Resetting network settings in Windows is usually the last resort for dealing with complex issues with local network or Internet access. This feature allows resetting network and TCP/IP settings to their default values, removes and reinstalls all network adapters on a computer. Let’s look at how to reset network settings in Windows using a GUI and the command line.
Before you reset network settings, make sure that you have tried all typical network diagnostic tools: checked IP settings, switch/router/provider operability, updated network adapter drivers, restarted your computer, used the built-in Windows Network Troubleshooter tool (the command to run it: msdt.exe /id NetworkDiagnosticsNetworkAdapter ), etc. If neither of the methods helped you to fix the network issue, you can try to reset the network settings.
Save Current Windows Network Settings
When resetting network settings in Windows, you will lose all network settings you configured manually: IP addresses, static routes, network driver settings, saved Wi-Fi networks/passwords will be cleared, etc. Therefore, it is important to save your current network settings before resetting.
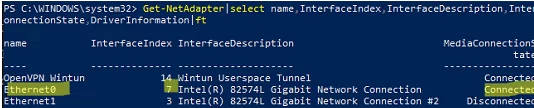
List network adapters:
Get-NetAdapter|select name,InterfaceIndex,InterfaceDescription,InterfaceOperationalStatus,MediaConnectionState,DriverInformation|ft
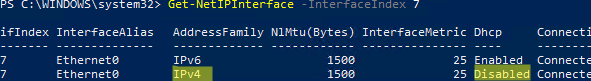
For all connected network adapters, check if they receive IP settings automatically (via DHCP) or manually:
Get-NetIPInterface -InterfaceIndex 7
If the interface value is Dhcp=Disabled, then the IP settings for the adapter are set manually and you have to save the current settings to a file:
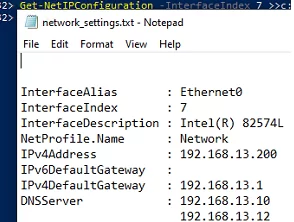
Get-NetIPConfiguration -InterfaceIndex 7 >>c:\backup_network_settings.txt
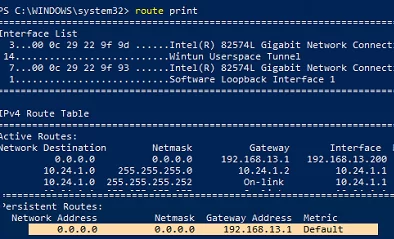
Display and write down all static routes in the routing table (from the Persistent Routes section):
route print
Using PowerShell, display a list of configured VPN connections and write down their settings:
Get-VpnConnection
List WLAN profiles and save Wi-Fi network settings to a file:
netsh wlan show profile
netsh wlan export profile name="WiFi2022" key=clear folder=c:\ps
Export Winsock settings:
netsh winsock show catalog > c:\winsock-backup.txt
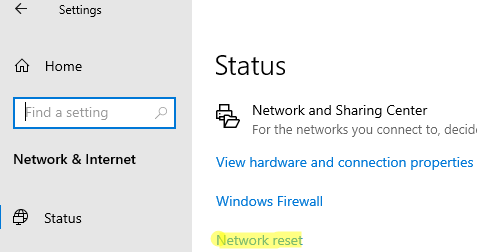
How to Reset Network from Windows Settings
In Windows 10 (1607+), Windows 11, and Windows Server 2019/2022, you can reset network adapters from the Settings panel. Go to Settings -> Network (or use a quick access command to open ms-settings: ms-settings:network). Click Network reset -> Reset now.
Confirm the reset. Windows will clear all network settings and remove network adapters (your network adapters will not be shown in the Control Panel). The network settings will be reset to the default ones. Windows will restart automatically in 5 minutes.
After the restart, Windows will detect all connected network adapters and install drivers. Then you just have to configure network connection settings and make sure that the problem is fixed.
Performing Network Reset in Windows Using CMD
You can also reset your network configuration in Windows manually using the command line tools.
Reset the DNS cache:
ipconfig /flushdns
Reset WinSock:
netsh winsock reset
Sucessfully reset the Winsock Catalog.
You must restart the computer to complete the reset.
Protocol_Catalog_Before_Reset key. 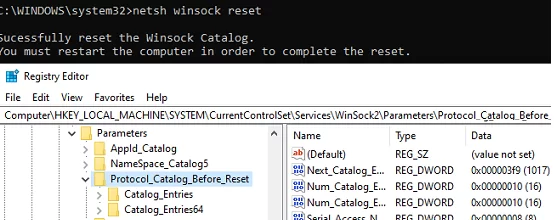
To reset TCP/IP v4 stack settings:
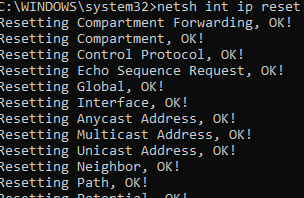
netsh int ip reset
To reset TCP/IPv6 stack:
netsh int ipv6 reset
Resetting Compartment Forwarding, OK! Resetting Compartment, OK! Resetting Control Protocol, OK! Resetting Echo Sequence Request, OK! Resetting Global, OK! Resetting Interface, OK! Resetting Anycast Address, OK! Resetting Multicast Address, OK! Resetting Unicast Address, OK! Resetting Neighbor, OK! Resetting Path, OK! Resetting Potential, OK! Resetting Prefix Policy, OK! Resetting Proxy Neighbor, OK! Resetting Route, OK! Resetting Site Prefix, OK! Resetting Subinterface, OK! Resetting Wakeup Pattern, OK! Resetting Resolve Neighbor, OK! Resetting , OK!
Restart the computer to complete this action.
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters and \SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DHCP\Parameters registry keys.Remove all network adapters:
netcfg -d
Successfully removed all MUX Objects. Removing device "Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection" Removing device "WAN Miniport (PPPOE)" Skipping the removal of "Wintun Userspace Tunnel" Removing device "WAN Miniport (PPTP)" Removing device "WAN Miniport (IKEv2)" Check to see if the "Microsoft Kernel Debug Network Adapter" bindings should be reset "Microsoft Kernel Debug Network Adapter" binding check complete Removing device "WAN Miniport (Network Monitor)" Removing device "WAN Miniport (IP)" Removing device "WAN Miniport (SSTP)" Removing device "WAN Miniport (IPv6)" Removing device "WAN Miniport (L2TP)" Please reboot the computer...
To reset Windows Defender Firewall rules run the command:
netsh advfirewall reset
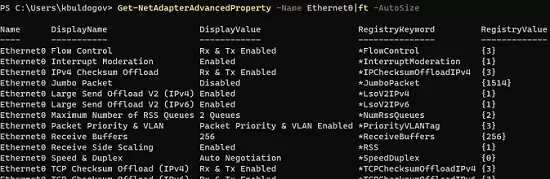
Also, PowerShell has a separate command to reset the advanced settings of a specific network adapter. List current adapter’s settings:
Get-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty -Name Ethernet0|ft -AutoSize
Name DisplayName DisplayValue RegistryKeyword RegistryValue
---- ----------- ------------ --------------- -------------
Ethernet0 Flow Control Rx & Tx Enabled *FlowControl {3}
Ethernet0 Interrupt Moderation Enabled *InterruptModeration {1}
Ethernet0 IPv4 Checksum Offload Rx & Tx Enabled *IPChecksumOffloadIPv4 {3}
Ethernet0 Jumbo Packet Disabled *JumboPacket {1514}
Ethernet0 Large Send Offload V2 (IPv4) Enabled *LsoV2IPv4 {1}
Ethernet0 Large Send Offload V2 (IPv6) Enabled *LsoV2IPv6 {1}
Ethernet0 Maximum Number of RSS Queues 2 Queues *NumRssQueues {2}
Ethernet0 Packet Priority & VLAN Packet Priority & VLAN Enabled *PriorityVLANTag {3}
Ethernet0 Receive Buffers 256 *ReceiveBuffers {256}
Ethernet0 Receive Side Scaling Enabled *RSS {1}
Ethernet0 Speed & Duplex Auto Negotiation *SpeedDuplex {0}
Ethernet0 TCP Checksum Offload (IPv4) Rx & Tx Enabled *TCPChecksumOffloadIPv4 {3}
Ethernet0 TCP Checksum Offload (IPv6) Rx & Tx Enabled *TCPChecksumOffloadIPv6 {3}
Ethernet0 Transmit Buffers 512 *TransmitBuffers {512}
Ethernet0 UDP Checksum Offload (IPv4) Rx & Tx Enabled *UDPChecksumOffloadIPv4 {3}
Ethernet0 UDP Checksum Offload (IPv6) Rx & Tx Enabled *UDPChecksumOffloadIPv6 {3}
Ethernet0 Adaptive Inter-Frame Spacing Disabled AdaptiveIFS {0}
Ethernet0 Interrupt Moderation Rate Adaptive ITR {65535}
Ethernet0 Log Link State Event Enabled LogLinkStateEvent {51}
Ethernet0 Gigabit Master Slave Mode Auto Detect MasterSlave {0}
Ethernet0 Locally Administered Address -- NetworkAddress {--}
Ethernet0 Wait for Link Auto Detect WaitAutoNegComplete {2}To reset them, use the command below:
Reset-NetAdapterAdvancedProperty -Name Ethernet0
Restart your computer and configure all network settings again. If your computer is configured to obtain an IP address and network settings automatically from a DHCP server, you have nothing to set manually.
1 comment
Only one computer in my house refused to give internet access to my starlink. I followed the CMD commands properly and now it works very fine, thx this info was a great help