows/Remote-Desktop-Services/patch-termsrv_dll
Hi Nel –
Does the result of this script enable someone to use the console and simultaneous RDP connection without any prompts or user input to allow/disallow?
Hi,
RDPWrap solved the problem to use simultaneous RDP session but brought another problem: if I close RDP and reconnect than all running applications from the old session were closed and some applications running in background also are closed.
Anybody with the same behaviour and a possible solution?
Try to use the “Single Session Per User” option and configure the RDP timeouts correctly.
For new termsrv.dll version 19041.1202
Tested with
Windows Build 21H2 19042.1083
May work fine with other builds
Note for this build: The file changed but the string is the same as in 19041.1081
So…
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 DB 61 01 00
Replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember:
The entire string is 12 pairs.
For a different version, search for the first 8 pairs (39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84) and fill in the rest with the last 4 pairs you will find on your version.
Then replace the entire 12 pairs with the string (Replace it with)
Great Content!!! would the termsrv.dll editing method work for this version “Windows Server 2016 Essentials
Version 1607(OS Build 14393.4704)”. Has anyone tried? Below is the string i could locate 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 4D 94 02 00. This server of mine has an domain controller on same servr as well hence posting to confirm before going ahead to edit.
I have not tested the termsrv.dll file fix for Windows Server 2016 Essentials.
I think the easiest way for you is to deploy a clean VM with an evaluation version of Windows Server 2016 Essentials and try to edit the termsrv.dll. This will not affect your production environment.
Has anyone the hex changes for version 10.0.19041.1348?
The pattern 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 does’t seam to exist anymore.
@LUKE – yes.. I have patched it on this version without issues… I even used the AutoPatcher with the following pattern.
x64, 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 * * * *, B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Running 20H2 though, but I suppose if the DLL version is the same that would make no difference
Thanks for powershell script. Works as intended on Win 10 Pro 21H1.
For new termsrv.dll version 19041.1503
Tested with
Windows Build 21H2 19044.1526
May work fine with other builds
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 CB 56 01 00
Replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember:
The entire string is 12 pairs.
For a different version, search for the first 8 pairs (39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84) and fill in the rest with the last 4 pairs you will find on your version.
Then replace the entire 12 pairs with the string (Replace it with)
Edition Windows 11 Pro
Version 21H2
OS build 22000.493
find:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 9F 6A 01 00
replace :
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Dear Author of this tutorial,
THIS IS FABULOUS !!
Your instructions worked perfectly, on the first try, in Windows 11 Pro 22000.493.
I have donated to you on Paypal.
It’s a simply wonderful tool, this RDPWrap.
I can’t thank you enough!
Best regards from Keaau Hawaii, USA
sonya
Glad to help 😎
Thanks! This made things very easy for me. Cheers.
Had trouble finding the Hex for windows build so i couldn’t patch. Script obviously didn’t work.
Windows 10 Pro 20H2 1/8/2021 OS Build 19042.1526
anyone got this working?
For new termsrv.dll version 19041.1620
Tested with
Windows Build 21H2 19044.1620
May work fine with other builds
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 AB 4A 01 00
Replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember:
The entire string is 12 pairs.
For a different version, search for the first 8 pairs (39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84) and fill in the rest with the last 4 pairs you will find on your version.
Then replace the entire 12 pairs with the string (Replace it with)
Great tool and explanation and guide for how to use it! Thanks!
But yesterday I had to install all the pending updates of our Windows Pro and RDP stop to work, only one session was allowed. I tried everything, RDPupdate, uninstall re install, reboot the system, new .ini download… no way. I suspected it could be a problem of a new termsrv.dll and, yes, there was a new .dll dated just in yesterday, 30/03/22. So, I recovered an old .dll I had in a backup taken on 14/03/22 and it worked again.
Any idea of what other thing I could have done?
Thanks again
You are clever thank you very much
For which string must I search on Windows 10 x86 ?
I dont have 39 81 3C 06 00 ….
I’m running Windows 10 Enterprise x86 2009 (termsrv.dll 10.0.19041.1503)
Thank you very much
Excelente!!!!
Funcionó perfectamente modificando termserv.dll con PowerShell.
Gran post, muy bien explicado todo.
Muchas gracias.
Un genio BEN!!!
That powershell script is the bees knees! thanks!!!
Is there a solution for Windows 10 x64 v21H2 termsrv.dll 10.0.19041.1566?
Is there a solution for Windows 10 x64 v21H2 termsrv.dll 10.0.19041.1682?
Is there a solution for Windows 10 x64 v21H2 termsrv.dll 10.0.19044.1706?
About termsrv.dll (x64): 10.0.19041.1682
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 2B 86 01 00
Replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
And I made these steps also for Windows 10 x64 v21H2 termsrv.dll 10.0.19044.1706,
and it works also!
But I made it with my own Risk, so be carefull, backup original version of termsrv.dll.
Thanks for the termsrv.dll (x64): 10.0.19041.1682
Do you maybe have a solution for Is there a solution for Windows 10 x64 v21H2 termsrv.dll 10.0.19041.1566?
found it:
Windows 10 Pro
Version: 21H2
OS Build: 19044.1566
termsrv.dll (x64): 10.0.19041.1566
===============================
Replace:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 2B 4D 01 00
With:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Hello.
I’ve been using the RDPWrapper for several years now.
Everything works fine, all green, fully supported, all is good.
But there is one thing I’d like to ask to those who can help.
When enabling “multiple «per-user» sessions”…
Is there a way to choose which specific session to login into?
If there’s currently only 1 logged in session, is it possible for RDP to choose this very same session regardless of enabling the concurrent per-user option
Furthermore, is there also a way to use this as some sort of a remote assistance manner?
(as in, being in the exact same session of another location, both sharing the same mouse/keyboard)?
I see some shadowing mode options, but never really figured out how to use that.
Been using RDP Wrapper for many years. Updated to H1H2 and all was fine. Then about 2 weeks ago it stopped working. No updates have been installed since the last time it worked. Says supported and listening, all is green. But two different users cannot be logged in at the same time. The guy that runs the Github can’t figure it out either. It’s happening to many people. Start with issue #353.
https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/353
https://github.com/stascorp/rdpwrap/issues/1873
This is an old issue that once it pops up, no one can fix it. Every single machine on my network is now hosed. I’ll looking into running this script but only if I can automate it.
For new termsrv.dll version 19041.1741
Tested with
Windows Build 21H2 19044.1741
May work fine with other builds
Search for:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 73 55 01 00
Replace it with:
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Remember:
The entire string is 12 pairs.
For a different version, search for the first 8 pairs (39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84) and fill in the rest with the last 4 pairs you will find on your version.
Then replace the entire 12 pairs with the string (Replace it with)
It works with termsrv.dll version 19041.1741, thanks!
Replacement of bits for termsrv version 10.0.19044.1949 not working.
Found: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 C3 2A 01 00
replaced with: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 C3 2A 01 00
Resul is a error after entering of correct password and no options for login “The object invoked has disconnected from it’s clients.”.
*replaced with: B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Sorry there is no options for edit, maybe because I’m not a registered user.
Found solution in other forum:
termsrv.dll x64 19041.1949
Multi-user: File offset: 1E1C5. Find: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 C3 2A 01 00 and replace with B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Multi-session: File offset: 10D32. replace 01 with 00.
Replacing only 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 C3 2A 01 00 resulting in error.
@KALOYAN
I did patch the file as you described and am facing an “interesting” behaviour now. If I log into the machine locally and open a program, this program is not visible in the RDP session. It happens vice versa as well. The processes of the programs I opened however are still running (just not visible).
Hi, RAYNOR,
It’s due to replacing offset at 10D32, witch unlocks multi-session. You can have one session locally and another with same user from RDP. Try it locally opening RDP to localhost with same user.
For Windows version 21H2 19044.2006 (september update)
Found: 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 C3 2A 01 00
Replace with: B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
also works
patch for termsrv.dll (x64): 10.0.19041.2075
===============================
Replace:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 85 45 01 00
With
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
Thank you. This worked!
22000.1042
how to fix this version?
how can we run single application not full computer access thru this RDP process
Holy Crap!! This is GREAT – SWEET!
22H2
19045.2311
Do you have this version?
REMORT DEXTOP SERVICES IN IS NOT STARTIN ERROR CODE 126 THE SPECIFIED MODULE COULD NOT BE FOUND
many thanks bro, but just 1 notes before running that ps1 script is ensure to stop RDP services or you can found that termsrv is still running. Other than that this process should be successful.
regards,
haikal shiddiq
thank you it works
What can be done for RDP to work on Win11 with ver 10.0.22621.608
the “Hex edit” works for W10 but there isn’t a code for “The Birdie” / Canary release.
The Git hub MSI version of rdp wrapper gives a Windows Defender popup of “This program contains malware” if you try download it, the download can still be done. Not willing to try that -but works on W10 with the Hex edit.
Hey guys, check out my PowerShell script on GitHub! I’m working on doing a better job, thank you very much! https://github.com/fabianosrc/TermsrvPatcher
The whole purpose of purchasing a MS Professional version OS is to join it to a domain. If while someone is working, and you can’t login with an administrator account to update programs and OS updates, whats the purpose of having a professianal MS OS Joined to your domain? Just so that I can see it on AD? No, its so that it can be managed. Managing is part of updating, and doing work on multiple computers a time. I get so frusterated with MS, because they know it can be done, but do nothing about it, even try to force windows to now allow multiple users. Its fine if they force this on home edition, or something less that professional.
Agreed – Microsoft could have at least made Windows Pro support TWO concurrent RDS sessions as is with Server Edition.
One can make a PowerShell session connection, BUT NOT a RDS session, so you first have to log a user off, before you can check something on a computer!
Assistance Needed: `termsrv.dll` v10.0.22621.2861 – Regex Pattern Not Found
Hey guys,
Encountering an issue with a PowerShell script for `termsrv.dll` version 10.0.22621.2861. The script uses this regex to identify a byte sequence:
$patternregex = ([regex]’39 81 3C 06 00 00(\s\S\S){6}’)
However, it fails to find the pattern in the specified termsrv.dll. It seems the byte sequence might differ in this version.
Seeking insights or an updated regex pattern compatible with v10.0.22621.2861.
Best Regards,
Thanks, good to see it is been update to support win11
I just used and it is working for win11.
Please Update new ini.file
Very usefull with the powershell, congratulations and thank you very much!
I´m unable to register my windoews to skms kms-srv.woshub.local:1688 server. Could you please help?
Hi,
thanks for the how to on the topic. I was trying the update on the enterprise multiple sessions version successfully until activation with the given kms-srv.woshub.local:1688 server adress. which ended with an error. It was unable to reach it. Can you help/advise? Is the server currently down?
kms-srv.woshub.local:1688is not a real world KMS server. It’s just an example. You should replace it with your own KMS host FQDN.Has anyone gotten the Termsrv.dll patch method to work in Windows 11 24H2?
Just to elaborate, I get a “0x904 0x0” rdp error shortly after logging in with credentials and the connection drops. Remote desktop works fine with the original .dll, but not after the hex edit. The size of the termsrv.dll has changed a lot in 24H2 I believe… I tried a manual hex edit and also used the powershell script. The powershell script appears to replace values in two locations which I doubt is right. But the manual edit, when changed in just the one spot (which I think I was able to find correctly), I get the error mentioned above after login.
Hello guys. Please, look at this: https://github.com/fabianosrc/TermsrvPatcher
Thanks but I did try that already but from what I could see it replaces the hex code in two places in the .dll (not just one) and it doesn’t work for me (I get disconnected shortly after entering my credentials during logon via remote desktop with error code “0x904 0x0”).
I’ve been using the termsrv.dll hex edit for half a decade in Windows 10 with great success, but now that I am trying to use it in Windows 11 24H2 I am not having much luck. This is the output of the powershell script you mentioned on Win11 24H2:
PS C:\users\setup\Desktop> .\TermsrvPatcher.ps1
Status Name DisplayName
—— —- ———–
Stopped UmRdpService Remote Desktop Services UserMode Po…
Stopped TermService Remote Desktop Services
Owner of termsrv.dll: NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller
SUCCESS: The file (or folder): “C:\WINDOWS\System32\termsrv.dll” now owned by user “decast\setup”.
processed file: C:\WINDOWS\System32\termsrv.dll
Successfully processed 1 files; Failed processing 0 files
Pattern matching!
Comparing files C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\termsrv.dll.patched and C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\TERMSRV.DLL
0005EA82: B8 39
0005EA83: 00 81
0005EA84: 01 3C
0005EA85: 00 06
0005EA87: 89 00
0005EA88: 81 0F
0005EA89: 38 85
0005EA8A: 06 8D
0005EA8D: 90 00
00094BB5: B8 39
00094BB6: 00 81
00094BB7: 01 3C
00094BB8: 00 06
00094BBA: 89 00
00094BBB: 81 75
00094BBC: 38 16
00094BBD: 06 48
00094BBE: 00 8D
00094BBF: 00 15
00094BC0: 90 3C
Running TermService Remote Desktop Services
It replaces entries in two spots on the termsrv.dll:
Offset 5EA82 and 94BB5
I don’t think it should be replacing it on two spots… Windows 10 it would just replace it in one… something isn’t right here from what I can tell for Win11 24H2… maybe Microsoft changes something major in the termsrv.dll for 24H2? I don’t know…
Thanks for reporting this bug. I’ll fix the regex in the script so it doesn’t replace the pattern twice.
Awesome, that would be great, thanks. Hopefully I’ll have better results with the upgraded script. I suspect, however, that I may still get the same error code “0x904 0x0” disconnection after logging in with our username and password. I’ll have to wait to see.
Same issue here. It seems that the 08 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 does not work on 24H2…Anyone with a solution?
try my solution find the first pattern that doesn’t change for the last major builds
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 and fill the 4 missing numbers pattern … and finally replace with the same hex value listed in table above
24H2 is the latest version of Win11. Have you tested it with that? That is the one that is broken. 23H2 is not.
The 24H2 the string 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 does not match, the closest is:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 85 8D 00 00 00
The 24H2 the string 39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 does not match, the closest ones:
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 85 8D 00 00 00
39 81 3C 06 00 00 75 16 48 8D 15
The script to modify the termsrv.dll is not working for me either after instaling Windows 11 24H2.
Based on my understanding, I replaced $patternregex = ([regex]’39 81 3C 06 00 00(\s\S\S){6}’) with $patternregex = ([regex]’39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F(\s\S\S){5}’) but it did not work and getting the standard message Another user is signed in. If you continue, they’ll be disconnected. Do you want to sign in anyway?
Appears to me that $patch = ‘B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90’ doesn’t work for Windows 11 24H2.
for windows 11 – 23H2 Build 22631.4460
find with hex editor
39 81 3C 06 00 00 0F 84 91 AE 01 00
and replace it with
B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90
site owner please add this update to table above, i think this is the latest build of windows 11 in 1 dec 2024
I have Version 10.0.22631 Build 22631
can you tell me what to look for and the replacement
Sadly, it doesn’t work anymore for Windows 11 24H2. 🙁
Looking for another method.
Hi, please What method i can use in Windows 11 v24h2? thank you
work for me w11 24h2 26100.2605
1. first install wrapper 1.6.2
2. stop service termserv
3. just copy-paste then replace rdpwrap.ini from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sebaxakerhtc/rdpwrap.ini/master/rdpwrap.ini — to C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper
4. start again termserv from service
5. Done
my set +image https://ibb.co.com/4j8F2wF
Thanks but the wrapper isn’t an option for everyone (due to AV picking it up as a virus, etc). So we are trying to find a non-wrapper option (hex editing the termsrv.dll) like we’ve used for a decade or so in Win7/Win10 and earlier versions of Win11.
I see that this Github site now has a working termsrv.dll patch: https://github.com/fabianosrc/TermsrvPatcher
Can anyone confirm that this is indeed working? I’m not on Windows 11 24H2 so I’m unable to test it.
Yes, it does work! I have tested it successfully. Thank you to fabianosrc for getting it going for us!
I’ve tried this before and when I try to copy the edited terms.dll onto system32, it says I can’t copy it because the system32 folder is in use. I have not been able to fix this issue for a while. Would someone be able to help?
Has anyone the hex string for the current Windows 10 LTSC version (2021), both x86 and x64?
Thanks
in Windows 11 24H2 replace 8B 81 38 06 00 00 39 81 3C 06 00 00 75 by B8 00 01 00 00 89 81 38 06 00 00 90 EB
God bless you
I don’t know how you got this, but thanks… seriously!
A true hero!
also works in Version 10.0.26100.3323 thx
really appreciate the effort put in to by you ROBERTO
Is it possible to also share how one understand what it does , i am not able to find the right dll version to understand and debug with x64dbg
I don’t understand how to do it, I just saw the comment above by SH, https://github.com/fabianosrc/TermsrvPatcher and I find the part that need to be replaced in that code.
great , it works . Thank you
On Windows 11 24H2 ver. 26100.3624 it no longer works…
Hello. I will fix it.
Hello. I will fix it.
Hello, which hex do we need to replace for Windows 11 24H2 ver. 26100.3624?
Thank you !!!!!
I pasted the new code lines into .ini file, but it doesn’t work on Windows 11 24H2 ver. 26100.3624.
I pasted the code and now IT WORKS !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
THANK YOU !!!!!!!!!!!!
Which code? Which .ini file?
When you install RDP Wraper in C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper, there are 2 files in that folder, rdpwrap.dll and rdpwrap.ini. You STOP the service named Remote Desktop Service (Win key +R -> services.msc), you open rdpwrap.ini with notepad, you delete all the lines and paste the new code. When you hit save, it will say you cannot save in that location. You save it in Downloads or Desktop or any other location. You go to where you saved it and you copy it over the one in C:\Program Files\RDP Wrapper. You then START back the service Remote Desktop Service and run RDPConf.exe to make sure all is green light.
Thank you, that works, but i thought there is new binary for the termsrv file, which I need
It appears that the updated strings that Roberto posted above (using the code from https://github.com/fabianosrc/TermsrvPatcher) is longer working after the April security patches when running Windows 11 24H2.
After more research, I realized that Windows wasn’t letting me copy the modified termsrv.dll file to the C:\Windows\System32 folder. it appeared to copy, but wasn’t actually and it never errored out.
I was able to successfully run the TermsrvPatcher PowerShell script successfully, however.
Alguien que haya logrado el wrap con windows 11 23H2 ?
Need it badly for the very latest 24H2 26100.4061. Anyone please?